Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For Infection
Uploaded by
Anne Jillian0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views1 pageInfection and others
Original Title
Infection and others
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInfection and others
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views1 pageCancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For Infection
Uploaded by
Anne JillianInfection and others
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
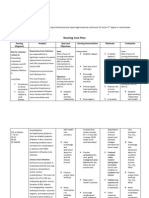
Cancer Nursing Care Plan(NCP) -Risk for Infection
Nursing actions Rationale
Promote good handwashing
procedures by staff and visitors.
Screen/limit visitors who may
have infections. Place in reverse
isolation as indicated.
Protects patient from sources of infection, such as visitors and staff
who may have an upper respiratory infection (URI).
Emphasize personal hygiene. Limits potential sources of infection and/or secondary overgrowth
Monitor temperature.
Temperature elevation may occur (if not masked by corticosteroids
or anti-inflammatory drugs) because of various factors, e.g.,
chemotherapy side effects, disease process, or infection. Early
identification of infectious process enables appropriate therapy to
be started promptly.
Assess all systems (e.g., skin,
respiratory, genitourinary) for
signs/symptoms of infection on a
continual basis
Early recognition and intervention may prevent progression to more
serious situation/sepsis.
Reposition frequently; keep
linens dry and wrinkle-free.
Reduces pressure and irritation to tissues and may prevent skin
breakdown (potential site for bacterial growth)
Promote adequate rest/exercise
periods.
Limits fatigue, yet encourages sufficient movement to prevent stasis
complications, e.g., pneumonia, decubitus, and thrombus formation.
Stress importance of good oral
hygiene.
Development of stomatitis increases risk of infection/
secondary overgrowth.
Avoid/limit invasive procedures.
Adhere to aseptic techniques.
Reduces risk of contamination, limits portal of entry for infectious
agent.
Monitor CBC with differential
WBC and granulocyte count,
and platelets as indicated.
Bone marrow activity may be inhibited by effects of chemotherapy,
the disease state, or radiation therapy. Monitoring status of
myelosuppression is important for preventing further complications
(e.g., infection, anemia, or hemorrhage) and scheduling drug
delivery. Note:The nadir (point of lowest drop in blood count) is
usually seen 710 days after administration of chemotherapy.
Obtain cultures as indicated. Identifies causative organism(s) and appropriate therapy.
Administer antibiotics as
indicated.
May be used to treat identified infection or given prophylactically in
immunocompromised patient.
You might also like
- Fast Facts: Managing immune-related Adverse Events in Oncology: Early recognition, prompt intervention, effective managementFrom EverandFast Facts: Managing immune-related Adverse Events in Oncology: Early recognition, prompt intervention, effective managementNo ratings yet
- Cancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesCancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Infection RiskDocument2 pagesMinimizing Infection RiskEllmaaanNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection: Risk Factors May IncludeDocument2 pagesRisk For Infection: Risk Factors May IncludeCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPf_jm06_gNo ratings yet
- Bacteremia - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf EnglishDocument5 pagesBacteremia - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf EnglishKhalda Sausan AzharNo ratings yet
- Cancer Colon and Rectum (Wardah)Document23 pagesCancer Colon and Rectum (Wardah)WardahAliNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Protection NCPDocument2 pagesIneffective Protection NCPTerry Mae Atilazal Sarcia83% (6)
- BarbsrevisionsnpDocument9 pagesBarbsrevisionsnpapi-255084253No ratings yet
- Nurse Practitioner Clinical Protocol: Management of CellulitisDocument11 pagesNurse Practitioner Clinical Protocol: Management of CellulitisJason MarshallNo ratings yet
- 2017 Article 146Document15 pages2017 Article 146Anggy de RinconNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk Infection Papillary Thyroid CADocument2 pagesNCP Risk Infection Papillary Thyroid CAjazvNo ratings yet
- TB Nursing CareplanDocument14 pagesTB Nursing CareplanEstherThompson100% (1)
- NCP Elective (Risk For Infection)Document1 pageNCP Elective (Risk For Infection)student_019No ratings yet
- Vii Nursing Management Ideal & SoapieDocument13 pagesVii Nursing Management Ideal & SoapiebeingfiredNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationPaul Cubacub100% (1)
- Medical Problem That Needs Antibiotic ProphylaxisDocument6 pagesMedical Problem That Needs Antibiotic ProphylaxisPing KyNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Abx Prophylaxis o Surgical Wounds - AFPDocument16 pagesGuidelines For Abx Prophylaxis o Surgical Wounds - AFPyusmaniqistinaNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument6 pagesPreoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfAshen DissanayakaNo ratings yet
- Hand Infections CpsDocument11 pagesHand Infections CpsDavid SidhomNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic SsiDocument6 pagesAntibiotic Ssim8wyb2f6ngNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Infection ControlDocument53 pagesConcepts of Infection ControlPak Pandir0% (1)
- Risk Factors For Surgical Site InfectionDocument5 pagesRisk Factors For Surgical Site InfectionElizabeth Mautino CaceresNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument4 pagesReportKyle DapulagNo ratings yet
- NeutrotoppppcDocument10 pagesNeutrotoppppcapi-255084253No ratings yet
- Authors: Section Editor: Deputy EditorDocument16 pagesAuthors: Section Editor: Deputy Editortaufik sofistiawanNo ratings yet
- Infections in ICUDocument7 pagesInfections in ICUNikolay ToméNo ratings yet
- PeritonitisDocument4 pagesPeritonitisAlthof SonaNo ratings yet
- Rev 3 NeutropolicyDocument11 pagesRev 3 Neutropolicyapi-255084253No ratings yet
- Cellulitis and Skin Abscess in Adults - Treatment - UpToDateDocument16 pagesCellulitis and Skin Abscess in Adults - Treatment - UpToDateIsabella Gutierrez CarabaliNo ratings yet
- UrosepsisDocument6 pagesUrosepsisParama AdhikresnaNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis and Skin Abscess in Adults - Treatment - UpToDateDocument21 pagesCellulitis and Skin Abscess in Adults - Treatment - UpToDatesekarmentari16193No ratings yet
- Prophylactic Use of Anti-Microbial Agents: Presented By: Jagir R. Patel Assistant ProfessorDocument18 pagesProphylactic Use of Anti-Microbial Agents: Presented By: Jagir R. Patel Assistant ProfessorJagirNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis For TonsillitisDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis For TonsillitisVaneca Go67% (9)
- Urosepsis PanduanDocument6 pagesUrosepsis Panduanagus bonardoNo ratings yet
- NCP Gastric CancerDocument7 pagesNCP Gastric CancerAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (4)
- Early Ambulation and Prevention of Post-Operative Thrombo-Embolic RiskDocument4 pagesEarly Ambulation and Prevention of Post-Operative Thrombo-Embolic RiskAnderson LondoñoNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis StatPearls NCBI BookshelfDocument1 pagePreoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis StatPearls NCBI BookshelfJEAN BAILEY RAMOS ROXASNo ratings yet
- Rev 9 NeutroDocument10 pagesRev 9 Neutroapi-255084253No ratings yet
- Surgical InfectionsDocument20 pagesSurgical InfectionsDr-Mohammad Ali-Fayiz Al TamimiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Manangement and Administration Assignment ON Standard Protocol of The UnitDocument9 pagesNursing Manangement and Administration Assignment ON Standard Protocol of The UnitNisha MwlzNo ratings yet
- TransplantationDocument11 pagesTransplantationmardsz100% (1)
- Febrile Neutropenia UptodateDocument25 pagesFebrile Neutropenia UptodateMayar MoustafaNo ratings yet
- Nur 111 Session 19 Sas 1Document6 pagesNur 111 Session 19 Sas 1Zzimply Tri Sha UmaliNo ratings yet
- Ssi Protocol 2015Document11 pagesSsi Protocol 2015Megersa AleneNo ratings yet
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: Treatment of Severe Drug ReactionsDocument8 pagesStevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: Treatment of Severe Drug ReactionsHaidir MuhammadNo ratings yet
- CH-1i INFECTION PREVENTION AND PATIENT SAFETY - MODULE 1Document40 pagesCH-1i INFECTION PREVENTION AND PATIENT SAFETY - MODULE 1Sisay Fesseha AmbayeNo ratings yet
- Current Guidelines For Antibiotic Prophylaxis of Surgical WoundsDocument7 pagesCurrent Guidelines For Antibiotic Prophylaxis of Surgical WoundsPavan VelineniNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics in SurgeryDocument18 pagesAntibiotics in SurgeryGiovanni HenryNo ratings yet
- Rev 1 NeutroDocument9 pagesRev 1 Neutroapi-255084253No ratings yet
- Meningitis: Morbidity and MortalityDocument9 pagesMeningitis: Morbidity and MortalityRenz Henry AbagatnanNo ratings yet
- Tiempo Ideal de Tto en Infecciones de PielDocument8 pagesTiempo Ideal de Tto en Infecciones de PielRances OllarvesNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIOm 2Document7 pagesINTRODUCTIOm 2shakeebrabi326No ratings yet
- Risk For InfectionDocument7 pagesRisk For InfectionAnn Michelle TarrobagoNo ratings yet
- Violeta 2Document10 pagesVioleta 2Georgiana StoicaNo ratings yet
- SCHISTOSOMIAISDocument5 pagesSCHISTOSOMIAISEunice OrdonezNo ratings yet
- OsteomyelitisDocument7 pagesOsteomyelitis4kscribd100% (1)
- INFECTIONS IN ORGAN TRANSPLANT PATIENTS Essential LearningDocument76 pagesINFECTIONS IN ORGAN TRANSPLANT PATIENTS Essential Learningtummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- Census For WardDocument1 pageCensus For WardAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Lt. Antonio Carvajal: The Arrival of The SpaniardsDocument5 pagesLt. Antonio Carvajal: The Arrival of The SpaniardsAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- ExpressionismDocument2 pagesExpressionismAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- ExpressionismDocument2 pagesExpressionismAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesEndocrine SystemAnne Jillian83% (6)
- Surgical Dressing TechniqueDocument2 pagesSurgical Dressing TechniqueAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- The Seven Ages of ManDocument1 pageThe Seven Ages of ManAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Bowing: Bowing Fracture - Incomplete Fractures of Tubular Long Bones in Paediatric Patients (EspeciallyDocument9 pagesBowing: Bowing Fracture - Incomplete Fractures of Tubular Long Bones in Paediatric Patients (EspeciallyAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Mental Health MedsDocument5 pagesMental Health MedsAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Values Formation Through Literary PiecesDocument17 pagesValues Formation Through Literary PiecesAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Santiago To LaucpaoDocument1 pageSantiago To LaucpaoAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Swot Ana and SchedulingDocument2 pagesSwot Ana and SchedulingAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument2 pagesAcute GlomerulonephritisdesaatibagosNo ratings yet
- Management by ObjectivesDocument3 pagesManagement by ObjectivesAnne JillianNo ratings yet