Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Risk For Infection: Risk Factors May Include
Uploaded by
Charm Tanya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesrisk
Original Title
Risk for Infection
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentrisk
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesRisk For Infection: Risk Factors May Include
Uploaded by
Charm Tanyarisk
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
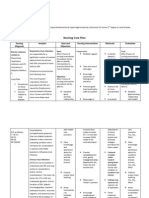
Risk for Infection
Risk factors may include
Inadequate secondary defenses and immunosuppression, e.g., bone
marrow suppression (dose-limiting side effect of both chemotherapy and
radiation).
Desired Outcomes
Remain afebrile and achieve timely healing as appropriate.
Identify and participate in interventions to prevent/reduce risk of infection.
Nursing Interventions
Rationale
Promote good handwashing
Protects patient from sources of
procedures by staff and visitors.
infection, such as visitors and staff
Screen and limit visitors who may
who may have an upper respiratory
have infections. Place in reverse
infection (URI).
isolation as indicated.
Emphasize personal hygiene.
Limits potential sources of infection
and secondary overgrowth.
Monitor temperature.
Temperature elevation may occur (if
not masked by corticosteroids or antiinflammatory drugs) because of
various factors (chemotherapy side
effects, disease process, or infection).
Early identification of infectious
process enables appropriate therapy
to be started promptly.
Assess all systems (skin, respiratory,
Early recognition and intervention
genitourinary) for signs and symptoms
may prevent progression to more
of infection on a continual basis.
serious situation or sepsis.
Nursing Interventions
Rationale
Reposition frequently; keep linens dry
Reduces pressure and irritation to
and wrinkle-free.
tissues and may prevent skin
breakdown (potential site for bacterial
growth).
Promote adequate rest and exercise
Limits fatigue, yet encourages
periods.
sufficient movement to prevent stasis
complications (pneumonia, decubitus,
and thrombus formation).
Stress importance of good oral
Development of stomatitis increases
hygiene.
risk of infection and secondary
overgrowth.
Avoid or limit invasive procedures.
Reduces risk of contamination, limits
Adhere to aseptic techniques.
portal of entry for infectious agents.
Monitor CBC with differential WBC
Bone marrow activity may be inhibited
and granulocyte count, and platelets
by effects of chemotherapy, the
as indicated.
disease state, or radiation therapy.
Monitoring status of
myelosuppression is important for
preventing further complications
(infection, anemia, or hemorrhage)
and scheduling drug delivery.
You might also like
- Cancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionDocument2 pagesCancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- Minimizing Infection RiskDocument2 pagesMinimizing Infection RiskEllmaaanNo ratings yet
- Cancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageCancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionAnne JillianNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPf_jm06_gNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Infection PreventionDocument32 pagesEpidemiology and Infection Preventionbkbaljeet116131No ratings yet
- NCP Elective (Risk For Infection)Document1 pageNCP Elective (Risk For Infection)student_019No ratings yet
- Questions For OSCE Exam - Model Answers 2Document8 pagesQuestions For OSCE Exam - Model Answers 2Farah FarahNo ratings yet
- Role of Physiotherapy in COVID-19Document43 pagesRole of Physiotherapy in COVID-19ajaykumar soddalaNo ratings yet
- Infections in ICUDocument7 pagesInfections in ICUNikolay ToméNo ratings yet
- Strategy of Disease Prevention and Disease Surveillance 8Document32 pagesStrategy of Disease Prevention and Disease Surveillance 8sanjivdas100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationPaul Cubacub100% (1)
- Mc3g5report Bsn1aDocument58 pagesMc3g5report Bsn1aJhon Mhark GarinNo ratings yet
- Arjumand Zargar Anp@AARUSIMIDocument69 pagesArjumand Zargar Anp@AARUSIMIArjumand ZargarNo ratings yet
- Legal ResponsibilityDocument4 pagesLegal ResponsibilityNwambe VanessaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Summary of Findings, Conclusion and RecommendationsDocument5 pagesChapter Five Summary of Findings, Conclusion and RecommendationsKojo AduNo ratings yet
- General Principles of Prevention and Control of Communicable DiseasesDocument38 pagesGeneral Principles of Prevention and Control of Communicable DiseasesMazinNo ratings yet
- Risk For Infection: Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesRisk For Infection: Nursing DiagnosisdollythesheepNo ratings yet
- Hand Infections CpsDocument11 pagesHand Infections CpsDavid SidhomNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Communicable Diseases (Include Epidemiology)Document19 pagesIntroduction To Communicable Diseases (Include Epidemiology)Kubra RasoolNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Surgical Site InfectionDocument10 pagesPrevention of Surgical Site InfectionValiant Baybay100% (1)
- Strategy of Disease Prevention and Disease Surveillance 8Document31 pagesStrategy of Disease Prevention and Disease Surveillance 8sanjivdas100% (1)
- CD Part 2 - Communicable Diseases With Pics (1) ConDocument239 pagesCD Part 2 - Communicable Diseases With Pics (1) ConMackoi SalamanesNo ratings yet
- Introduction IPCDocument28 pagesIntroduction IPCbiniyam NigussieNo ratings yet
- INFECTIOUS PROC-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesINFECTIOUS PROC-WPS OfficeNifemi AketanNo ratings yet
- Levels of PreventionDocument5 pagesLevels of PreventionSofia JuliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Healthcare EpidemiologyDocument10 pagesChapter 12 Healthcare EpidemiologyRegiena Tamargo100% (1)
- CH-1i INFECTION PREVENTION AND PATIENT SAFETY - MODULE 1Document40 pagesCH-1i INFECTION PREVENTION AND PATIENT SAFETY - MODULE 1Sisay Fesseha AmbayeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Infection Prevention and ControlDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Infection Prevention and ControlElaine MacalandaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Abx Prophylaxis o Surgical Wounds - AFPDocument16 pagesGuidelines For Abx Prophylaxis o Surgical Wounds - AFPyusmaniqistinaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Infection ControlDocument53 pagesConcepts of Infection ControlPak Pandir0% (1)
- NCP Neonatal SepsisDocument1 pageNCP Neonatal SepsisGen-GenMedranoGirayNo ratings yet
- Prophylactic Use of Anti-Microbial Agents: Presented By: Jagir R. Patel Assistant ProfessorDocument18 pagesProphylactic Use of Anti-Microbial Agents: Presented By: Jagir R. Patel Assistant ProfessorJagirNo ratings yet
- Medical Problem That Needs Antibiotic ProphylaxisDocument6 pagesMedical Problem That Needs Antibiotic ProphylaxisPing KyNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument9 pagesMICROBIOLOGYAmr Ramazan IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Infection Control Policies and ProceduresDocument9 pagesInfection Control Policies and ProceduresKelly J WilsonNo ratings yet
- Pencegahan Dan Kontrol InfeksiDocument49 pagesPencegahan Dan Kontrol InfeksiTettanya Iyu Sama Ariqah100% (1)
- Questions For OSCE Exam 2Document7 pagesQuestions For OSCE Exam 2Farah FarahNo ratings yet
- Hiv AidsDocument7 pagesHiv AidsPrecious UncianoNo ratings yet
- EpidemiologyDocument24 pagesEpidemiologyferrer_michaelangeloNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nadia Aziz C.A.B.C.M Baghdad Medical CollegeDocument39 pagesDr. Nadia Aziz C.A.B.C.M Baghdad Medical CollegeMazinNo ratings yet
- INFECTION CONTROL by Sandra WilsonDocument24 pagesINFECTION CONTROL by Sandra WilsonsandraNo ratings yet
- Infection Prevention & ControlDocument4 pagesInfection Prevention & ControlAmit HalderNo ratings yet
- Infection ControlDocument12 pagesInfection Controlghufran khanNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Study Guide-2Document5 pagesExam 2 Study Guide-2Enoch SuhNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors For Surgical Site InfectionDocument5 pagesRisk Factors For Surgical Site InfectionElizabeth Mautino CaceresNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Infection: Infectious Diseases Global HealthDocument12 pagesPrevention of Infection: Infectious Diseases Global HealthsaravananNo ratings yet
- Meningitis: Morbidity and MortalityDocument9 pagesMeningitis: Morbidity and MortalityRenz Henry AbagatnanNo ratings yet
- Nanda 1Document4 pagesNanda 1Ethel GeorgeNo ratings yet
- National T.B Control Programme: Presented By: Ayushi Raina Clinical InstructorDocument57 pagesNational T.B Control Programme: Presented By: Ayushi Raina Clinical Instructorayushi rainaNo ratings yet
- Cancer Colon and Rectum (Wardah)Document23 pagesCancer Colon and Rectum (Wardah)WardahAliNo ratings yet
- Medical Dan Surgical AsepsisDocument49 pagesMedical Dan Surgical AsepsisTahtawi 'Afid' Rifai RidhoNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument43 pagesInfectious DiseasesClaire SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Questions For OSCE Exam - Model AnswersDocument9 pagesQuestions For OSCE Exam - Model AnswersFarah FarahNo ratings yet
- Profilaxis AntiibioticaDocument6 pagesProfilaxis AntiibioticaAndrés RezucNo ratings yet
- Thesis Prevention of Nosocomial Infections As Percieved by Staff NursesDocument7 pagesThesis Prevention of Nosocomial Infections As Percieved by Staff NursesDhonnalyn Amene Caballero100% (1)
- Laskin The Use of Prophylactic AntibioticsDocument6 pagesLaskin The Use of Prophylactic Antibioticsapi-265532519No ratings yet
- Nur 111 Session 19 Sas 1Document6 pagesNur 111 Session 19 Sas 1Zzimply Tri Sha UmaliNo ratings yet
- Nurse Practitioner Clinical Protocol: Management of CellulitisDocument11 pagesNurse Practitioner Clinical Protocol: Management of CellulitisJason MarshallNo ratings yet
- Hospital Associated Infections (HAI)Document19 pagesHospital Associated Infections (HAI)Asmaa MostafaNo ratings yet
- Usual CodesDocument2 pagesUsual CodesCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Cradled by Majestic MountainsDocument4 pagesCradled by Majestic MountainsCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Employment Contract Staff Nurse 1Document3 pagesEmployment Contract Staff Nurse 1Charm Tanya100% (2)
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesRepublic of The PhilippinesCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- PDS-Work Experience SheetDocument2 pagesPDS-Work Experience SheetCes Camello100% (1)
- Give Love On Christmas DayDocument2 pagesGive Love On Christmas DayCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Vission Mission GoalsDocument3 pagesVission Mission GoalsCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- By Benelyne MDocument9 pagesBy Benelyne MCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Nurse Supervisor Job DescriptionDocument1 pageNurse Supervisor Job DescriptionCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Visitors Pass 001Document1 pageVisitors Pass 001Charm TanyaNo ratings yet
- 6 CS Form 100 Revised September 2016 PDFDocument2 pages6 CS Form 100 Revised September 2016 PDFNiel Edar Balleza100% (2)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of RefrigeratorsDocument4 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of RefrigeratorsCharm Tanya60% (5)
- Mabz PoDocument1 pageMabz PoCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- J.D of Family PhysicianDocument1 pageJ.D of Family PhysicianCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Nclex Reviewer - CHN (Nurses Labs)Document30 pagesNclex Reviewer - CHN (Nurses Labs)Wilma Baludo100% (1)
- Activity - Brain DissectionDocument8 pagesActivity - Brain DissectionCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- PreDocument2 pagesPreCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Developmental of Mental Task Summary of Observation Recommendation More Examples Intermodal Jean Piaget (Concrete Operational Stage)Document4 pagesDevelopmental of Mental Task Summary of Observation Recommendation More Examples Intermodal Jean Piaget (Concrete Operational Stage)Charm TanyaNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Laparoscopic CholecystectomyDocument10 pagesLaparoscopic CholecystectomyCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Sample QuestionsDocument21 pagesMicrosoft Word - Sample QuestionsCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- What Is The DASH Eating Plan - (Printer-Friendly)Document2 pagesWhat Is The DASH Eating Plan - (Printer-Friendly)Charm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Cranial NerveDocument17 pagesCranial NerveCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Course RequirementDocument27 pagesCourse RequirementCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- MCN Exam Questions 2Document15 pagesMCN Exam Questions 2Emer Joy T. Vale67% (6)
- How To Solve Drug Dosage Problems August 2012Document9 pagesHow To Solve Drug Dosage Problems August 2012Charm TanyaNo ratings yet
- The Aquino Health Agenda: Achieving Universal Health Care For All FilipinosDocument9 pagesThe Aquino Health Agenda: Achieving Universal Health Care For All FilipinosAlbert DomingoNo ratings yet
- Han 1Document1 pageHan 1Charm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Topics Included AreDocument9 pagesTopics Included AreCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- TipsDocument75 pagesTipsCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningFrom EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)No ratings yet
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingFrom EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1138)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassFrom EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)