Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Penanganan Trauma Kepala
Uploaded by
Akbarian Noor0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views14 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views14 pagesPenanganan Trauma Kepala
Uploaded by
Akbarian NoorCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
Penanganan Trauma Kepala
Kuliah Pakar Neuropsikiatri
2014
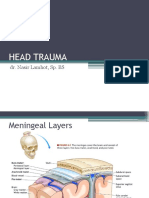
Anatomi
Cedera Kepala
Scalp Wounds
Skull Injuries
Traumatic Brain Injury
Scalp Injuries
Skull Fractures
Traumatic Brain Injury
Cedera otak primer
Cedera otak sekunder
Tekanan Intrakranial
TIK ==> CSF, Blood, Brain
CPP = MAP - TIK
Sindroma Herniasi Serebri
GCS < 9 dengan deceberate
GCS < 9 dilatasi pupil, pupil bilateral, no reflek
GCS < 9, kemudian turun > 2 poin
Klasifikasi TBI
Gegar otak
Kontusio serebri
Perdarahan subarakhnoid
Cedera aksonal difuse
Intracranial hemorrhage
Hematom epidural akut
Hematom subdural akut
Intraserebral hemorrhage
Anoxic Brain Injury
Management
Scene Size Up
Assesment
LOC : AVPU, GCS
Vital Signs:
Jarang menyebabkan syok, jika syok mungkin
multiple injury
Cushing Syndrome
Pupil: Dilated, unequal, absent response
Herniation syndrome
10
Management of Head Injury
ABCs with C-spine control
C-collar, long board
Ensure adequate oxygenation
If signs of cerebral herniation present, controlled hyperventilation
with BVM at 20-24 breaths/minute
Any patient with significant head injury has neck injury
until proven otherwise
11
Management of Head Injury
Controlled hyperventilation
Lowers blood carbon dioxide levels
Causes constriction of blood vessels in brain
As vessels constrict brain shrinks
As brain shrinks intracranial pressure drops
Circulation:
delayed resuscitation Vs early
resuscitation
Koloid Vs Cristaloid
12
Management of Head Injury
Do NOT apply pressure to open or
depressed skull fractures
Do NOT attempt to stop flow of blood
or CSF from nose, ears
Do NOT remove penetrating objects
You might also like
- Head TraumaDocument5 pagesHead TraumaChynthea ParamithaNo ratings yet
- Injuries To Head, Spine, and FaceDocument8 pagesInjuries To Head, Spine, and FaceNina OaipNo ratings yet
- Head TraumaDocument54 pagesHead TraumaVidelia ArlitaNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma: Yoon Seung-Hwan, M.DDocument53 pagesHead Trauma: Yoon Seung-Hwan, M.DAhmed ZahranNo ratings yet
- Cedera Kepala Dan Otak: Dr. Isnaniah, Sp. S Bagian Saraf Fkik UntadDocument91 pagesCedera Kepala Dan Otak: Dr. Isnaniah, Sp. S Bagian Saraf Fkik UntadSiwa MerthadinataNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma: Yoon Seung-Hwan, M.DDocument53 pagesHead Trauma: Yoon Seung-Hwan, M.Dilham darnoNo ratings yet
- Head Injuries 2015Document41 pagesHead Injuries 2015jimmyNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma: Kelompok 2: Andry Wongso Rhiza M.I.S Terri S. S PriscillaDocument22 pagesHead Trauma: Kelompok 2: Andry Wongso Rhiza M.I.S Terri S. S PriscillaJenadi BinartoNo ratings yet
- Head Injury Management GuideDocument58 pagesHead Injury Management GuideMuvenn KannanNo ratings yet
- ATLS - Head Trauma ImodifiedDocument39 pagesATLS - Head Trauma ImodifiedSammon TareenNo ratings yet
- ATLS - Head Trauma ImodifiedDocument39 pagesATLS - Head Trauma ImodifiedSammon TareenNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma: Dr. Nasir Lamhot, Sp. BSDocument31 pagesHead Trauma: Dr. Nasir Lamhot, Sp. BSYohannes KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Brain Injury Dr. Shema Dr. MuyimboDocument58 pagesBrain Injury Dr. Shema Dr. MuyimboTIMOTHY MUYIMBONo ratings yet
- Head Trauma Chapter 6Document43 pagesHead Trauma Chapter 6Aray Al-AfiqahNo ratings yet
- WEBINAR Trauma Kepala PREMIER IDKI Mei 2020 FinalDocument130 pagesWEBINAR Trauma Kepala PREMIER IDKI Mei 2020 FinalAndiNo ratings yet
- 3 Common Neurologic Problems of Altered PerceptionDocument10 pages3 Common Neurologic Problems of Altered PerceptionSTEFFANIE VALE BORJANo ratings yet
- TBI FinalDocument28 pagesTBI Finalawais mpNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument50 pagesHead InjuryThiagarajah RaviNo ratings yet
- Med SurgDocument98 pagesMed SurgKimsha Concepcion88% (8)
- Traumatic Brain Injury Guide by Neurology ProfessorDocument51 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury Guide by Neurology ProfessorRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument42 pagesHead InjuryMohammad Husni Banisalman100% (3)
- Raised ICP, SOL, HerniationDocument5 pagesRaised ICP, SOL, HerniationGrilled CroweNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Head Injury MakasarDocument113 pagesKuliah Head Injury MakasarJerrod WilsonNo ratings yet
- Nervous System AlterationsDocument45 pagesNervous System AlterationsMajesty ParkerNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain Injury PresentationDocument51 pagesTraumatic Brain Injury PresentationKah Sui Tan100% (2)
- Subdural Hematoma FinalDocument34 pagesSubdural Hematoma FinalMariam AntonyNo ratings yet
- ATLS - Head Trauma ModifiedDocument30 pagesATLS - Head Trauma ModifiedAmsal Darmawan DakhiNo ratings yet
- ATLS - Head Trauma ModifiedDocument30 pagesATLS - Head Trauma ModifiedAmsal Darmawan DakhiNo ratings yet
- Cedera KepalaDocument33 pagesCedera Kepalahali100% (1)
- Understanding Traumatic Brain InjuryDocument59 pagesUnderstanding Traumatic Brain InjuryYusfitaria AlvinaNo ratings yet
- TREPANATION AT RURAL HOSPITAL-englishDocument35 pagesTREPANATION AT RURAL HOSPITAL-englishTom KristiantoNo ratings yet
- Increased ICP and Neurological Trauma GuideDocument14 pagesIncreased ICP and Neurological Trauma GuideMhoy CostesNo ratings yet
- LP Moderate Head InjuryDocument16 pagesLP Moderate Head InjuryDes JuniarniNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument66 pagesHead Injurynur muizzah afifah hussinNo ratings yet
- Cerebrospinal TraumaDocument37 pagesCerebrospinal TraumaMarcus Wong KSNo ratings yet
- 3 - Head Injured PatientDocument94 pages3 - Head Injured PatientAmmarNo ratings yet
- 4.head TraumaDocument33 pages4.head TraumaKANYAMAHANGA JUSTINNo ratings yet
- Brain TraumaDocument32 pagesBrain Traumafrengki kobogauNo ratings yet
- Head Injury Causes and TreatmentDocument47 pagesHead Injury Causes and TreatmentnikowareNo ratings yet
- Childhood Head InjuriesDocument26 pagesChildhood Head InjuriesNatnael ShifferawNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 3 - Test 1 Nursing Management of Patients With Acute Intracranial Problems Chapter 55 &56Document7 pagesMed Surg 3 - Test 1 Nursing Management of Patients With Acute Intracranial Problems Chapter 55 &56Julx0No ratings yet
- Traumatic Brain InJuryDocument21 pagesTraumatic Brain InJuryShara SampangNo ratings yet
- Monitor blood glucose levels closely and maintain euglycemiaDocument74 pagesMonitor blood glucose levels closely and maintain euglycemiaLuther ThengNo ratings yet
- Managing Head Injuries: Medical and Surgical ApproachesDocument38 pagesManaging Head Injuries: Medical and Surgical ApproachesAmanuel AyladoNo ratings yet
- TBI & Spinal Injury ManagementDocument33 pagesTBI & Spinal Injury ManagementBibaswan ChakrabartyNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument34 pagesHead Injuryrxmskdkd33No ratings yet
- Cedera KepalaDocument102 pagesCedera KepalaNesaNo ratings yet
- Med Surg Study GuideDocument98 pagesMed Surg Study Guideprogramgrabber100% (23)
- Case Study SDHDocument34 pagesCase Study SDHLisa Daniel HouselNo ratings yet
- Emd166 Slide Head InjuryDocument40 pagesEmd166 Slide Head Injuryarikashafa6No ratings yet
- Head Injury Outline of Management CDocument89 pagesHead Injury Outline of Management CPanna SahaNo ratings yet
- Head Injury PPT 160219094543Document49 pagesHead Injury PPT 160219094543Claire De VeraNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma: Classification, Diagnosis and Management of Head InjuriesDocument13 pagesHead Trauma: Classification, Diagnosis and Management of Head InjuriesEdwin OkonNo ratings yet
- Head Injury: Ibrahim Mahguob, M.DDocument44 pagesHead Injury: Ibrahim Mahguob, M.DAmir SharifNo ratings yet
- Head Trauma: Initial Assessment and ManagementDocument38 pagesHead Trauma: Initial Assessment and Managementi wayan dediyanaNo ratings yet
- Trauma Kapitis RevisiDocument54 pagesTrauma Kapitis RevisiRatika Ayu PiliangNo ratings yet
- Head and Spinal Cord Injury (Ci)Document111 pagesHead and Spinal Cord Injury (Ci)azmerawNo ratings yet
- Cranio Cerebral TraumaDocument10 pagesCranio Cerebral TraumaAlexandrutzu356No ratings yet
- Lec 1 Head InjuriesDocument43 pagesLec 1 Head Injurieshina MinaNo ratings yet
- Jks 200607 001103 - 15 19Document5 pagesJks 200607 001103 - 15 19Fatchul ChoiriNo ratings yet
- Lamp IranDocument16 pagesLamp IranAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocument18 pagesNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- PENDEKATAN ETIKA DALAM MERAWAT PASIEN ANSIETASDocument9 pagesPENDEKATAN ETIKA DALAM MERAWAT PASIEN ANSIETASAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- Askep Case Study 1Document19 pagesAskep Case Study 1Akbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- Kaolin Pektin: Makalah Farmakologi KeperawatanDocument1 pageKaolin Pektin: Makalah Farmakologi KeperawatanAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- WHOenlguideDocument2 pagesWHOenlguideOctoNo ratings yet
- Lecture15B MSDocument12 pagesLecture15B MSAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- Peranan Cairan Perioperative RevDocument26 pagesPeranan Cairan Perioperative RevAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- Erythema MultiformeDocument5 pagesErythema MultiformeNicco MarantsonNo ratings yet
- Prot LoseDocument7 pagesProt LoseAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- Jurnal TBCDocument8 pagesJurnal TBCAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- 065 WoundDocument0 pages065 WoundAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- Br. J. Anaesth. 2000 Nicholson 599 610Document0 pagesBr. J. Anaesth. 2000 Nicholson 599 610MarcS218No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument8 pagesDocumentAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- Clustering Spasial Dan Temporal Dari Kawasaki Syndrome Kasus - FilesDocument13 pagesClustering Spasial Dan Temporal Dari Kawasaki Syndrome Kasus - FilesAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- Praesentation Brigitta BuschDocument21 pagesPraesentation Brigitta BuschAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Konsentrasi EstradiolDocument15 pagesEvaluasi Konsentrasi EstradiolAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- 1704 05Document10 pages1704 05Vebby 'bee' AstriNo ratings yet
- Akbarian NoorDocument2 pagesAkbarian NoorNisya Andesita HNo ratings yet
- StenosisDocument5 pagesStenosisAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet
- English: Simple, Compound & Complex SentencesDocument12 pagesEnglish: Simple, Compound & Complex SentencesPaRaDoX eLaKSaMaNaNo ratings yet
- Efek Perawatan Luka Terkontaminasi Dengan Ekstrak Bawang Putih Lanang Dalam MemperDocument1 pageEfek Perawatan Luka Terkontaminasi Dengan Ekstrak Bawang Putih Lanang Dalam MemperAkbarian NoorNo ratings yet