Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IOS Interior Routing Protocols
Uploaded by
cutefrenzyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IOS Interior Routing Protocols
Uploaded by
cutefrenzyCopyright:
Available Formats
G
l
o
b
a
l
C
o
n
f
i
g
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
packetlife.net
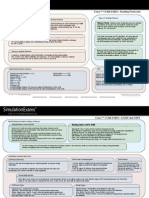
Unicast Routing Protocols Comparison
Type
Algorithm
Distance Vector
Bellman-Ford
RIP
Distance Vector
DUAL
EIGRP
Link State
Dijkstra
OSPF
Link State
Dijkstra
IS-IS
Path Vector
Path Selection
BGP
Admin Distance
Standard
120
RFCs 2080, 2453
90/170 (external)/5 (summary)
Cisco proprietary
110
RFCs 2328, 5340
115
ISO 10589, RFC 1142
20/200 (IBGP)
RFC 4271
Supported Protocols
Transport
IPv4, IPv6
UDP/520
IPv4, IPv6, IPX, Appletalk
IP/88
IPv4, IPv6
IP/89
IPv4, IPv6, CLNP
Layer 2
IPv4, IPv6
TCP/179
Authentication Plain, MD5 MD5 Plain, MD5, AH (v3) Plain, MD5 MD5
RIP
Metric Formula
bw = 10
7
/ minimum path bandwidth in kbps
delay = interface delay in secs / 10
! Enable EIGRP for an autonomous system
[ipv6] router eigrp AS-number
! Specify a router ID formatted in IPv4 dotted-decimal
[eigrp] router-id router-ID
! Disable automatic classful summarization (IPv4 only)
no auto-summary
! Enable EIGRP on interfaces by network (IPv4 only)
network IPv4-address wildcard-mask
! Modify maximum paths for equal-cost load balancing
maximum-paths 1-16
! Configure multiplier for unequal-cost load balancing
variance 1-128
! Configure K values to manipulate the metric formula
metric weights 0 k1 k2 k3 k4 k5
! Explicitly identify neighbors on NBMA links
neighbor IP-address interface
! Designate passive interfaces
passive-interface {interface | default}
! Enable stub routing
[eigrp] stub [receive-only | connected | static | summary | redist]
Default K Values Packet Types
K1 1
K2 0
K3 1
K4 0
K5 0
1 Update
3 Query
4 Reply
5 Hello
8 Acknowledge
Feasible Distance
The distance advertised by a neighbor plus the cost
to get to that neighbor
Reported Distance
The metric for a route advertised by a neighbor
Stuck In Active (SIA)
The condition when a route becomes unreachable
and not all queries for it are answered; adjacencies
with unresponsive neighbors are reset
Passive Interface
An interface which does not participate in EIGRP
but whose network is advertised
Stub Router
A router which advertises only a subset of routes,
and is omitted from the route query process
EIGRP
Terminology
Multicast Address 224.0.0.9 224.0.0.10 224.0.0.5-6 N/A N/A
EIGRP Configuration
I
n
t
e
r
f
a
c
e
C
o
n
f
i
g
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
interface type number
! Enable EIGRP for IPv6 on the interface
ipv6 eigrp AS-number
! Set the maximum bandwidth EIGRP can consume (can be >100%)
ip[v6] bandwidth-percent eigrp AS-number 1-999999
! Configure manual summarization of outbound routes
ip summary-address eigrp AS-number IPv4-address subnet-mask [AD]
ipv6 summary-address eigrp AS-number IPv6-prefix [AD]
! Enable MD5 authentication
ip[v6] authentication mode eigrp AS-number md5
ip[v6] authentication key-chain eigrp AS-number key-chain
! Modify interface hello and hold timers
ip[v6] hello-interval eigrp AS-number seconds
ip[v6] hold-time eigrp AS-number seconds
! Toggle split horizon
[no] ip[v6] split-horizon eigrp AS-number
Troubleshooting
show ip[v6] eigrp {interfaces | neighbors }
show ip[v6] eigrp topology
clear ip[v6] eigrp [AS-number] neighbors
debug ip[v6] eigrp [neighbor]
Default Timers
Hello 5 sec
Hold 15 sec
LAN (>T1)
60 sec
180 sec
WAN (<=T1)
256 * (K1 * bw + + K3 * delay) *
K2 * bw
256 - load
K5
rel + K4
Router Roles
Internal Router
All interfaces reside within the same area
Backbone Router
A router with at least one interface in area 0
Area Border Router (ABR)
Connects two or more areas
AS Boundary Router (ASBR)
Connects to additional routing domains
(redistribution to or from other protocols)
Troubleshooting
show ip[v6] ospf [process] interface
show ip[v6] ospf database [LSA-type]
OSPFv2 Link State Advertisements
Router Link (Type 1)
Lists neighboring routers and the cost to each;
flooded within an area
Network Link (Type 2)
Generated by a DR; lists all routers on an
adjacent segment; flooded within an area
Network Summary (Type 3)
Generated by an ABR; advertises routes
between areas
ASBR Summary (Type 4)
Injected by an ABR into the backbone to
advertise the presence of an ASBR in a non-
backbone area
External Link (Type 5)
Generated by an ASBR and flooded throughout
the AS to advertise a route external to OSPF
NSSA External Link (Type 7)
Generated by an ASBR in a not-so-stubby area;
converted into a type 5 LSA by the ABR when
leaving the area
Area Types
Standard Area
Default OSPF area type
Stub Area
External link (type 5) LSAs are replaced with
a single default route
Totally Stubby Area
Type 3, 4, and 5 LSAs are replaced with a
default route
Not-So-Stubby Area (NSSA)
A stub area containing an ASBR; type 5 LSAs
are converted to type 7 within the area
External Route Types
E1
Considers the cost to the advertising ASBR
plus the external cost of the route
E2 (Default)
The external cost of a route as seen by the
ASBR; internal OSPF cost is not considered
show ip[v6] ospf border-routers
show ip[v6] ospf virtual-links
debug ip[v6] ospf []
Metric Formula
DR/BDR Election
The BDR also maintains
adjacencies with all routers in
case the DR fails
Does not occur on point-to-
point or multipoint links
Default priority (0-255) is 1;
highest priority wins; 0 cannot
be elected
DR preemption will not occur
unless the current DR is reset
Virtual Links
Tunnel formed to join two
areas across an intermediate
Both end routers must share
a common non-stub area
At least one end must reside
in area 0
Adjacency States
1
2
Down
Attempt
5
6
ExStart
Exchange
3
4
Init
2-Way
7
8
Loading
Full
The DR serves as a common
point for all adjacencies on a
multiaccess segment
Network Types
DR/BDR Elected
Nonbroadcast
(NBMA)
Multipoint
Broadcast
Neighbor Discovery
Hello/Dead Timers
Defined By
Supported Topology
Multipoint
Nonbroadcast Broadcast Point-to-Point
Yes
No
30/120
RFC 2328
Full Mesh
No
Yes
30/120
RFC 2328
Any
No
No
30/120
Cisco
Any
Yes
Yes
10/40
Cisco
Full Mesh
No
Yes
10/40
Cisco
Point-to-Point
OSPF
Integrated IS-IS
Network Types
DIS Elected Yes
Broadcast
Neighbor Discovery Yes
Hello/Dead Timers 10/30
Adjacency Requirements
Interface MTUs must match
Areas must match (if level 1)
System IDs must be unique
Authentication must succeed
show [clns | isis] neighbors
show clns interface
show isis [ipv6] topology
Levels must match
NSAP Addressing
Interdomain Part (IDP)
Portion of the address used in routing between autonomous systems;
assigned by ISO
Domain-Specific Part (DSP)
Portion of the address relevant only within the local AS
Authority and Format Identifier (AFI)
Identifies the authority which dictates the format of the address
Initial Domain Identifier (IDI)
An organization belonging to the AFI
High Order DSP (HODSP)
The area within the AS
System ID
Unique router identifier; 48 bits for Cisco devices (often taken from an
Ethernet MAC address)
NSAP Selector (SEL)
Identifies a network layer service; always 0x00 in a NET
No
Point-to-Point
Yes
10/30
Troubleshooting
show isis [database | spf-log]
debug [clns | isis] []
ISO Routing Levels
Level 0
Level 1
Level 2
Used to locate end systems
Routing within an area (IS-IS)
Routing between areas (IS-IS)
Level 3 Inter-AS routing
Terminology
Type-Length-Value (TLV)
Variable-length modular datasets carried by PDUs
Link State PDU (LSP)
Carry TLVs encompassing link state information
DIS Election
Highest-priority interface elected
Highest system ID breaks SNPA tie
Default interface priority is 64
Current DIS may be preempted, unlike OSPF
Highest SNPA (e.g. MAC or DLCI) breaks tie
Sequence Number Packet (SNP)
Used to request and advertise LSPs; can be complete
(CSNP) or partial (PSNP)
Network Entity Title (NET)
Unique router ID; includes area ID
Designated Intermediate System (DIS)
A pseudonode responsible for emulating point-to-
point links across a multi-access segment
G
l
o
b
a
l
C
o
n
f
i
g
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
! Create an OSPF process
[ipv6] router ospf process-ID
! Specify a router ID formatted as IPv4 dotted-decimal
router-id router-ID
! Modify the default reference bandwidth
auto-cost reference-bandwidth speed-in-mbps
! Assign interfaces to areas by network (OSPFv2)
network IPv4-address wildcard-mask area area
! Identify neighbors for NBMA links (OSPFv2)
neighbor IPv4-address [cost 1-65535]
! Configure summaries on area border routers
area area range { IPv4-address subnet-mask | IPv6-prefix }
! Summarize external routes (ASBRs only)
summary-address IPv4-address subnet-mask [not-advertise]
summary-prefix IPv6-prefix [not-advertise]
! Originate a default route
default-information originate [always]
! Designate stub, totally stubby, or not-so-stubby areas
area area { stub | nssa } [no-summary]
! Create a virtual link
area area virtual-link router-ID
OSPF Configuration
I
n
t
e
r
f
a
c
e
C
o
n
f
i
g
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
interface type number
! Enable OSPF on the interface
ip[v6] ospf process-ID area area
! Identify neighbors for NBMA links (OSPFv3)
ipv6 ospf neighbor IPv6-address
! Set interface cost manually
ip[v6] ospf cost 1-65535
! Configure DR election priority
ip[v6] ospf priority 0-255
! Specify network type (broadcast, point-to-point, etc.)
ip[v6] ospf network type
! Modify interface hello and dead intervals
ip[v6] ospf hello-interval seconds
ip[v6] ospf dead-interval seconds
! Enable MD5 authentication (OSPFv2)
ip ospf authentication message-digest
ip ospf message-digest-key key-id md5 key-string
! Enable IPsec authentication (OSPFv3)
ipv6 ospf auth ipsec spi spi-number { md5 | sha1 } string
OSPFv3 Link State Advertisements
0x2001
0x2002
Router LSA
Network LSA
0x2003
0x2004
Inter-area prefix LSA
Inter-area router LSA
0x4005
0x2007
0x0008
0x2009
AS-external LSA
Type-7 LSA
Link LSA
Intra-area prefix LSA
Name v2 Equiv.
Type 1
Type 2
Type 3
Type 4
Type 5
Type 7
N/A
N/A
Group Membership (Type 6)
Used by Multicast OSPF; unsupported by IOS
0x2006 Group membership LSA Type 6
G
l
o
b
a
l
C
o
n
f
i
g
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
! Enable IS-IS routing
router isis
! Specify one or more NET addresses
net NET
! Set global routing level (default level-1-2)
is-type { level-1 | level-1-2 | level-2-only }
! Configure IPv4 route summaries
summary-address IP-address subnet-mask [level]
! Configure IPv6 route summaries
address-family ipv6
summary-prefix IPv6-prefix [level]
! Originate a default route
default-information originate
IS-IS Configuration
I
n
t
e
r
f
a
c
e
C
o
n
f
i
g
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
interface type number
! Enable IS-IS on an interface
ip[v6] router isis
! Specify interface routing level
isis circuit-type { level-1 | level-1-2 | level-2-only }
! Set interface metric
isis [ipv6] metric { 1-16777214 | maximum }
! Designate the network as point-to-point
isis network point-to-point
! Configure DIS election priority
isis priority 0-127 [ level-1 | level-2 ]
! Modify interface hello and dead intervals
isis hello-interval seconds [ level-1 | level-2 ]
isis hello-multiplier 3-1000 [ level-1 | level-2 ]
! Enable MD5 authentication
isis authentication mode md5
isis authentication key-chain key-chain
RIP Implementations
RIPv1
Original RIP implementation, limited to
classful routing (obsolete)
RIPv2
Introduced support for classless routing,
triggered updates, and multicast
announcements (RFC 2453)
RIPng (RIP Next Generation)
Extends RIPv2 to support IPv6 routing
(RFC 2080); functions very similarly to
RIPv2 and is subsequently as limited
G
l
o
b
a
l
C
o
n
f
i
g
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
! Enable RIPv2 IPv4 routing
router rip
version 2
! Disable RIPv2 automatic summarization
no auto-summary
! Designate RIPv2 interfaces by network
network IPv4-network
! Identify unicast-only neighbors
neighbor IP-address
! Originate a default route
default-information originate
! Designate passive interfaces
passive-interface {interface | default}
! Modify equal-cost load balancing
maximum-paths 1-16
! Modify timers
timers basic update invalid hold flush
! Enable RIPng IPv6 routing
ipv6 router rip name
! Toggle split-horizon and poison-reverse
[no] split-horizon
[no] poison-reverse
RIP Configuration
I
n
t
e
r
f
a
c
e
C
o
n
f
i
g
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
interface type number
! Enable RIPng on the interface
ipv6 rip name enable
! Configure manual route summarization
ip summary-address rip IPv4-address subnet-mask
ipv6 rip name summary-address IPv6-prefix
! Enable MD5 authentication (RIPv2 only)
ip rip authentication mode md5
ip rip authentication key-chain key-chain
Troubleshooting
show ip[v6] protocols
show ip[v6] rip database
debug ip rip { database | events }
debug ipv6 rip [interface]
Message Types
Hello
DB Descr.
LS Request
LS Update
LS Ack
RIP Configuration
Terminology
Split-Horizon
Mitigates routing loops by ensuring a
route is never advertised back to the
neighbor from which it was learned
Poison Reverse
Learned routes are advertised back to
their originator as explicitly invalid
show ip[v6] ospf [process] neighbor
Transition tool; not ideal for
permanent designs
IS-IS Hello (IIH)
Establish and maintain neighbor adjacencies
1
2
3
4
5
cost =
reference-bandwidth
link speed
AFI IDI
49
Area
HODSP
0005.80ff.f800.0000 0001
System ID
0000.0c00.1234
SEL
00
Interdomain Part Domain-Specific Part
Condensed
NSAP
Example
You might also like
- Configuring MPLSDocument12 pagesConfiguring MPLSvenu_aNo ratings yet
- List of Network ProtocolsDocument5 pagesList of Network Protocolsanon_563889070No ratings yet
- Lab1 HPDocument9 pagesLab1 HPVictor Hugo Garay SaezNo ratings yet
- IP ServicesDocument22 pagesIP ServicesPaaNiiNo ratings yet
- VoIP BookDocument52 pagesVoIP Bookapi-3742832No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Network Analyzers NewDocument18 pagesAn Introduction To Network Analyzers NewpadmaiyerNo ratings yet
- Network Tap - WikipediaDocument48 pagesNetwork Tap - Wikipediaلمسة امل100% (1)
- IOS XR BGP Commands PDFDocument420 pagesIOS XR BGP Commands PDFTylorKytasaariNo ratings yet
- OSPF Troubleshoot LabDocument9 pagesOSPF Troubleshoot LabMoïse GuilavoguiNo ratings yet
- Domain Name System: Introduction To DNS, The Internet'S Distributed Naming SystemDocument17 pagesDomain Name System: Introduction To DNS, The Internet'S Distributed Naming SystemsrinivasNo ratings yet
- CCNA Security Module 6Document4 pagesCCNA Security Module 6XanatorNo ratings yet
- Computer Network System Administrator Interview QuestionDocument4 pagesComputer Network System Administrator Interview Questionkk4953No ratings yet
- Network Administrator Technical Interview QuestionsDocument12 pagesNetwork Administrator Technical Interview QuestionskaleebuNo ratings yet
- Network TroubleshootingDocument19 pagesNetwork TroubleshootingKevin NeshNo ratings yet
- Apds Unified Communications AssessmentDocument17 pagesApds Unified Communications AssessmentHeart FragileNo ratings yet
- WSWATCH1Document7 pagesWSWATCH1bebel_ccardoso3782No ratings yet
- OpenSSL Command-Line HOWTODocument18 pagesOpenSSL Command-Line HOWTOcatacol100% (1)
- What Is My IP Address - See Your Public Address - IPv4 & IPv6Document5 pagesWhat Is My IP Address - See Your Public Address - IPv4 & IPv6gamhewage madushanNo ratings yet
- The Monk Who Sold His FerrariDocument2 pagesThe Monk Who Sold His FerrariAyush RanjanNo ratings yet
- Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) One Picture SummaryDocument2 pagesHot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) One Picture SummaryNameNo ratings yet
- Ccna 3d v4 Module 3 ExamDocument7 pagesCcna 3d v4 Module 3 Exami'll_help_you100% (3)
- Switching PDFDocument104 pagesSwitching PDFRajkeen ChamanshaikhNo ratings yet
- Ccna R&SDocument77 pagesCcna R&SarunNo ratings yet
- Ccnasecurity Sba FinalDocument12 pagesCcnasecurity Sba FinalBilly Zomg100% (2)
- Configure AAA Authentication On Cisco RoutersDocument4 pagesConfigure AAA Authentication On Cisco Routersrumors158No ratings yet
- IOS Interior Routing ProtocolsDocument1 pageIOS Interior Routing ProtocolsPotosi LoleteNo ratings yet
- IGP: Open Shortest Path First v3: Dr. Dimitrios Kalogeras GrnetDocument39 pagesIGP: Open Shortest Path First v3: Dr. Dimitrios Kalogeras GrnetHariprasad RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lab 3Document39 pagesChapter 3 Lab 3luis vladimir cubillos sanchezNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document68 pagesChap 2Vladimir NdoyouNo ratings yet
- 01 Ospf ConfigDocument21 pages01 Ospf Configgabi_marisNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Single-Area Ospfv2 Configuration: Instructor MaterialsDocument76 pagesModule 2: Single-Area Ospfv2 Configuration: Instructor MaterialsHồngPhúcNo ratings yet
- CCNPv7 ROUTE Lab3-3 OSPFv3-Address-Families InstructorDocument26 pagesCCNPv7 ROUTE Lab3-3 OSPFv3-Address-Families InstructorHuanChiHuaNo ratings yet
- Ospf Notes Ospf Single AreaDocument5 pagesOspf Notes Ospf Single AreaIvan Estuardo Echeverría CatalánNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Ospfv3 Address Families: TopologyDocument21 pagesChapter 3 Lab 3-3, Ospfv3 Address Families: TopologyHarrison Hayes100% (1)
- OSPFDocument2 pagesOSPFAris CarrascoNo ratings yet
- IPv6 RoutingDocument45 pagesIPv6 RoutingNguyễn Tiến HoàiNo ratings yet
- Lab 3-3, OSPFv3Document12 pagesLab 3-3, OSPFv3Angel Mauricio Mercado AguirreNo ratings yet
- © 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Ospfv3, 2/03Document21 pages© 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Ospfv3, 2/03Jorge Luis Gomez PonceNo ratings yet
- Write A Report Which Details A Comparison of The IPv6 RIPDocument8 pagesWrite A Report Which Details A Comparison of The IPv6 RIPjonathanNo ratings yet
- Enabling OSPF: Determining IP RoutesDocument17 pagesEnabling OSPF: Determining IP RoutesSandoval El MonoNo ratings yet
- Configuring OSPF: Cisco's OSPF ImplementationDocument32 pagesConfiguring OSPF: Cisco's OSPF ImplementationTariq ElmoussaouiNo ratings yet
- 24 - Single-Area OSPFv2 ConfigurationDocument60 pages24 - Single-Area OSPFv2 ConfigurationJana MassadehNo ratings yet
- Instructor Materials Chapter 8: Single-Area Ospf: CCNA Routing and Switching Scaling NetworksDocument26 pagesInstructor Materials Chapter 8: Single-Area Ospf: CCNA Routing and Switching Scaling NetworksAji Tetap OutsiderNo ratings yet
- CCIE Routing and SwitchingDocument10 pagesCCIE Routing and SwitchingTuan Kiet LeNo ratings yet
- CCNP - FlashcardsDocument19 pagesCCNP - Flashcardsnacho_456No ratings yet
- Sybex CCNA 640-802: Chapter 7: EIGRP and OSPFDocument32 pagesSybex CCNA 640-802: Chapter 7: EIGRP and OSPFhoangNo ratings yet
- Configuring OSPF Brandon&KatieDocument8 pagesConfiguring OSPF Brandon&KatieLuis GonzalezNo ratings yet
- RIB CommandsDocument98 pagesRIB CommandsJorge VicuñaNo ratings yet
- Overview of IPv6 Static RoutingDocument18 pagesOverview of IPv6 Static RoutingjbgibarraNo ratings yet
- Enabling OSPF: Determining IP RoutesDocument14 pagesEnabling OSPF: Determining IP Routeshendra_01No ratings yet
- Chapter 7ccnaDocument32 pagesChapter 7ccnaashenafi animawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lect 5 Network Layer-Routing Protocols ConfigurationDocument28 pagesChapter 2 Lect 5 Network Layer-Routing Protocols Configurationmie_zan85No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Ospfv3 Address Families: TopologyDocument26 pagesChapter 3 Lab 3-3, Ospfv3 Address Families: TopologyGuruparan PrakashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lab 3-3, Ospfv3 Address Families: TopologyDocument26 pagesChapter 3 Lab 3-3, Ospfv3 Address Families: TopologyAhmed AlmussaNo ratings yet
- VRF MP BGP PDFDocument21 pagesVRF MP BGP PDFjnahamedNo ratings yet
- Mikrotik Ipv6Document6 pagesMikrotik Ipv6AfrilexxNo ratings yet
- Network Enterprise CourseDocument46 pagesNetwork Enterprise CourseNasser MohammedNo ratings yet
- CCNA ICND2 CheatsheetDocument10 pagesCCNA ICND2 CheatsheetLulzim BruçajNo ratings yet
- Ospf Lab: Router Types Used in The LabDocument5 pagesOspf Lab: Router Types Used in The LabmahadvikaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Iscom2110ea-Ma 20120830Document5 pagesDatasheet Iscom2110ea-Ma 20120830Vu Minh TuanNo ratings yet
- SLR5500 DataSheet ENG LorDocument4 pagesSLR5500 DataSheet ENG Lordot16eNo ratings yet
- GH-1AD-SW, GH-1KD-SW InstrDocument1 pageGH-1AD-SW, GH-1KD-SW InstrCostel GavrilasNo ratings yet
- Common Conversion Tables and EquationsDocument1 pageCommon Conversion Tables and Equationsshilpa_rehalNo ratings yet
- Configure ComputerDocument95 pagesConfigure ComputerHanz Dela Cruz100% (6)
- Digital Terrestrial Migration in The Philippines Part 1 - Melvin AcostaDocument10 pagesDigital Terrestrial Migration in The Philippines Part 1 - Melvin AcostaCullado Christian JosephNo ratings yet
- s1160 Cas FinalDocument22 pagess1160 Cas FinalASRUL HELMINo ratings yet
- FS5015 Install PosterDocument2 pagesFS5015 Install PosterJMARMOLSNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Wireless TechnologiesDocument2 pagesComparison of Wireless TechnologiesMuhammad SalmanNo ratings yet
- CC1121 High-Performance Low-Power RF Transceiver: 1 Device OverviewDocument36 pagesCC1121 High-Performance Low-Power RF Transceiver: 1 Device OverviewyandexNo ratings yet
- CUBE-CME SIP Trunk-ExampleDocument6 pagesCUBE-CME SIP Trunk-ExampleDenisa PriftiNo ratings yet
- Unit I Internet and The World Wide WebDocument3 pagesUnit I Internet and The World Wide WebSiddhesh DandekarNo ratings yet
- DHCPDocument23 pagesDHCPmichaelNo ratings yet
- UMTS Access and Retainability Performance Improvement Solution 01 (20120709)Document14 pagesUMTS Access and Retainability Performance Improvement Solution 01 (20120709)Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Integration Patterns Flash CardsDocument6 pagesEnterprise Integration Patterns Flash Cardstheht100% (1)
- M.tech - Advanced Communication and Information SystemsDocument45 pagesM.tech - Advanced Communication and Information SystemsSiji VargheseNo ratings yet
- Call Manager 8.6 AdDocument10 pagesCall Manager 8.6 AdEnemigo MioNo ratings yet
- Smart Device Functionality Gateway: TreetechDocument14 pagesSmart Device Functionality Gateway: TreetechRobson DeusdetteNo ratings yet
- Backdoor AndroidDocument1 pageBackdoor Androidyulika_vNo ratings yet
- Product Catalog: End-To-End Networking Solutions Serving The Needs of Small and Medium BusinessesDocument63 pagesProduct Catalog: End-To-End Networking Solutions Serving The Needs of Small and Medium BusinessesLuis Santiago Lillo GascaNo ratings yet
- Motorola Driver LogDocument13 pagesMotorola Driver LogClarice M. StarlingNo ratings yet
- Manual 2146 PDFDocument11 pagesManual 2146 PDFhallgate1No ratings yet
- Architecture Brief: The Brocade Data Center Fabric Reference Architecture For Vmware Vsphere 4Document18 pagesArchitecture Brief: The Brocade Data Center Fabric Reference Architecture For Vmware Vsphere 4xfireloveNo ratings yet
- Fttx/Pon Testing Reference PosterDocument3 pagesFttx/Pon Testing Reference PosterDjnsilva SilvaNo ratings yet
- Wireless H3CDocument40 pagesWireless H3CMichael David Samaniego VillarroelNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Cable Spectrum MibDocument4 pagesHarmonic Cable Spectrum MibJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Samsung Ua32eh50x0r 40eh50x0r Ua42eh5000r Ua46eh50x0r-50eh50x0r Ua22es500xr Chassis U73a 74pagesDocument74 pagesSamsung Ua32eh50x0r 40eh50x0r Ua42eh5000r Ua46eh50x0r-50eh50x0r Ua22es500xr Chassis U73a 74pagesWilinton PissoNo ratings yet
- EchoLife EG8145V5-V2 Datasheet 01Document3 pagesEchoLife EG8145V5-V2 Datasheet 01carlos medina berrospiNo ratings yet
- Atr4518r3 PDFDocument2 pagesAtr4518r3 PDFanon_556921642No ratings yet
- Cables, Adapters, Accessories - 1Document8 pagesCables, Adapters, Accessories - 1Nguyen Danh HuyNo ratings yet