Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Banun Kusumawardani Dept. Biomedic - Faculty of Dentistry Univ. Jember
Uploaded by
Trianike Nur Aini0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views15 pagesThe document summarizes the results of several histological studies examining the effects of various pathogens and treatments on periodontal tissues in rats. In the control group, the junctional epithelium was located at the cemento-enamel junction with parallel fiber attachments and minimal inflammation. Rats infected with P. gingivalis or T. denticola showed migration of the junctional epithelium and inflammatory cell infiltration. Rats given a mixed infection displayed more severe inflammation. The periodontitis group exhibited bone resorption and epithelial migration not seen in the control group, while vitamin C decreased inflammation. Dental tissues were unchanged over 12 months in controls.
Original Description:
perio
Original Title
Perio
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the results of several histological studies examining the effects of various pathogens and treatments on periodontal tissues in rats. In the control group, the junctional epithelium was located at the cemento-enamel junction with parallel fiber attachments and minimal inflammation. Rats infected with P. gingivalis or T. denticola showed migration of the junctional epithelium and inflammatory cell infiltration. Rats given a mixed infection displayed more severe inflammation. The periodontitis group exhibited bone resorption and epithelial migration not seen in the control group, while vitamin C decreased inflammation. Dental tissues were unchanged over 12 months in controls.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views15 pagesBanun Kusumawardani Dept. Biomedic - Faculty of Dentistry Univ. Jember
Uploaded by
Trianike Nur AiniThe document summarizes the results of several histological studies examining the effects of various pathogens and treatments on periodontal tissues in rats. In the control group, the junctional epithelium was located at the cemento-enamel junction with parallel fiber attachments and minimal inflammation. Rats infected with P. gingivalis or T. denticola showed migration of the junctional epithelium and inflammatory cell infiltration. Rats given a mixed infection displayed more severe inflammation. The periodontitis group exhibited bone resorption and epithelial migration not seen in the control group, while vitamin C decreased inflammation. Dental tissues were unchanged over 12 months in controls.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
Banun Kusumawardani
Dept. Biomedic - Faculty of Dentistry
Univ. Jember
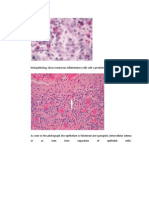
The overall histological image of the control animal. Junctional
epithelium was located at the cemento-enamel junction level.
Parallel and well organized fiber attachments were observed
below the epithelium with minimal inflammatory cell infiltration
(A) H&E stain, 200, (B) H&E stain, 400
Comparative maxillary histology
(hematoxylin and eosin) of alveolar
bone sections from maxilla of rat
infected with P. gingivalis and/or T.
denticola at 12 weeks. (a) from sham-
infected control rat displaying minimal
inflammation, lack of migration of
junctional epithelium (JE) and minimal
inflammation in the connective tissue
(CT); (b) from the P. gingivalis infected
rat showing prominent epithelium
hyperplasia (EH), migration of JE and
increase in number of blood vessels
(BV) (indicated by black arrows); (c)
from the T. denticola infected rat also
exhibits migration of JE and EH; and (d)
from the mixed infection with P.
gingivalis + T. denticola infected rat
demonstrates dense inflammation (DI)
(indicated by white arrows) along with
migration of JE. JE indicates junctional
epithelium, CT connective tissue, EH
epithelial hyperplasia, BV blood vessels,
DI dense inflammation. All images at
20 magnification
Histological view of the periodontal tissues (HE staining). No pathological changes are evident in the
control group (A). The periodontitis group (B) showed alveolar bone resorption (distance between the
white lines), apical migration of junctional epithelium (asterisk) and infiltration of polymorphonuclear
leukocytes in the connective tissue adjacent to the junctional epithelium [arrows in (C) where (C) shows
the area in the black box of (B) magnified]. The vitamin C group showed alveolar bone resorption (white
lines) and apical migration of junctional epithelium (asterisk), and decreased infiltration of
polymorphonuclear leukocytes (arrows in (E) where (E) shows the area in the black box of (D) magnified).
Arrowheads show cemento-enamel junction: AB, alveolar bone; CT, connective tissue; D, dentin. Scale
bar = 200 m (A, B and D); Scale bar = 50 m (C and E).
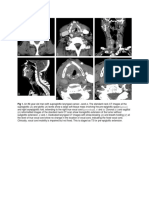
Absence of pathological changes in dental and periodontal tissues in control group.
Animals were evaluated for dental and periodontal histological changes at 1 (a, b), 3
(c, d), 6 (e, f), 9 (g, h) and 12 (i, j) months
Thank
you
You might also like
- Banun Kusumawardani Dept. Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Dentistry Univ. JemberDocument18 pagesBanun Kusumawardani Dept. Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Dentistry Univ. JemberdiianiitarahmaNo ratings yet
- The Many Faces of Osteomyelitis: A Pictorial ReviewDocument28 pagesThe Many Faces of Osteomyelitis: A Pictorial ReviewAnnisa' Ma'rufahNo ratings yet
- Imaging in OtorhinolaryngologyDocument38 pagesImaging in OtorhinolaryngologyNurin AlifatiNo ratings yet
- 2AMELOBLASTOMADocument5 pages2AMELOBLASTOMAROSVITA EUFEMIA SANCHEZ VALENZUELANo ratings yet
- Head & Neck: Paranasal Sinuses & NoseDocument132 pagesHead & Neck: Paranasal Sinuses & NoseHuyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- Diseases 05 00017Document6 pagesDiseases 05 00017Syarif MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising in A Previous Calcifying CystDocument8 pagesGhost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising in A Previous Calcifying CystAntonio Álvarez FloresNo ratings yet
- Muta LikDocument4 pagesMuta Likoral pathNo ratings yet
- BBRC Vol 14 No 04 2021-03Document4 pagesBBRC Vol 14 No 04 2021-03Dr Sharique AliNo ratings yet
- Video Atlas of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: Louis Michel Wong-Kee-Song, Mark TopazianDocument8 pagesVideo Atlas of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: Louis Michel Wong-Kee-Song, Mark Topazianmike_helplineNo ratings yet
- GhgfdsDocument4 pagesGhgfdsUser NameNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 2Document6 pagesJurnal 2alexxxxxNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Palatal Swelling: A Diagnostic EnigmaDocument6 pagesCase Report: Palatal Swelling: A Diagnostic EnigmaPrince AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ghost Cell TumourDocument5 pagesGhost Cell TumourrgrthhnNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Bone Cyst of Idiopathic Origin? A Report of Two CasesDocument5 pagesTraumatic Bone Cyst of Idiopathic Origin? A Report of Two CasesjulietNo ratings yet
- Artigo Cisto Odontogênico CalcificanteDocument3 pagesArtigo Cisto Odontogênico CalcificanteivnalousadaNo ratings yet
- Surface Aneurysmal Bone Cyst: Arn Van Royen, Filip Vanhoenacker and Jeoffrey de RoeckDocument3 pagesSurface Aneurysmal Bone Cyst: Arn Van Royen, Filip Vanhoenacker and Jeoffrey de RoecktaufikolingNo ratings yet
- Jzusb15 1064Document8 pagesJzusb15 1064Irfan Cahya PermanaNo ratings yet
- Gambar Conjungtivitis VernalDocument6 pagesGambar Conjungtivitis VernalVenansius Ratno KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis Fungal Sinusitis and Odontogenic SinuitisDocument8 pagesDifferential Diagnosis Fungal Sinusitis and Odontogenic Sinuitispunct_org3256No ratings yet
- OFCDDocument4 pagesOFCDTamiris MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Maxillary Ameloblastic Fibroma: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesMaxillary Ameloblastic Fibroma: A Case ReportJeyachandran MariappanNo ratings yet
- CT Findings of Trifid Mandibular Condyle in A 12-Year-Old Patient: A Case Report and ReviewDocument6 pagesCT Findings of Trifid Mandibular Condyle in A 12-Year-Old Patient: A Case Report and ReviewHabeeb AL-AbsiNo ratings yet
- Andreasen 1971Document64 pagesAndreasen 1971crispompittas41No ratings yet
- Tonsillolith: A Report of Three Clinical CasesDocument4 pagesTonsillolith: A Report of Three Clinical CasesTatianaGonzalezNo ratings yet
- v17n1 62imagingDocument8 pagesv17n1 62imagingvanessa wijayaNo ratings yet
- ' Dr. Eliza Dragan: Medic Specialist Implantologie Si Chirurgie OralaDocument93 pages' Dr. Eliza Dragan: Medic Specialist Implantologie Si Chirurgie OralaAnaMariaNo ratings yet
- Cystic Echinococcosis in The ThighDocument10 pagesCystic Echinococcosis in The ThighShakti pawadiaNo ratings yet
- Imaging. HemophiliaDocument7 pagesImaging. HemophiliacdsaludNo ratings yet
- Primarily Solid IntraventricularDocument18 pagesPrimarily Solid IntraventricularDedy SavradinataNo ratings yet
- Aneurysmal Bone CystDocument5 pagesAneurysmal Bone CystDipti PatilNo ratings yet
- In Microscopy, As in Nature, One Recognizes Only What One Already Knows.Document30 pagesIn Microscopy, As in Nature, One Recognizes Only What One Already Knows.4umNo ratings yet
- Learnultrasonography 170804145010Document105 pagesLearnultrasonography 170804145010Nailul RosyidaNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Buccal Bifurcation Cyst: Case Report and Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesMandibular Buccal Bifurcation Cyst: Case Report and Literature Reviewboooow92No ratings yet
- Practice: Bilateral Peritonsillar Abscesses Complicating Acute TonsillitisDocument4 pagesPractice: Bilateral Peritonsillar Abscesses Complicating Acute TonsillitisRegina SeptianiNo ratings yet
- SaucerizationDocument12 pagesSaucerizationSaran NuiNo ratings yet
- JournalDocument6 pagesJournalYessi PerlitasariNo ratings yet
- Linfoma Extranodal en Cabeaza y CuelloDocument5 pagesLinfoma Extranodal en Cabeaza y CuelloCARLOS DARIO MERINO BUSTAMANTENo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cemento Ossifying Fibroma of The Anterior Mandible A Case ReportDocument6 pagesPediatric Cemento Ossifying Fibroma of The Anterior Mandible A Case ReportDessy Dwi UtamiNo ratings yet
- An Unusual Case of 177 Pieces of Mandibular Compound Odontoma: 10-Year Follow-UpDocument4 pagesAn Unusual Case of 177 Pieces of Mandibular Compound Odontoma: 10-Year Follow-UpTrianita DivaNo ratings yet
- Fig 1. An 89-Year-Old Man With Supraglottic Laryngeal Cancer. Aand B, The Standard Neck CT Images at TheDocument7 pagesFig 1. An 89-Year-Old Man With Supraglottic Laryngeal Cancer. Aand B, The Standard Neck CT Images at TheNur Amiera Farahanum FairulNo ratings yet
- Tejidos Gingivales (14-25)Document12 pagesTejidos Gingivales (14-25)marcos.marinNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document120 pagesPresentation 1Khurram ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Imaging: SciencedirectDocument16 pagesClinical Imaging: Sciencedirectraul zea calcinaNo ratings yet
- Bony Lesions in Pediatric Acute LeukemiaDocument16 pagesBony Lesions in Pediatric Acute LeukemiaRani Henty NovitaNo ratings yet
- Radiographic, CT and MRI Features of Cherubism: CasereportDocument6 pagesRadiographic, CT and MRI Features of Cherubism: CasereportTaufik ShidkiNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Peri-Implant and Periodontal Marginal Soft Tissues in Health and Diseas Perio 2000 Vol 76 PDFDocument15 pagesComparison of Peri-Implant and Periodontal Marginal Soft Tissues in Health and Diseas Perio 2000 Vol 76 PDFchandana100% (2)
- Refinement of Gingival Margins: Biological Depth vs. Zone, and A Diode LaserDocument5 pagesRefinement of Gingival Margins: Biological Depth vs. Zone, and A Diode LaserAly OsmanNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Third Molar Associated With A Cyst in The Sigmoid NotchDocument3 pagesEctopic Third Molar Associated With A Cyst in The Sigmoid NotchDanis Diba Sabatillah YaminNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument3 pagesDownloadnoname19191No ratings yet
- Knife-Edge Residual Ridges: A Clinical: Material and MethodsDocument4 pagesKnife-Edge Residual Ridges: A Clinical: Material and MethodsSyed Abdul BasitNo ratings yet
- S - Lession of The Infratemporal Fossa and Parapharyngeal Region, Congenital and Developmental Anomalies - RGDocument38 pagesS - Lession of The Infratemporal Fossa and Parapharyngeal Region, Congenital and Developmental Anomalies - RGanon_744980746No ratings yet
- Case Report: Surgical Management of Compound Odontoma Associated With Unerupted ToothDocument7 pagesCase Report: Surgical Management of Compound Odontoma Associated With Unerupted ToothDame rohanaNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@s00056 019 00196 4Document9 pages10.1007@s00056 019 00196 4leoncio cabrera rojasNo ratings yet
- 1 Alani A 2008Document14 pages1 Alani A 2008Andrew HuNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Three-Dimensional Imaging From CDocument6 pagesThe Importance of Three-Dimensional Imaging From CRifki KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Oral Bilateral Collagenous Fibroma A Previously Unreported Case and Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesOral Bilateral Collagenous Fibroma A Previously Unreported Case and Literature ReviewRichard LimaNo ratings yet
- Cone Beam Tomographic Imaging PDFDocument22 pagesCone Beam Tomographic Imaging PDFOsan CiprianNo ratings yet
- High Resolution Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in The Evaluation of Tendinoligamentous Injuries Around Ankle JointDocument47 pagesHigh Resolution Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in The Evaluation of Tendinoligamentous Injuries Around Ankle JointflosimarmataNo ratings yet