Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy Physiology PP
Uploaded by
api-2624652290 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
156 views19 pagesOriginal Title
anatomy physiology pp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
156 views19 pagesAnatomy Physiology PP
Uploaded by
api-262465229Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
Cell / Tissues/ Metabolism
Anatomy & Physiology
Basic Structure of the Human Body
The normal function of the human body is
compared to an organized machine
The machine malfunctions, disease occurs
Anatomy: study of form and structure
Physiology: study of processes
Pathophysiology: study of how disease occurs
and bodys response
Cells
Made of protoplasm
Microscopic organisms
Carry on all functions of life
Body contains trillions of cells
Vary in shape and size
Perform different functions
Basic Parts of Cells
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Organelles
Nucleus
Nucleolus
Chromatin
Genome
(continues)
Basic Parts of Cells
(continued)
Centrosome
Mitochondria
Golgi apparatus
Endoplasmic reticulum
Vacuoles
Lysosomes
Pinocytic vesicles
Mitosis
Asexual reproduction process used
by most cells
Different types of cells reproduce at
different rates
Process of mitosissee Figure 7-2
in text
Meiosis
Process by which sex cells reproduce
Uses two separate cell divisions
Female cells (ova) and male cells (spermatozoa
or sperm) divide to
produce 23 chromosomes each
When ova and sperm combine, 46 chromosomes
result to form zygote
Abnormal Cell Conditions
Atrophy
Hyperplasia
Metaplasia
Dysplasia
Neoplasia
Tissues
Cells of same type joined together
60%99% water
Groups of tissues
Epithelial
Connective
Nerve
Muscle
Organs and Systems
Organ
System
Lesson 1 Organs and Systems
The major body systems
include:
Integumentary system
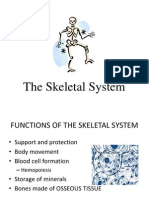
Skeletal system
Muscular system
Nervous system
Sensory system
Cardiovascular system
Lymphatic system
Respiratory system
Digestive system
Urinary system
Endocrine system
Reproductive system
Interdependence of Body Systems
Systems must work together
in order to support human life
Problem in one system may
have effects on other systems
Metabolism
Metabolism
Anabolism
Catabolism
Homeostasis
Keeping a state of balance in
the body
Must preserve a balance of
fluids, temperature, oxygen,
electrolytes, and nutrients for
survival.
Acquired Immunity
Natural acquired immunity
Artificial acquired immunity
Passive acquired immunity
Active acquired immunity
Immunity
Bodys ability to resist
invaders and diseases they
cause
Two general types:
Natural immunity
Acquired immunity
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Answer Key Practice Exam 2Document4 pagesAnswer Key Practice Exam 2api-262465229No ratings yet
- Muscle PowerpointDocument7 pagesMuscle Powerpointapi-262465229No ratings yet
- WellnessDocument18 pagesWellnessapi-262465229No ratings yet
- Simmers HST Chapter09Document30 pagesSimmers HST Chapter09api-262465229No ratings yet
- Powerpoint BookDocument25 pagesPowerpoint Bookapi-262465229No ratings yet
- Skeletal Systemnotes For StudentsDocument3 pagesSkeletal Systemnotes For Studentsapi-262465229No ratings yet
- Stress and WellnessDocument10 pagesStress and Wellnessapi-262465229No ratings yet
- Student Skeleton PP 2Document21 pagesStudent Skeleton PP 2api-262465229No ratings yet
- Student Skeleton PP 1Document15 pagesStudent Skeleton PP 1api-262465229No ratings yet
- Skull ColoringDocument1 pageSkull Coloringapi-262465229No ratings yet
- The Mystery of The Bones ProjectDocument2 pagesThe Mystery of The Bones Projectapi-262465229No ratings yet
- Fish Video WorksheetDocument1 pageFish Video Worksheetapi-262465229No ratings yet
- Rubric For Disease PresentationDocument2 pagesRubric For Disease Presentationapi-262465229No ratings yet
- Skeletal Disease Explanation SheetDocument1 pageSkeletal Disease Explanation Sheetapi-262465229No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)