Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 6 Student Edition
Chapter 6 Student Edition
Uploaded by
Mugaes KumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 6 Student Edition
Chapter 6 Student Edition
Uploaded by
Mugaes KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-1
CHAPTER 6 : NUTRITION
Multiple Choice Questions:
For question 6-1 to 6-76, each question is followed by four alternative options A,B,C and D.
Choose one correct answer for each question and blacken the corresponding space in your
objective answer
6.1 Understanding Types Of Nutrition
1. Organisms which are not able to synthesize their own food are
A autotrophs.
B heterotrophs.
C parasites.
D pathogens.
2 Plants are
A autotrophs.
B heterotrophs.
C saprophytes.
D parasites.
3 Which of the following plants is not capable of carrying out photosynthesis?
A Bamboo
B Sunflower
C Pitcher plant
D Mushroom
4 Which is the mode of nutrition of decomposers?
A Saprophytism
B Parasitism
C Holozoic nutrition.
D Autotrophic nutrition
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-2
5 Which of the following organisms practice parasitism?
A Ferns
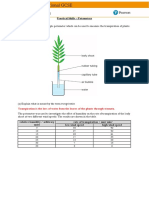
B Saprophytic bacteria
C Tapeworms
D Amoeba sp
6.2 Applying The Concept Of Balanced Diet
6 Why is vitamin E essential in our diet?
A Aids absorption of calcium and phosphates.
B Needed for maintenance of a healthy skin.
C Reduces muscle cramps.
D Prevents sterility in both sexes.
7 What vitamins can be produced by bacterial action in the large
intestine?
I Vitamin A
II Vitamin B complex
III Vitamin E
IV Vitamin K
A I and III only
B II and IV only
C I, II and III only
D IV only
8 Rich sources of vitamin A are
I Spinach.
II Tomato.
III Bread.
IV Liver.
A I and III only
B II and IV only
C I, II and IV only
D I and II only
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-3
9 Which of the following regarding roughage is true?
I It prevents constipation.
II It has high energy content.
III It is made up of plant fibres and cellulose.
IV It helps in peristalsis.
A I and III only
B II and IV only
C I, II and III only
D I, III and IV only
10 A sample of urine taken from a person suffering from diabetes mellitus was boiled with
Benedict's solution. Which of the following results can be obtained?
A The mixture becomes purple.
B A purple precipitate was formed.
C A brick-red precipitate was formed.
D The mixture becomes blue.
6.3 Malnutrition
11 Lack of vitamin D in the diet will cause
A scurvy.
B beri-beri.
C rickets.
D pellagra.
12 Which of the following is the result of calcium deficiency?
I Delayed blood clotting
II Bow legs
III Dental caries
IV Dry skin
A I, II and III only
B I and II only
C II, and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-4
13 Shortage of lipids in a cell will cause
I incomplete formation of cell membrane.
II adipose tissue does not exist.
III protein synthesis does not occur.
IV muscles will not contract.
A I and II only
B II and III only
C II and IV only
D III and IV only
14 What happens to the excess amino acid that is absorbed?
A Changed to protein to be stored.
B Changed to urea to be excreted.
C Changed to adipose tissue to be stored.
D Changed to digestive enzymes to be used.
15 Which of the following diseases is due to the lack of vitamin in the
diet?
I Xerophthalmia
II Rickets
III Pellagra
IV Haemophilia
A I and III only
B II and IV only
C I, II and III only
D I, III and IV only
6.4 Food Digestion
16. What enzyme does saliva contain ?
A Amylase
B Lipase
C Protease
D Sucrase
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-5
17.
A
B
D
C
DIAGRAM 6.1
Which of the following parts of the human digestive system shown Diagram .6.1. does
not produce enzymes?
18. Which part of the human digestive system has an enzyme that hydrolyses fats ?
A Mouth
B Oesophagus
C Stomach
D Duodenum
19. Diagram 6.2 below shows a part of the human digestive system.
DIAGRAM 6.2
What will happen if tube X is blocked ?
A No enzymes can go into the duodenum
B The digestion of carbohydrate will decrease
C The digestion of fat will decrease
D Digested food cannot be carried to the liver.
FF
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-6
20.
What organisms living in the stomach of the cow digest the grass and what enzymes are
produced by the organisms?
21. Which of the following graphs show the effect of optimal pH on the rate of reactions of
pancreatic enzymes?
Partially chewed grass is digested in the stomach of a cow.
The cow does not produce enzymes to digest the grass.
Organisms living in the stomach of the cow produce an enzyme to digest
the grass.
Organism Enzymes produced
A Bacteria Cellulase
B Fungi Amylase
C Viruses Protease
D Fungi Lipase
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-7
6.5 Absorption And Assimilation Of Digested Food
22. Which of the following are functions of the liver?
I Destruction of red blood cells
II Regulation of blood sugar level
III Conversion of excess amino acids into urea
IV Synthesis of bile
A I and III only
B II and III only
C II and IV only
D I,II, III and IV
23. Amino acids are used for
I respiration
II photosynthesis
III cell growth and cell repair
IV making enzymes and proteins of plasma membrane
A I and III only
B II and III only
C III and IV only
D II, III and IV only
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-8
Based on diagram 6.3, answer questions 24 and 25
Y
X
DIAGRAM 6.3
24. Nutrients that can be found in X are
I glucose
II vitamin D
III vitamin C
IV amino acids
A I, II and III only
B I, III and IV only
C II, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
25. What is the function of the part labelled Y ?
I to absorb amino acids
II to transport fatty acids
III to increase the surface area of the villus
IV to transport glucose and blood
A II only
B I and IV only
C II and III only
D I, III and IV only
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-9
26. Which of the following processes can take place in the colon of the human body?
I Absorption of vitamin K
II Absorption of water
III Absorption of mineral salts
IV Secretion of enzymes
A I, II and III only
B I, II and IV only
C II, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
6.6 Formation Of Faeces And Defaecation
27. Which of the following are absorbed through the colon?
A Ions and water
B Ions, water and nutrients
C Ions and nutrients
D Nutrients and undigested food
28. In which part of the large intestine shown in the below diagram 6.4 are heamorrhoids
found?
DIAGRAM 6.4
A Anus
B Colon
C Rectum
D Appendix
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-10
29. Which of the following nutrient are absorbed into the blood capillaries of the villi?
I Fatty acids
II Simple sugars
III Vitamin C
IV Iron
A I, II and IV only
B I, III and IV only
C II, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
30. What is the function of dietary fibre?
A Make food stay longer in intestine
B Give colour to faeces
C Stimulate peristalsis
D Prevent diseases
31. Constipation is due to faeces being in the large intestine for too long. What type of food
can help to overcome constipation?
A Food with fat-soluble vitamins like vegetables
B Liquid food or with high water content
C High fibrous food like vegetables
D Food rich in proteins and vitamins
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-11
6.7 Evaluating Eating Habit
32. The statement above describes a condition of En. Mails stomach. He is most likely
suffering from
A obesity
B gastritis
C bulimia
D anorexia nervosa
33. Patients with the symptoms above may risk getting
A ulcer
B gastritis
C bulimia
D obesity
34. Diagram 6.5 shows an obese person.
DIAGRAM 6.5
He is predisposed to diseases below except
A hypertension
B cardiovascular
C kidney damage
D diabetes mellitus
Symptoms:
Abdominal pain, nausea, belching, vomiting
The epithelial lining of stomach becomes inflamed
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-12
35.
The statement describe the patient of
A diabetes
B bulimia nervosa
C anorexia nervosa
D muscular dystrophy
36. The victim with the characteristic above refer to
A obesity
B bulimia nervosa
C diabetes mellitus
D anorexia nervosa
37. Good eating habits ensure good health. Besides eating regulars meals, the types of
food are also important. Which of the following statement is not true?
A Suitable mineral salts
B High amount of calories
C Sufficient water and roughage
D Contains fats, carbohydrate and proteins
6.8 Importance Of A Healthy Digestive System
38. What are the ways to maintain a healthy digestive system?
I Avoid junk food
II Have a good eating habits
III Cut down on starchy food
IV Reduce intake of fatty food
A I and II only
B III and IV only
C I, II and IV
D I, II, III and IV
They lost both fat and muscle and lead to disruptions
of the function of the heart and endocrine system
They may have a normal body mass but engage in consuming huge
amounts of food within a short period of time
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-13
39. If the pancreatic duct is blocked, a man may have difficulty digesting
A fat
B proteins
C vitamins
D carbohydrates
40. Diagram 6.6 shows part of the human alimentary canal.
DIAGRAM 6.6
The movement of food along the alimentary canal is called
A chewing
B peristalsis
C absorption
D emulsification
41. Which of the following are not associated with poor digestion?
A Nausea
B Indigestion
C Diarrhoea
D Ingestion
42. A persons diet contains more protein than is needed for growth and repair. What is the
effect of this situation?
A An increase in the production of urea
B An increase in the production of pepsin
C An increase in the production of lactic acid
D An increase in the production of carbon dioxide
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-14
43 Diagram 6.7 shows parts of the human alimentary canal.
DIAGRAM 6.7
Structure P stores bile. A patient in hospital has had the structure removed and
needs a special diet. Which menu would be most suitable for this patient?
A Fish in cheese sauce and fruit pie
B Sausages, boiled potato and cream cake
C Skinless chicken, green salad and fresh orange
D Fried fish, potato chips and sweet rice
44. A patient suffers from a malfunctioning pancreas. Which biological process would be
affected?
I Digestion of food
II Secretion of pancreatic juice
III Conversion of glucose to glycogen
IV Conversion of glycogen to glucose
A I and III only
B II and IV only
C I, II and III only
D I, II, III and IV
6.9 The Importance of Macronutrients and Micronutrients in Plants
45. Which of the following statements are true about macronutrients and micronutrients for
plant?
I Each nutrient plays the same role in the growth of plant
II Macronutrients and micronutrients are essential for the growth of plants
III Plants only require macronutrient for healthy growth
IV All macronutrients and micronutrients are needed by plant in different quantities
A I and II only
B I and III only
C II and III only
D II and IV only
Structure P
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-15
46. Which of the following is not the correct match of materials ions and their functions?
Mineral ions Function
A Calcium Major component of the middle of cell wall
B Magnesium Component of chlorophyll
C Nitrate Important constituent of cellulose
D Phosphate Component of tonoplast
47. Which of the following are examples of major elements in plant nutrition?
I Boron
II Nitrogen
III Calcium
IV Phosphorus
A I, II and III only
B I, II and IV only
C II, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
48. Which of the following elements are needed in large quantities to form chlorophyll?
A Calcium and iron
B Iron and nitrogen
C Calcium and magnesium
D Nitrogen and magnesium
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-16
TABLE 1
49. An experiment is carried out to study the effect of deficiency of macronutrients. The
aquatic plant, Lemna which has green leaves is grown in solution X and solution Y. After
six weeks, the observation are as shown in Table 1. Which of the following is true about
solution X and solution Y?
Solution X Solution Y
A No phosphorus No nitrogen
B No magnesium No phosphorus
C No nitrogen No phosphorus
D No nitrogen No magnesium
50. Diagram 6.8 shows the apparatus set up of an experiment to study the need of nutrient
for plant growth.
DIAGRAM 6.8
Tube X is connected to an air pump. What is the function of tube X?
A To add nutrient to the culture solution
B To add oxygen to the culture solution
C To remove water from the culture solution
D To remove microorganisms from the culture solution
Observation after six weeks
Solution
Number of leaves Colour of leaves
X Same Yellow
Y More Yellow
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-17
51. The leaves of plant A are dark green, its roots do not develop well and its growth is
stunted. Plant A probably lacks
A iron
B sodium
C phosphorus
D magnesium
6.10 Photosynthesis
52. Plant requires carbon dioxide and water to synthesise food. Water used by plant comes
from
A. air
B. soil
C. nutrient
D. leaf
53. Which of the following substances required for photosynthesis?
I. O2
II. CO2
III. H2O
IV. C6H12O6
A. I, II and III only
B. I and IV only
C. II and III only
D. I, II, III and IV
54. Which of the following substances are produced from photosynthesis?
A. Glucose, Oxygen and water
B. Glucose, Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
C. Glucose and Energy
D. Energy, Water and Carbon Dioxide
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-18
55. Diagram 6.9 below shows a section through a leaf of a plant
DIAGRAM 6.9
What is the adaptation of the structure P to optimise photosynthesis?
A. Have a lot of chloroplast
B. Large air spaces between cell
C. Cylindrical cell arranged end to end in long row
D. Waterproof layer on the surface
56. Plants from different habitats are adapted to carry out photosynthesis. Which of the
following is not the right adaptation for the following plant?
A. Bunga Raya or Hibiscus have more stomata at the lower epidermis
B. Water Lily have only stomata at the upper surface of the leaf
C. Hydrilla only have chloroplast at the leaf
D. The stem of cactus have many chloroplast
6.11 The Mechanism Of Photosynthesis
57. Diagram 6.10 below shows the structure of an organelle in plant cell.
DIAGRAM 6.10
Which of the following process occurs in structure Q?
A. Reduction of carbon dioxide
B. Water photolysis
C. Respiration
D. Synthesis of protein
Q
P
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-19
58. Which of the following statement is true?
A. The Hydrogen atoms produced during dark reaction are used in light reaction
B. Light reaction occurs in the granum of the chloroplast
C. Dark reaction only occurs at the night
D. The product of light reaction is converted into starch
59. In the light reaction
A. hydrogen atom reduce carbon dioxide
B. four hydroxyl group combine together to form water and oxygen
C. six unit of (CH2O) combine together to form a molecule of glucose
D. energy from sunlight is absorbed to split water molecules into hydroxyl ions and
oxygen ions
60. Which of the following is true about dark reaction of photosynthesis
A. The dark reaction take places in grana
B. Happens both when there is a light and when it is dark
C. Occurs only when it is dark
D. The dark reaction produced water and oxygen
61. Which of the following equation is the general equation of photosynthesis?
A. H2O ---- H
+
+ OH
-
B. H
+
+ electron --- H
C. 6H + 6CO2 -- C6H12O6 + 6 H2O
D. 6 H2O + 6 CO2 C6H12O6 + 6 O2
6.12 The Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
62. The following statements are the factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis, except
A. light intensity
B. concentration of carbon dioxide
C. temperature
D. pH
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-20
63. Diagram 6.11 below shows the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis at
different levels of carbon dioxide
DIAGRAM 6.11
Based on the above figure, which of the following statement is true
A. The temperature and concentration not constant
B. Carbon dioxide is the limiting factor
C. Light intensity is the limiting factor
D. The rate of photosynthesis can be increased by increasing the carbon dioxide
concentration
64. Generally, an increase of 10
o
C in the surrounding temperature will double the rate of
photosynthesis. However, when the temperature is too high, the photosynthesis stop.
Which of the following statement is true?
A. When the temperature is too high, enzymes are denatured
B. The plant cannot absorb any more water
C. When the temperature is too high, the stomata are closed
D. No more carbon dioxide is supplied
65. Why the rate of photosynthesis is low in the morning and evening and high during
midday?
A. Light intensity are low and temperature is high in the morning
B. Light intensity are high and temperature are low in the morning
C. Light intensity and temperature are at the highest during midday
D. Dark reaction starts at night when there is no light
.
0.08% Carbon Dioxide
0.04% Carbon Dioxide
0.02% Carbon Dioxide
Rate of
photosynthesis
Light intensity
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-21
DIAGRAM 6.12
66. The apparatus shown in diagram 6.12 has been set up to investigate the effect of light
intensity on the rate of photosynthesis. The experiment is repeat a few times by
adjusting the distant between lamp and Hydrylla sp. Which of the following is true about
this experiment?
A. The number of bubbles is used to represent the rate of photosynthesis.
B. The light intensity is decreased progressively by bringing the light bulb nearer to
the plant
C. The results shows that the number of bubbles per minute increases as the
distance between the light bulb and Hydrylla
D. The rate of photosynthesis decreases with light intensity
6.13 A Caring Attitude towards Plants
67. Why do we need to take good care of plants?
I Plants supply food for us
II Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the air to prevent the green house effect
III Plants play an important role in the water cycle
IV Plants prevent soil erosion
A I and II only
B I and II and III only
C II and III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
lamp Hydrylla
Sodium
bicarbonate
solution
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-22
68. Why are green plants essential to all other living things?
I Green plants convert sunlight into chemichal energy which is made available to other living
things which eat these plants.
II Green plants remove carbon dioxide from the air during photosynthesis
III Green plants remove sulphur dioxide from the air during photosyntesis.
IV Green plants produce oxygen which is used by all living things
A. I and III only
B. I,II and IV only
C II, III and IV only
D. I, II, III and IV only
6.14 Technology Used in Food Production
69. Which of the following is the necessity for food processing?
I Ensuring sufficient food supply
II Avoiding food wastage
III Preventing food from going bad
IV Creating varieties of food
A I and II only
B II and III only
C I, II and III only
D I, II III and IV
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-23
70. Diagram 6.13 shows the products of a method of food production
DIAGRAM 6.13
Which of the following are true about the method?
I Foods can be preserved over a year
II Used only for preservation of fish and vegetables
III Can destroy enzymes and kill microorganisms
IV Discovered by Louis Pasteur
A I and II only
B I and III only
C II and IV only
D I. III and IV only
71. Which of the following technology of food production is explained by the information
above?
A Direct planting
B Tissue culture
C Aeroponics
D Hydroponics
Method of planting by replacing the soil medium with culture solution for the
plants to grow.
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-24
6.15 Technological Development in Food Processing
72. Which of the following is true about canning?
I The f ood i s heat ed, sterilized and sealed in airtight containers.
II Pathogens and bacteria are destroyed.
III The food can be kept for a long period of time.
IV The quality of food is lost in canned food.
A I and II only
B II and III only
C I, II and III
D I, II, III and IV
73. A food processing method which involves culturing microorganism is
A pasteurisation.
B fermentation
C refrigeration.
D dehydrat ion
74. The benef i t s f r om t he technological development in food processing are
I avoiding food wastage.
II producing high quality food.
III extending the lifespan of food.
IV reducing the spoilage food.
A I and II only
B I, II and III only
C I, II and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-25
75. Diagram 6.14 shows a type of fruit.
DIAGRAM 6.14
Which of the following food processing methods can be used to prevent the fruit from
going bad?
I Canning
II Drying
III Pasteurisation
IV Using salt and sugar
A I and II only
B I and III only
C II and IV only
D I, II and III only
76. The following is correct about pasteurisation of milk except
A milk is heated to 63C for 15 minutes
B milk is rapidly cooled after heating
C sudden change in temperature kills the microorganisms in milk
D heating milk for a short period preserves the nutrient content in food
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-26
Structured Items
Answer all questions. Write your answer in the spaces provided in the question paper
6.1 Understanding Types Of Nutrition
1. Diagram 6.15 shows different types of nutrition.
Nutrition
Autotrophic Heterotrophic
X Y P Q R
Diagram 6.15
(a) Give the definitions of:
i. Autotrophic nutrition
ii. Heterotrophic nutrition
[2 marks]
(b) Name the types of nutrition represented by P, Q and R
P:
Q :
R :
[ 3 marks]
(c) Give one example for each type of the nutrition named in (b)
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-27
[ 3 marks]
(d) What are represented by X and Y ?
[2 marks]
(e) Give one example for each type of the nutrition named in (d)
[ 2 marks]
6.2 Applying The Concept Of Balanced Diet
2. Diagram 6.16 shows a food pyramid. The correct proportion for the various classes of
food is shown in a food pyramid
P
Q
R
S
DIAGRAM 6.16
(a) Name the class of food for each level labelled as P,Q,R and S
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-28
[4 marks]
(b) Give an example for each of the food class mentioned in (a).
[4 marks]
(c) Give four factors that affect the daily energy requirements of a person
[4 marks]
6.3 Malnutrition
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-29
3. Diagram 6.17 shows individuals suffering from malnutrition
DIAGRAM 6.17
(a) What disease are the individuals P, Q and R suffering from?
[ 3 marks]
(b) Which substance is deficient in the diet of each of individuals P, Q and R?
P:
Q:
R:
[ 3 marks]
(c) Name the disease caused by deficiency of each of the following vitamins?
i. vitamin B1:
ii. vitamin C :
[2 marks]
(d) State two symptoms for each of the diseases in (c)
[4 marks]
6.4 Food digestion
R Q P
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-30
4. Diagram 6.18 below shows the stomach of a herbivorous animal.
DIAGRAM 6.18
(a) i. Name an example of an animal that has this type of stomach.
ii. What is the name of this group of animals?
[ 2 marks]
(b) i Name the labelled parts of the stomach.
[ 5 marks]
ii State one function for each part.
[5 marks]
(c) i. Which part of the stomach contains micro-organisms?
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-31
ii. Name the group of micro-organism found in this animals stomach.
iii. What is the main role of these micro-organisms?
[ 3 marks]
6.5 Absorption And Assimilation Of Digested Food
5. Diagram 6.19 below shows the vertical section of the head and mouth of a person.
DIAGRAM 6.19
(a) State two processes that happen to the food in the mouth.
[2 mark ]
(b) State two important reasons for these processes.
[2 mark ]
(c) Name the labelled parts.
P
Q
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-32
[ 2 marks]
(d) Explain how the process of swallowing occurs in the diagram.
[3 marks ]
(e) Food can also enter into tube P. Explain.
[ 1 mark]
(f) What is the name of the movement of food along tube Q?
[ 1 mark]
6.
(a) What class of food found in fruits, vegetables and cereals that will help him to
prevent constipation?
[ 1mark]
(b) Explain why the above class of food prevents constipation.
[ 4mark]
An individuals diet consists of white bread, sweet food, meat and high fat foods and this
leads to constipation. The doctor advises him to eat more fruits, vegetables and cereals
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-33
(c) Name two diseases ( other than constipation ) that can be prevented with more
intake of the above class of food.
[ 2 marks]
6.6 Formation Of Faeces And Defaecation
DIAGRAM 6.20
7. Diagram 6.20 shows the human digestive system.
(a) Name organs C and B
Organ C
Organ B
[ 2 marks]
(b) Name the enzyme and the product of the food digested in B.
Enzyme :
Product :
[ 2 marks]
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-34
(c) Name two processes in R. Explain how the ileum is adapted for these
processes.
[ 4mark]
(d) i. In the box below draw a labelled diagram of the structures found
on the cell wall of D.
[ 3 mark ]
ii State three characteristics of the structure, which help it to perform
efficiently.
[ 3 mark ]
Epithelium Blood capillaries
Lacteal
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-35
iii. State the functions of the blood circulatory system and lymphatic system
in the structure.
[ 4 mark ]
(e) i. Explain the difference between a human and herbivore digestive system.
[ 2 marks]
ii State where cellulose digestion takes place in rabbits and cattle.
[ 2 marks]
6.7 Evaluating Eating Habits
8. Table 1 shows an analysis of the contents of a biscuits packets.
TABLE 1
Carbohydrate 35.9 %
Proteins 20.7 %
Fats 8.5 %
Minerals 3.3 %
Vitamins 0.7 %
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-36
a. i. Which of the food substances is used for growth and repair a damage
cell?
[ 1 mark ]
ii Which of the food substances may contain a simpler sugar?
[ 1 mark ]
iii What is the percentage of the food contents that are not included in
the list?
[ 1 mark ]
b. i What kind of food substances is not in the list?
[ 1 mark ]
ii Which food in your answer in (b)(i) could help a person to avoid
constipation?
Explain briefly how it works.
[ 4 marks ]
c. Iron is one of the minerals that our body need. Iron requirement is higher in a girl
but lower in a boy of the same age. Suggest your answer for this statement.
[ 2 marks ]
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-37
d. Explain the effects of smoking cigarettes on health problem during pregnancy.
[ 2 mark ]
6.8 Importance Of A Healthy Digestive System
9 (a) i What type of food is digested in the stomach?
[ 1 mark ]
ii Why is the stomach wall not digested even though there are enzymes
inside it?
.
[ 2 marks ]
(b) i State one function of colon.
ii State one food which does not need to be digested.
]
iii What happen to the undigested food?
[ 3 marks ]
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-38
(c). Explain why most of the food need to be digested.
[ 2 mark ]
6.9 The Importance of Macronutrients and Micronutrients in Plants
10 Table 2 shows an experiment to study the effects of the lack of nutrient in plants.
Bottle
Salt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
0.8 g/ l calcium nitrate X / NaNO3 / X / / /
0.2 g / l calcium nitrate X / / / X / / X
0.2g / l potassium dihydrogen
phosphate
/ KCl / / / / / X
0.2 g / l magnesium sulphate / / / / / / K2SO4 /
Ferrum phosphate / X / X / / / /
1000 cm
3
distilled water / / / / / / / /
TABLE 2
(a) Which of the bottles contained a complete Knops culture solution?
[1 mark ]
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-39
(b) State the mineral nutrients that are not present in the following bottles:
[3 marks ]
(c) State one effect from the lack of mineral nutrients in the following bottles:
[3 marks]
(d) State the mineral nutrients missing in Bottle 4.
[1 mark ]
(e) Give one function of
i Phosphorus
ii Magnesium
[2 marks]
[ 2 marks ]
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-40
6.10 Photosynthesis
DIAGRAM 6.21
11. Diagram 6.21 shows a cross section of a leaf.
(a) The leaf is adapted to optimise photosynthesis through external features and
internal features.
i. State two adaptation to the structure for external features to optimise
photosynthesis
ii. Explain your answer.
[ 4marks]
(b) Label the boxes in the diagram [ 2 marks ]
(c) i. State one adaptation of structure P to optimise photosynthesis
]
ii. Explain your answer in c (i)
[ 2 mark ]
P:
Q:
R:
S:
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-41
(d) State one adaptation of structure S of the plant to optimise photosynthesis
and give your explanation.
Cactus
Water Lily
[4 mark]
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-42
Process M
6.11 The Mechanism Of Photosynthesis
Process N
DIAGRAM 6.22
11. (a) State what is X?
Name the process N
[ 2 marks ]
(b) Explain your answer
[2 marks ]
Reduced Carbon
dioxide to form
glucose
Receive electron to form atom X
Sun
Water X
+
+ OH
-
Process S
Process R
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-43
(c) Water used in Process N. Where does the water come from?
[1 mark]
(d) Process R occurs in one part of chloroplast. Name the part.
[1 mark ]
(e) Write down the general equation of photosynthesis
[1 mark]
(f) State two differences between dark reaction and light reaction
[ 2 marks ]
[2 marks ]
(g) State one difference between photosynthesis and Process M
[1 mark ]
(h) State what happens to the Hidroxide ions during Process S
[1 mark]
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-44
0.13% CO2 at 30
o
C
6.12 The Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
13. Diagram 6.23a and 6.23 b shown factor affect the rate of photosynthesis
The concentration of carbon dioxide and temperature are controlled at constant levels
(a) i. In Diagram 6.23a, before point P, what is shown by the graph?
ii. What happens to the rate of photosynthesis up to point P
[ 2marks ]
(b) State two limiting factors which limit the reaction along PQ
[ 2 marks ]
(c) In Diagram 6.23a draw the graph if the concentration of carbon dioxide is more
than 0.13 % at 30
o
C [ 1mark ]
Q
P
DIAGRAM 6.23a
DIAGRAM 6.23b
Rate of
photosynthesis
Rate of
photosynthes
is
Light intensity temperature
P
0.03% CO2 at 30
o
C
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-45
(d). Based on Diagram 6.23b, explain the relationship between the rate
of photosynthesis and temperature
[ 3 mark ]
(e) Photosynthesis stops at 50
o
C . Explain why?
[ 1 mark ]
(f) Under what condition does carbon dioxide concentration become a limiting
factor?
[ 1 mark ]
(g) The rate of photosynthesis in plant is not constant throughout the day.
Explain why the rate of photosynthesis is low in the morning and high during
midday.
[ 2 marks ]
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-46
6.14: Understanding the technology used in food production
14. The population of Malaysia is increasing rapidly. Hence, there is a need to increase the
quantity as well as the quality of food to fulfill the demand.
Diagram 6.24 shows one of the method used to increase food production.
(a) (i). Name the method.
[1 mark]
(ii) What is fluid X?
[1 mark]
(b) The method in (a)(i) does not use soil to grow vegetables. Explain why.
-
[2 marks]
DIAGRAM 6.24
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-47
(c) Aeroponics is another way to grow plants without using soil.
How does it differ from the method (a)(i).
[Any two correct answers: 2 marks]
(d) State 2 advantages of using this method to grow vegetables
[Any two correct answers: 2 marks]
e) Beside the method in (a)(i) and the aeroponics, explain two other ways that
could be used to increase the food production.
[2 marks]
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-48
6.15 Technology in food processing
P Q
DIAGRAM 6.25
15. State one method to preserve P and Q so the food can be kept for a long time.
P:
Q:
[ 2 marks]
(a) Explain the process in (a)
P:
[4 marks]
Q:
[4 marks]
(b) Explain why it is not good to eat too much preserved food
-
[2 marks]
P
Q
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-49
Essay Items
Answer all questions
6.1 Understanding Types Of Nutrition
1. Compare and contrast the following modes of nutrition:
(a) autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition [4 marks]
(b) photoautotrophic and chemoautotrophic nutrition [5 marks]
(c) Saprophytic nutrition and parasitic nutrition [4 marks]
6.2 Applying The Concept Of Balanced Diet
2 (a) What is meant by a balanced diet? [2 marks]
(b) Discuss the importance of the following classes of food:
i. roughage
ii. water [8 marks]
(c) Discuss briefly a diet appropriate for the following target group:
i. children
ii. pregnant mothers [10 marks]
6.3 Malnutrition
3. (a) The table shows an analysis of the percentage nutrient content of a
balanced diet that should be taken by a person daily.
Nutrient Percentage intake
Carbohydrate 60
Lipid 30
Protein 10
Vitamin & mineral salts Small quantity
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-50
The table shows the daily eating habits of Siti and Devi
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the eating habits of Devi compared
to Siti over a period of time. [10 marks]
(b) Obesity and anorexia nervosa are two diseases caused by malnutrition. Discuss.
6.4 Food Digestion
4. a Name the parts of the digestive system labelled P, X, R, and S
in Figure 27. [ 4 marks]
b Describe the functions of the part labelled P [ 8 marks ]
c. Digestion of food occurs actively in the part labelled S which receives juices
secreted by the part labelled P and R. Explain the digestion of food in the part
labelled S. Word equations should be given to show the reactions which occur
during digestion. [ 8 marks ]
Siti Devi
Eats regularly at a fixed time.
Drinks at least 7 glasses of
water daily.
Chooses food that contains
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
vitamins and mineral salts
based on the standard of a
balanced diet.
Eats irregularly as and when she
remembers or when she is free.
Drinks very little water.
Likes to eat fast food and junk
food that does not contain the
right amount of carbohydrates,
lipids, proteins, vitamins and
mineral salts, does not follow the
standard of a balanced diet.
P
p
R
S
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-51
6.5 Absorption And Assimilation Of Digested Food
5. (a) Explain what is digestion. [2 marks]
(b) Discuss the digestion of cellulose in ruminants. [10marks]
(c) State the differences between the processes of cellulose digestion in
I . humans
II. ruminants
III. rodents [ 8 marks]
6.6 Formation Of Faeces And Defaecation
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-52
6.7 Evaluating eating habit
6. Diagram 1 shows the menu for Susans breakfast. She takes a cup of milk and two
slides of whole meal bread spread with butter.
DIAGRAM 1
a. i. Is Susans breakfast menu a balanced diet for an adult? Give
reasons for your answer. [ 4 marks]
ii Explain how the food rich in carbohydrate is digested in the body of
Susan. [ 6 marks]
b. Table 1 shows the results of an analysis on a snack food such as Rempeyek
chips.
A boy frequently eats this snack food. He eats three packets everyday in the
evening. Are the Rempeyek chips suitable as a daily diet for the boy?
[ 2 marks]
c John likes to eat fried chicken, hamburger, chocolates and ice-cream and he
dislikes vegetables and fruits. Discuss why this is an unhealthy diet.
[ 8 marks ]
Content
Mass per 100g of
Rempeyek chips
Carbohydrate
Protein
Lipid
Fibre
Sodium chlorides
21.1
2.7
18.5
1.8
0.4
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-53
6.8 The Importance of a Healthy Digestive System
7 (a) i Rice and salt are important component of an individuals diet. Rice
need to be digested before it can be absorbed whereas salt can be
absorbed directly. Explain why. [8 marks]
ii Explain how bad eating habits can cause a health problem.
[2 marks]
(b)
Imagine that you are preparing a talk on Good eating habits for group of parents,
discuss some good eating habits that you may want to educate them. [10 marks]
6.9 The Importance of Macronutrients and Micronutrients in Plants
8. (a) Distinguish between major elements and essential elements in relation to a
plants nutritional requirements.
[12 marks]
(b) State two functions each for the following elements in plants. [ 8 marks]
6.10 Photosynthesis
9. a.. Based on the statement above, draw and label a diagram of cross section
of a leaf [ 4 Marks]
b. Explain how the leaf is adapted to optimise photosynthesis
[10 mark]
c. By using two examples, explain how plants from different habitats adapt
themselves to carry out photosynthesis [6 mark]
Malaysian families eat out very often because working parents do not have time
to prepare home cooked food. These eating habits lead to many health
problems.
Photosynthesis occurs in green leaves. The leaf is adapted for optimal photosynthesis.
PANITIA BIOLOGI NEGERI KELANTAN 2007
6-54
6.11 The Mechanism of Photosynthesis
10.
Based on the statement above, explain the process of light reaction and dark reaction
6.16 The Factor Affecting Photosynthesis
i. List down factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis [ 3 mark ]
ii. Explain that factor affect the rate of photosynthesis
[7 marks ]
6.17 Technological Development in Food Processing
12. (a) Describe the principles of food processing that may help your friend in deciding
a suitable food processing method
[10 marks]
Discuss the efforts taken to diversify our food production [10 marks]
The process of photosynthesis is divided into two principal type of reaction, the light
reaction and the dark reaction
Your friend intends to process a local food item to be exported
as light snacks to overseas market. He wants some guidance
on food processing so that his processed snacks can appeal
to the overseas consumers, and at the same time he can
make some profits.
The population of Malaysia is at 27 million in 2007. The concern of Malaysia is
that her imported food has been gradually rising since 2000.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5807)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Claim Evidence Reasoning WorksheetDocument5 pagesClaim Evidence Reasoning WorksheetRey Jr. Garin100% (1)
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 2.1-2.4 - Teacher'sDocument13 pagesForm 4 Physics Chapter 2.1-2.4 - Teacher'sPavithiran100% (2)
- Biology - Worksheet PotometersDocument3 pagesBiology - Worksheet PotometersDiyaNo ratings yet
- Revision: (Unit 5 - Unit 6)Document32 pagesRevision: (Unit 5 - Unit 6)李友志No ratings yet
- Muet Thesis Statements by MDM Audrey WilesDocument6 pagesMuet Thesis Statements by MDM Audrey Wiles李友志No ratings yet
- How To Get Excellent Results On Your ExaminationDocument5 pagesHow To Get Excellent Results On Your Examination李友志100% (1)
- The 50 Most Important English Proverbs - PhraseMix PDFDocument7 pagesThe 50 Most Important English Proverbs - PhraseMix PDF李友志No ratings yet
- Sosilawati and Three Others Brutally Murdered and BurntDocument2 pagesSosilawati and Three Others Brutally Murdered and Burnt李友志No ratings yet
- How To Remember SPM Biology FactsDocument4 pagesHow To Remember SPM Biology Facts李友志50% (2)
- Questions 1-10 Are Based On The Information GivenDocument5 pagesQuestions 1-10 Are Based On The Information Given李友志No ratings yet
- Compilation of Biology Essays Updated 140511050607 Phpapp01 PDFDocument26 pagesCompilation of Biology Essays Updated 140511050607 Phpapp01 PDFmiez17No ratings yet
- Journey To The Center of The Earth 1Document1 pageJourney To The Center of The Earth 1李友志No ratings yet
- PPWBP SPM Module 2012 - Teacher'sDocument24 pagesPPWBP SPM Module 2012 - Teacher's李友志100% (3)
- Useful ConnectorDocument3 pagesUseful Connector李友志No ratings yet
- Leaf Disc Lab SheetDocument2 pagesLeaf Disc Lab SheetMargaret Lee ChenNo ratings yet
- Test Yourself 3: Minerals in PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesTest Yourself 3: Minerals in PhotosynthesisLovy Le ErNo ratings yet
- EVS-3 (U2 Tutorial) 2020-21Document6 pagesEVS-3 (U2 Tutorial) 2020-21Digital MegatrendsNo ratings yet
- The Future of Quantum Biology: Headline ReviewDocument14 pagesThe Future of Quantum Biology: Headline Reviewcristian flore arreolaNo ratings yet
- Life ProcessesDocument36 pagesLife Processes2erwr100% (1)
- GenBio 1 - 2nd Quarter ReviewerDocument8 pagesGenBio 1 - 2nd Quarter Reviewerjoshua tejadaNo ratings yet
- Origin and Structure of The Earth - Earth The Four SubsystemsDocument3 pagesOrigin and Structure of The Earth - Earth The Four SubsystemsAnn QuiranteNo ratings yet
- Mobiliflora EdwardiiDocument3 pagesMobiliflora EdwardiiKijoci TharmapalanNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Gross Primary Productivity, Net Primary Productivity and Plant RespirationDocument25 pagesRelationship Between Gross Primary Productivity, Net Primary Productivity and Plant RespirationtahamidNo ratings yet
- Sjavs 23B256 261 PDFDocument6 pagesSjavs 23B256 261 PDFBer NawatiNo ratings yet
- Datos de Densidad de MicroalgaDocument148 pagesDatos de Densidad de MicroalgaViviana Quintero DallosNo ratings yet
- STPM Biology 964/1 4 Oktober 2017 1 Hour 30 Minutes: SulitDocument14 pagesSTPM Biology 964/1 4 Oktober 2017 1 Hour 30 Minutes: Sulitrevathy varatharajahNo ratings yet
- PHD Lutzu GiovanniDocument179 pagesPHD Lutzu GiovanniSuy-yinCorroteaVicencio0% (1)
- Photosynthesis Process For Education by SlidesgoDocument55 pagesPhotosynthesis Process For Education by SlidesgoMary De Los Angeles HerreraNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument35 pagesDocxqweqwe67% (3)
- Effect of Light Intensity On The Photosynthetic Pigment Production of Mung Bean Plants (Vigna Radiata)Document9 pagesEffect of Light Intensity On The Photosynthetic Pigment Production of Mung Bean Plants (Vigna Radiata)Lundgren Arce ReyesNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument75 pagesReviewerKurt SecretarioNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Living Things and Air: Able Education CentreDocument24 pagesUnit 7 Living Things and Air: Able Education CentreManyan KanNo ratings yet
- Oxygen: Oxygen Is The Chemical Element With The Symbol O andDocument28 pagesOxygen: Oxygen Is The Chemical Element With The Symbol O andHunNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions 1 PhotosynthesisDocument17 pagesPractice Questions 1 Photosynthesis사나No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis QuizDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis QuizFirdausia Rahma Putri100% (3)
- Short Answer Questions (S. A. Q.)Document3 pagesShort Answer Questions (S. A. Q.)Krishna Rathore100% (1)
- Life Sciences Grade 11 Telematics Workbook - 2023Document17 pagesLife Sciences Grade 11 Telematics Workbook - 2023preciousrebotile133No ratings yet
- Life Function: and Energy IntakeDocument24 pagesLife Function: and Energy IntakeSengzet FanlyNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Notes MapurangaDocument95 pagesO Level Biology Notes Mapurangapeterchiyanja100% (2)
- Tuto Cell RespirationDocument7 pagesTuto Cell RespirationFatin FatonahNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 6Document28 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 10 Science Chapter 6REJEENo ratings yet
- Crosswalk Lesson Plan 2Document8 pagesCrosswalk Lesson Plan 2api-398397642No ratings yet