Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Química de Heterociclos
Química de Heterociclos
Uploaded by
Francisco Felipe OrdoñezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Química de Heterociclos
Química de Heterociclos
Uploaded by
Francisco Felipe OrdoñezCopyright:
Available Formats
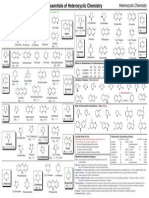
Deprotonation of NH, Deprotonation of CH, Deprotonation of Conjugate Acid
5
2
3
N1
H
Pyrrole
pKa: 23.0, 39.5
N1
N1
H
7
6
5
2
5
O1
Oxazole
pKa: 0.8
O1
Isoxazole
pKa: 3
8
3
N1
3
2
2
6
Quinoline
pKa: 4.92
N1
6
3
2
H
N
N3
N2
N1
H
5
6
5
6
7
8
Piperazine
N1
3
2N
Phthalazine
Pteridine
2
3
2
1,3,4-Thiadiazole
2-Imidazoline
pKa: 4.9
Imidazole
pKa: 6.9, 14.4, 33.7
HN
2
N1
H
3
5
Quinoxaline
SMe
3.6
4.4
6.0
S1
4
3
2
O1
1
5
O
O1
1,3-Dioxolane
O1
S1
H4
N
S1
2
5
6
Thiomorpholine
S1
4
3
2
1
1N
5
6
N7
H
Purine
pKa: 2.5, 8.9
N
H
S1
N 10
H
6
7
8
9
Phenoxazine
Christopher Lipinski (retired from Pfizer) formulated a set of
criteria fulfilled in most orally available drugs.
1. No more than five hydrogen bond donors.
2. No more than ten hydrogen bond acceptors.
3. A molecular weight under 500.
4. A LogP (partition coefficient) value under five.
Medicinal Chemistry Glossary:
4
5
6
1,4-Dithiane
5
3
2
H4
N
O1
N1
Pyridazine
pKa: 2.3
N1
H
1H-Indazole
Ph
4.5
4.8
5.5
vinyl
4.8
4.8
5.5
N
Me
Lipinski Rule of Five:
9
8
1,3,5-Trithiane
1,3-Dithiane
pKa: 31
N
2
CN
0.3
1.4
1.9
NO2
2.6
0.6
1.6
CH(OH)2
3.8
3.8
4.7
N
N
R
thermodynamic
N
H
S
N
kinetic
N
H
N
H
N
N
N1
H
3S
1,3,5-Triazine
pKa: <0
1,2,4-Triazole
pKa: 2.2, 10.3, 26.2
3
5
2
5
1,2,3-Oxadiazole
N
N
Phenothiazine
3
N1
H
Benzimidazole
pKa: 16.4
Pyrimidine
pKa: 1.3
N
N1
N1
Sites of Electrophilic Substitution: Major, Minor
Thiazole
pKa: 2.5, 29.4
N1
H
N 10
H
N1
H
1,2,3-Triazole
pKa: 9.3
1,4-Dioxane
N N
Cl
0.7
2.8
3.8
S1
5
5
Phenazine
OMe
3.3
4.9
6.6
Cinnoline
N10
Lithiation Positions: First, Second
N
Me
N
N
Tetrazole
pKa: 4.9
Imidazolidine
S1
N1
H
N1
H
4
5
N N
N1
N
3
3
1,2,4-Triazine
pKa: <0
N1
Quinazoline
Isothiazole
pKa: 0.5
Benzthiazole
pKa: 27.0
5
3
N
8
5
3
S1
Benzoxazole
pKa: 24.4
N1
N1
N1
H
Pyrazolidine
Effects of Substitution on Pyridine Basicity:
Me tBu NH2 NHAc
4
3
2-position 6.0 5.8
6.9
4.1
3-position 5.7 5.9
6.1
4.5
2
N1
4-position 6.0 6.0
9.2
5.9
1,8-Naphthyridine
pKa: 3.39
O1
5
6
N1
H
N2
1
Isoquinoline
pKa: 5.4
Tetrahydroquinoline
pKa: 5.0
4
Acridine
pKa: 5.6
3
S1
3
4
4H-Quinolizine
N10
3
4
5
6
N1
H
Pyrazine
pKa: 0.6
Thiophene
pKa: 33.0
Benzo[b]thiophene
pKa: 32.4
S1
Quinuclidine
pKa: 11.0
4H-Pyran
O1
Piperidine
pKa: 11.2
Pyridine
pKa: 5.2
8
3
2H-Pyran
Isobenzofuran
O1
Benzofuran
pKa: 33.2
O1
HN
5
6
2-Pyrazoline
N1
H
Indoline
pKa: 4.9
4
Indole
pKa: 21.0, 38.1
N1
H
Pyrazole
pKa: 19.8, 35.9
N1
H
7
2
Indolizine
2-Pyrroline
N1
H
Furan
pKa: 35.6
3H-Indole
7
5
N1
O1
3-Pyrroline 2H-Pyrrole
Isoindole
Carbazole
pKa: 19.9
N1
H
NH
7
3
2
N9
H
Pyrrolidine
pKa: 11.3,44
3
2
N1
H
Heterocyclic Chemistry
Essentials of Heterocyclic Chemistry-I
Baran, Richter
5
6
Morpholine
pKa: 8.4
N
H
Heterocyclic Aromaticity Values:
% (of PhH) -value
pyridine
tetrazole
pyrazole
quinoline
isoquinoline
pyrazine
1,2,5-triazole
pyrimidine
pyridazine
82
80
61
61
75
71
67
65
0.058
0.052
0.051
0.049
% (of PhH) -value
indole
benzothiophene
imidazole
pyrrole
benzofuran
thiophene
isoindole
furan
isobenzofuran
43
37
45
0.047
0.044
0.042
0.039
0.036
0.032
0.029
0.007
0.002
0.049
12
ED50: Dose required to yield maximum therapeutic effect in 50%
of test animals.
Efficacy: Description of the relative intensity with which agonists
vary in the response they produce, even with similar affinity.
Homologue: A compound belonging to a series of compounds differing from each other by a repeating unit (i.e. a CH2, a peptide residue, etc.).
Intrinsic activity: The maximal stimulatory response induced by a compound relative to that of a given reference comopund.
LD50: Dose required to kill 50% of test animals.
Partition coefficient (LogP): Log10 of the ratio of a compound's concentration in 1-octanol vs. water at equilibrium. A LogP<0 means that
a compound is more soluble in water than in 1-octanol.
Pharmacophore: The ensemble of steric and electronic features that is necessary to ensure the optimal supramolecular interactions with a
specific biological target structure and to trigger (or block) its biological response. This is not a real molecule or moiety, but rather an
abstract concept that is considered the largest common denominator shared by a set of active molecules.
Potency: The dose of a drug required to produce a specific effect of given intensity as compared to a standard reference.
Therapeutic index: LD50/ED50
Essentials of Heterocyclic Chemistry-I
Baran, Richter
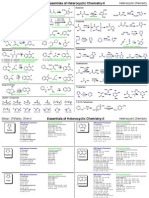
Indoles:
R'
R'
O
R'
NH2
N
H
Fischer Indole Synthesis
S
N
H
NHR
N
H
[H]
DMAD
N+
Ph
R1
BrMg
R'
i. DMFDMA
NO2
ii. Pd/C, H2
Me
H2NNH2
R
N
H
ii. H+
Base
N
R1
R2
R2
R2
N
R1
Madelung Indole Synthesis
R
H+
CO2H
N
H
NH2
Ph
Ph
N
H
OH
i. DMAD,
piperidine
CO2Me
HS
CO2Me
ii. NaOMe
S
MeO2C
Fiesselmann Thiophene Synthesis
Ph
Ph
R1
S
HO2C
Hinsberg Thiophene Synthesis
CN
CO2H
ii. acid
N
R3
i. LA
Cl
OH
N
H
ii. NaBH4
R1
i. S8
NH2
ii. Amine
S
R2
Gewald Aminothiophene Synthesis
R2
N
H
X = halide
CuOTf
NH2
Castro Indole Synthesis
CO2R
Cl
H+
CO2R
Hemetsberger Indole Synthesis
N
H
Ni0
N
R
Mori-Ban Indole Synthesis
K2CO3
N
H
R''
CO2X
R
R'
R
R1
R2
Ph
OH
O
N
O
N
N
R
R''
van Leusen Oxazole Synthesis
R'
TosMIC
R'
Robinson-Gabriel Oxazole Synthesis
N
H
Bischler Indole Synthesis
CHO
R'
HCl
CN
R'CHO
Fisher Oxazole Synthesis
Me
N3
R1
R1
Hantzsch Pyrrole Synthesis
Me
i. NaOEt,
S(CH2CO2Et)2
R2
Ar
H+
Ar
H2N
Br
O
Paal Thiophene Synthesis
Sugasawa Indole Synthesis
R2
R2
N
H
Et
Me
HO
R1
CN
+
NH2
Reissert Indole Synthesis
CO2Me
N
H
Oxazoles and Isoxazoles:
R
ii. [H],
OMe
Zn
Nenitzescu Indole Synthesis
i. (CO2Et)2,
Base
NO2
Me
P4S10
Me
Me
R1
R3HN
CoI2,
Graebe-Ullmann Carbazole Synthesis
HOAc
MeO2C
O
N
H
R3
O
Piloty Pyrrole Synthesis
X = OH, NH2
R3
N
R
Thiophenes:
N
N
Bucherer Carbazole Synthesis
CO2Me
MeO2C
Et
Me
Batcho-Leimgruber Indole Synthesis
HN
R'
Boger Pyrrole Synthesis
N
i. PhNHNH2
NaHSO3,
N
H
Paal-Knorr Pyrrole Synthesis
N
R
PdII
R
Bartoli Indole Synthesis
X
RNH2
N
R
X
R
RNH2
R'
MeO
N
H
R1
Me
O
X
Knorr Pyrrole Synthesis
Huisgen Pyrrole Synthesis
R''
R'
Me
R2
NH2
Ph
R2
NO2
CO2Me
Larock Indole Synthesis
Hegedus Indole Synthesis
CO2X
CO2Me
COY
N
H
Barton-Zard Pyrrole Synthesis
N
R
Pd(OAc)2,
base
NHR
R'
R'
O-
R''
R'
I
Me
CO2X
base
R'
Gassman Indole Synthesis
PdII;
CN
R'
iii. base
iv. Raney-Ni, H2
N
H
NO2
R'
O
Fukuyama Indole Synthesis
NH2
Pyrroles:
N
R
i. tBuOCl
ii.Me
S
Me
AIBN
N
R
N
R
N
H
nBu SnH
3
PdII
acid,
R'
R'
Pd0
Heterocyclic Chemistry
NH2OH
R'
N
O
R
Claisen Isoxazole Synthesis
O
R2
N
O
Cornforth Rearrangement
R1
HN
R
CO2H
O
Ac2O
R
O
O
Erlenmeyer-Plchl Azlactone Synthesis
You might also like
- Essentials PDF 2021Document8 pagesEssentials PDF 2021Ngô Tuấn KiệtNo ratings yet
- Rurouni Kenshin - Her Most Beautiful SmileDocument2 pagesRurouni Kenshin - Her Most Beautiful Smileivshadow100% (8)
- Lensky Aria From Eugen Onegin: For FluteDocument2 pagesLensky Aria From Eugen Onegin: For Flutemohamed basha100% (1)
- Essentials of Heterocycles IDocument2 pagesEssentials of Heterocycles Ianil_panmandNo ratings yet
- Hetero Cyclic CompoundsDocument2,451 pagesHetero Cyclic CompoundsMohini Bajaj100% (1)
- 55 Dive Mike Stern PDFDocument1 page55 Dive Mike Stern PDFHenrypavaquinteroNo ratings yet
- Dialysis - Clinical Science Questions and AnswersDocument2 pagesDialysis - Clinical Science Questions and AnswersSaqibKhan100% (8)
- Chemistry of Hetero AromaticsDocument139 pagesChemistry of Hetero Aromaticslalitarun100% (1)
- Certitude 1Document10 pagesCertitude 1NOGARD FELISCOSONo ratings yet
- Organic Chem MCQDocument2 pagesOrganic Chem MCQJer JerNo ratings yet
- The Logic of Chemical Synthesis - Elias James CoreyDocument463 pagesThe Logic of Chemical Synthesis - Elias James CoreyMarco GiampàNo ratings yet
- Quick Returning SyatersDocument5 pagesQuick Returning SyatersFloat KgbNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Kimberly CarterDocument175 pagesOrganic Chemistry Kimberly CarterPinaki MandalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry OlympiadDocument6 pagesChemistry OlympiadPaul Schumann0% (1)
- Essentials 1Document2 pagesEssentials 1aNo ratings yet
- DinahDocument4 pagesDinahrussettNo ratings yet
- Cacophony - The Ninja (Intro)Document2 pagesCacophony - The Ninja (Intro)Aristotelis Vrettakis100% (1)
- AmilieDocument3 pagesAmilieAmirhoosein MeshginiNo ratings yet
- Wipe-Out: Surfaris 164Document9 pagesWipe-Out: Surfaris 164dminor3rd7617No ratings yet
- Bolero: Arreglo IRMDocument6 pagesBolero: Arreglo IRMHugo Sanchez-BarrosoNo ratings yet
- Miguel's Happy Dance Bass NotationDocument2 pagesMiguel's Happy Dance Bass NotationMilo BrosamerNo ratings yet
- Vicente Amigo - RomaDocument7 pagesVicente Amigo - RomaCristobal Pérez MonteroNo ratings yet
- Bach Minueto 7 - Sol MaiorDocument1 pageBach Minueto 7 - Sol MaiorHelderCapuzzoNo ratings yet
- D7 G B em C D B: Standard TuningDocument2 pagesD7 G B em C D B: Standard TuningAaronNo ratings yet
- Body and Soul - Kurt RosenwinkelDocument2 pagesBody and Soul - Kurt RosenwinkelTyson HutchingsNo ratings yet
- Body and Soul - Kurt Rosenwinkel PDFDocument2 pagesBody and Soul - Kurt Rosenwinkel PDFRodrigo Leon100% (1)
- How About A Round of Gwent PDFDocument3 pagesHow About A Round of Gwent PDFAnonymous b2Zlx8iOYNo ratings yet
- Sari Galin: A E A E C ADocument4 pagesSari Galin: A E A E C AAhmed PajevićNo ratings yet
- Costa ChamameDocument6 pagesCosta ChamameLisandro HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Myfunnyvalentinelirycsand ChordsDocument1 pageMyfunnyvalentinelirycsand Chordspedimeh524No ratings yet
- Castlevania SOTN - Wood Carving PartitaDocument4 pagesCastlevania SOTN - Wood Carving PartitaJulio Cesar Lopes Nunes100% (2)
- Altered Scale Exercises GPR G7alt and E7altDocument1 pageAltered Scale Exercises GPR G7alt and E7altPete SklaroffNo ratings yet
- Patterns Diminués - G Dim Ou A Demi-Ton / Ton: Secondes Et Sixtes... C Lydien 2/2Document1 pagePatterns Diminués - G Dim Ou A Demi-Ton / Ton: Secondes Et Sixtes... C Lydien 2/2eric lohrerNo ratings yet
- Samambaia by Cesar Camargo MarianoDocument4 pagesSamambaia by Cesar Camargo MarianoLuca CapovillaNo ratings yet
- Breakbot - Baby - I'm - Yours - BASSDocument4 pagesBreakbot - Baby - I'm - Yours - BASSCarlos CastroNo ratings yet
- Cissy Strut The Meters BassDocument2 pagesCissy Strut The Meters BassAmbra NobileNo ratings yet
- Bach Organ BWV 562Document4 pagesBach Organ BWV 562DNo ratings yet
- Air On G String: Transcription by Fabio LimaDocument2 pagesAir On G String: Transcription by Fabio LimaJeffNo ratings yet
- Piano HanomDocument1 pagePiano HanomDiego HarmoniaNo ratings yet
- Tocando em FrenteDocument2 pagesTocando em FrenteFabiano BortolanNo ratings yet
- A Great New Sound in Your Jazz Solo: Am7 D7alt Gmaj7Document3 pagesA Great New Sound in Your Jazz Solo: Am7 D7alt Gmaj7Sĩ LêNo ratings yet
- Blue Bossa ARPEGGIO STUDYDocument1 pageBlue Bossa ARPEGGIO STUDYelisabeth.buccelliNo ratings yet
- Komi-San - Cinderella - BassDocument3 pagesKomi-San - Cinderella - Bassaidanfinncleary17No ratings yet
- Ave Maria Schubert EaseDocument3 pagesAve Maria Schubert Easecamarlingo camarlingoNo ratings yet
- Can Zone TtaDocument1 pageCan Zone TtaFrancescoModeoNo ratings yet
- La Catedral (3rd Movement)Document5 pagesLa Catedral (3rd Movement)OWEN MARCELIUS KEANENo ratings yet
- Comptine D'un Otre Ete - Guitar Accompaniment ScoreDocument2 pagesComptine D'un Otre Ete - Guitar Accompaniment ScoreFernando CorreaNo ratings yet
- B° 7 de Octubre Rio Blanco: AP5 AP1Document1 pageB° 7 de Octubre Rio Blanco: AP5 AP1ruben jujuyNo ratings yet
- Continued StoryDocument6 pagesContinued StoryForevaNo ratings yet
- Aula - Digitação - Arpejo (Xm7b5) - GuitarraDocument1 pageAula - Digitação - Arpejo (Xm7b5) - GuitarraClaudio SilvaNo ratings yet
- Tio MedericoDocument1 pageTio MedericoAlex MartinsNo ratings yet
- How To Play A Solo in Chord MelodyDocument2 pagesHow To Play A Solo in Chord MelodyKarel Brg100% (1)
- What A Wonderful WorldDocument2 pagesWhat A Wonderful WorldArturo AguadoNo ratings yet
- Poulbot Blues Tab PDFDocument2 pagesPoulbot Blues Tab PDFjilali mohcinNo ratings yet
- Poulbot Blues Tab PDFDocument2 pagesPoulbot Blues Tab PDFjilali mohcinNo ratings yet
- Poulbot Blues Tab PDFDocument2 pagesPoulbot Blues Tab PDFRedouane SaioudNo ratings yet
- Poulbot Blues TabDocument2 pagesPoulbot Blues Tabjilali mohcinNo ratings yet
- Somewhere Over The Rainbow Piano Arr Dayana NuezDocument1 pageSomewhere Over The Rainbow Piano Arr Dayana NuezAmanda LymaNo ratings yet
- IMSLP711981-PMLP181747-Flötensonate Nr. 5 in em BB Clarinet in CM BWV 1034 Generalbass OnlyDocument12 pagesIMSLP711981-PMLP181747-Flötensonate Nr. 5 in em BB Clarinet in CM BWV 1034 Generalbass OnlyvaglientimarianneNo ratings yet
- Paint The Sky With BloodDocument13 pagesPaint The Sky With Bloodjad0jad-176879No ratings yet
- Proposal Tips HintsDocument4 pagesProposal Tips HintsAravindan NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Heterocycles Essentials3-2009Document2 pagesHeterocycles Essentials3-2009Aravindan NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Heterocycles Essentials2-2009Document2 pagesHeterocycles Essentials2-2009Aravindan NatarajanNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry IIDocument10 pagesGeneral Chemistry IIAravindan NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15Document8 pagesLecture 15Aravindan NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Thin-Film Processing Routes For Combinatorial Materials Investigations A ReviewDocument15 pagesThin-Film Processing Routes For Combinatorial Materials Investigations A ReviewMony GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1: Matter and Its PropertiesDocument2 pagesChemistry 1: Matter and Its PropertiesLaika LaiNo ratings yet
- IAL Chemistry 4 Reactions For ExamDocument12 pagesIAL Chemistry 4 Reactions For ExamSilmaSubahHoqueNo ratings yet
- 9701 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesDocument6 pages9701 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesHammad AsifNo ratings yet
- 05-TBT Free Antifoul and Foul Release SystemsDocument14 pages05-TBT Free Antifoul and Foul Release Systemssweet203foolNo ratings yet
- CHEM 1235 Volumetric QuizDocument1 pageCHEM 1235 Volumetric QuizJesseca Calaunan QuintoNo ratings yet
- Production of Activated Carbon From Coconut ShellDocument17 pagesProduction of Activated Carbon From Coconut ShellNiraj NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of The Oxidation of O-Xylene To Phthalic AnhydrideDocument9 pagesMechanism of The Oxidation of O-Xylene To Phthalic AnhydrideJoseGarciaNo ratings yet
- ALKANOLSDocument25 pagesALKANOLSKoki KingNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Raw Materials SpecsDocument9 pagesCeramic Raw Materials SpecsNazanin Sabet100% (1)
- Effect of H2O2 Addition On The Photocatalyst Properties of Ag3PO4 For Methylene Blue PhotodegradationDocument10 pagesEffect of H2O2 Addition On The Photocatalyst Properties of Ag3PO4 For Methylene Blue PhotodegradationFebiyantoNo ratings yet
- Manual Flash PasteurizacionDocument114 pagesManual Flash Pasteurizacionalex100preNo ratings yet
- Summary of PathwaysDocument1 pageSummary of Pathwaysayan100% (1)
- Soil ClassificationDocument34 pagesSoil Classificationtarun23007100% (1)
- 1-Structure and BondingDocument26 pages1-Structure and BondingRayonesh RayanaNo ratings yet
- Expt 9Document3 pagesExpt 9Elaine P.No ratings yet
- Experimental Techniques 1 QPDocument6 pagesExperimental Techniques 1 QPImran MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Focus A Molecular View of Our World 6th Edition Tro Test Bank 1Document18 pagesChemistry in Focus A Molecular View of Our World 6th Edition Tro Test Bank 1alison100% (38)
- Selectivities in Ionic Reductions of Alcohols and Ketones With Triethyisilane - Trifluoroacetic AcidDocument4 pagesSelectivities in Ionic Reductions of Alcohols and Ketones With Triethyisilane - Trifluoroacetic AcidJan Andre EriksenNo ratings yet
- ChT03 - Applications of FTIR - Ed2Document10 pagesChT03 - Applications of FTIR - Ed2Science Experiment At Home.No ratings yet
- 738616703organic ConversionDocument8 pages738616703organic ConversionSakshi SinghNo ratings yet
- Atoms Molecules and IonsDocument46 pagesAtoms Molecules and Ionschandro57No ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes) (Answers)Document3 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 CLASS - XII CHEMISTRY (Haloalkanes and Haloarenes) (Answers)Shreyash KolekarNo ratings yet
- S Block Elements Bounce Back One ShotDocument112 pagesS Block Elements Bounce Back One ShotMd kaifeeNo ratings yet
- Spirapak 4033 HFM 183 VPP Uf DatasheetDocument2 pagesSpirapak 4033 HFM 183 VPP Uf DatasheetJohnNo ratings yet
- D1847Document3 pagesD1847Ненад КнежевићNo ratings yet
- Sku 3033 Environmental ChemistryDocument4 pagesSku 3033 Environmental ChemistryNurul AisahNo ratings yet
- Principles of Organic Synthesis 2th EditionDocument643 pagesPrinciples of Organic Synthesis 2th Editionminh leNo ratings yet
- Flexonyl Black ADocument2 pagesFlexonyl Black ALeandro EsvizaNo ratings yet