Professional Documents
Culture Documents
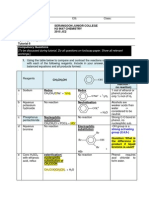
Reaction Summary
Reaction Summary
Uploaded by
shaframenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reaction Summary
Reaction Summary
Uploaded by
shaframenCopyright:
Available Formats
Reaction Summary
Nucleophilic substitution: alkyl-leaving group ! alkyl-nucleophile
Nucleophile
LG
Aprotic polar
solvent
Concerted reaction (SN2)
Nucleophile
Nu
Nu
Protic
solvent
Via carbocation intermediate (SN1)
LG
Elimination: alkyl-leaving group ! alkene
Strong base
LG
H2SO4
OH
heat
Concerted reaction (E2)
heat
Via carbocation intermediate (E1)
Halogen addition: alkene ! vicinal dihaloalkane or halohydrin
OH
Br2
Br2
H2O
CH2Cl2
Anti addition
(cyclic
bromonium
ion)
Br
Br
Br
ROH addition: alkene ! alcohol or ether
OH
H2SO4
R
H2SO4
Markovnikov
addition
(no stereochem
constraints)
Markovnikov
addition
(Anti addition)
H2O
ROH
Via carbocation intermediate
Oxymercuration/reduction: alkene ! alcohol or ether
OH 1. Hg(OAc) / H O
2
2
2. NaBH4
1. Hg(OAc)2 / ROH
2. NaBH4
Hydroboration/oxidation: alkene ! alcohol
1. BH3
Anti-Markovnikov
addition
(Syn addition)
OH
2. NaOH/H2O2
Ozonolysis: alkene ! carboxylic acids or aldehydes
OH
O O
OH
H
1. O3
1. O3
2. H2O2
2. (CH3)2S
H
O O
Tosylate synthesis: alcohol ! tosylate
Tosyl chloride O
(TsCl)
Cl S
CH3
R-OTs
O
OH
O S
CH3
Pyridine
Alkyl halide synthesis: alcohol ! alkyl halide
Br
PBr3
OH
Cl
SOCl2
Pyridine
Alcohol oxidation: alcohol ! aldehyde
(PCC)
OH
CrO3
Pyridine
Alcohol oxidation: alcohol ! carboxylic acid or ketone
OH
K2Cr2O7
OH
K2Cr2O7
OH
Glycol oxidation: glycol ! aldehyde and/or ketone
HO
OH
H5IO6
Nucleophilic substitution: alkyl-leaving group ! alcohol
O
NaOH/H2O
O
CH3
LG
Aprotic polar
solvent
O
CH3
Concerted reaction (SN2)
O
For secondary
substrates
OH
Hydrogenation: alkene ! alkane
H2
Pd/C
Hydrogenation: alkyne ! alkane
H2
Pd/C
Hydrogenation: alkyne ! alkene
trans
cis
Na
H2
NH3
Lindlar
Hydrogenation: aromatic ! aromatic or to alkane
H2
H2
Pd/C
Glycol synthesis: alkene ! glycol
OsO4
Pt, high pressure
HO
OH
Syn addition
H2O/t-butyl alcohol
pyridine/TMAO
Epoxide synthesis: alkene ! epoxide
O
m-chloroperoxy- Cl
OH
benzoic
O
acid
(MCPBA)
O
Syn addition
Epoxide synthesis: halohydrin ! epoxide
Br
NaOH (1 equiv)
O
OH
SN2 attack by hydroxyl
on carbon with Br
Epoxide ring-opening (basic): epoxide ! alcohol and nucleophile
O
OH
1. Nucleophile (basic conditions)
2. Protonate product
Nu
(Example: if the nucleophile is
an alcoxide (RO), the result
is an alcohol/ether; note that
the nucleophile is on the
less substituted carbon.)
Epoxide ring-opening (acidic): epoxide ! alcohol and nucleophile
O
Nu
Nucleophile
H2SO4
OH
(Example: if the nucleophile is
an alcohol, the result
is an alcohol/ether); note that
the nucleophile is on the
more substituted carbon.)
Epoxide ring-opening (Grignard) epoxide ! alcohol two carbons longer
O
Oxirane
1. R-Mg-Br
2. Protonate product
OH
Note: this only yields
predictable product
when using oxirane)
HX addition: alkyne ! vinyl halide
Note: excess HBr will
result in geminal dibromide
following second HBr addition
HBr
Br
Hydration: alkyne ! ketone
Hg2+/H2O
Markovnikov addition
followed by enol/keto
tautomerization
Hydroboration/oxidation: alkyne ! aldehyde
1. BH(amyl)2
2. NaOH/H2O2
O
H
Grignard synthesis: alkyne ! Grignard reagent
CH3CH2MgBr
MgBr
ether
Grignard synthesis: haloalkane ! Grignard reagent
Mg
R Br
R MgBr
ether
Anti-Markovnikov
addition
(Syn addition)
followed by
enol/keto
tautomerization
EAS Nitration: aromatic ! nitro-aromatic
NO2
HNO3
H2SO4
EAS Halogenation: aromatic ! halo-aromatic
X
X2
FeX3 (X= Cl, Br, I)
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation: aromatic ! alkyl-aromatic
R
R
R
+ others R
R-Cl
AlCl3
H2SO4
R
+ others
Friedel-Crafts Acylation: aromatic ! acyl-aromatic
O
O
R
Cl
AlCl3
EAS Sulfonation: aromatic ! aromatic sulfonic acid
SO3H
SO3
H2SO4
Benzylic/allylic bromination
O
CH3
N
Br
Br
O
NBS
CH2
Benzylic oxidation: alkyl-aromatic ! aromatic carboxylic acid
O
R
KMnO4
OH
Nucleophilic aromatic substitution: aryl halide ! aryl-nucleophile
Note: at least
X Nucleophile
Nu
one activating group in
ortho or para position is
necessry
A
A
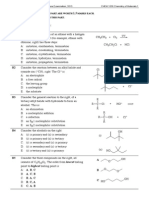
You might also like
- 02 Aldehydes & Ketones Que. Final EDocument14 pages02 Aldehydes & Ketones Que. Final EJagdish SinghNo ratings yet
- Oxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryDocument9 pagesOxidation and Reduction Reactions in Organic ChemistryTarun Lfc Gerrard100% (1)
- 2015 JC 2 H2 Hydroxyl Tutorial (Teachers)Document21 pages2015 JC 2 H2 Hydroxyl Tutorial (Teachers)JohnNo ratings yet
- Section-I (Single Correct Choice) : HC CH 1.1eq Nanh Nanh Nanh X XDocument14 pagesSection-I (Single Correct Choice) : HC CH 1.1eq Nanh Nanh Nanh X XPriyansh YadavNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 231 Final ExamDocument19 pagesOrganic Chemistry 231 Final ExamAlex Rose100% (1)
- Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesDocument10 pagesAlkanes Alkenes AlkynesPanda Boy100% (2)
- 235practice Exam 2 AnswerDocument9 pages235practice Exam 2 Answernbobs7No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 32-235 Practice Questions For Exam #2: 2. Consider The SDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry 32-235 Practice Questions For Exam #2: 2. Consider The Ssweta KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Test 1 MemorandumDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry Test 1 MemorandumSandile SynthaxError Mabika0% (1)
- All Year Chemistry Up To 2018 PDFDocument37 pagesAll Year Chemistry Up To 2018 PDFAGAH LUCKYNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument28 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and EthersDnyanesh Shinde100% (1)
- Welcome To Chem 206: Fall Term, 2005, David A. EvansDocument22 pagesWelcome To Chem 206: Fall Term, 2005, David A. EvanseraborNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry QustionsDocument43 pagesStereochemistry QustionsSwaraj Paul100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry ReviewerDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry ReviewerRanie Magpoc67% (3)
- Organic ChemistryDocument20 pagesOrganic ChemistryGirish RaguvirNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions-Conformational AnalysisDocument4 pagesPractice Questions-Conformational AnalysisHarry Zgambo100% (1)
- Orgo Reaction SheetDocument9 pagesOrgo Reaction SheetKyle Broflovski100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry 2 Practice Exam 1Document15 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2 Practice Exam 1KaybidoNo ratings yet
- PMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIFrom EverandPMR Spectroscopy: Solved Problems Volume : IIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- ACS Review 12 Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SDocument12 pagesACS Review 12 Reactions of Arenes - Electrophilic Aromatic SMohamad HabbabaNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument29 pagesAldehydes and KetonesJiya singhNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Exercise SolutionDocument22 pagesElectrochemistry Exercise SolutionGOURISH AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- 123.312 Advanced Organic Chemistry: Retrosynthesis: TutorialDocument10 pages123.312 Advanced Organic Chemistry: Retrosynthesis: TutorialĐàoTrungHiếuNo ratings yet
- (15 Points) Predict The Products of The Following Reactions. Show Relative Stereochemistry (Only One Stereoisomer) Where AppropriateDocument6 pages(15 Points) Predict The Products of The Following Reactions. Show Relative Stereochemistry (Only One Stereoisomer) Where AppropriateparnaNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Retrosynthesis: Organic Synthesis using Reaxys and SciFinderFrom EverandHybrid Retrosynthesis: Organic Synthesis using Reaxys and SciFinderNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesOrganic Chemistry Multiple Choice QuestionsRonald Angelo LopezNo ratings yet
- CHM 2210 Practice Exam 1Document12 pagesCHM 2210 Practice Exam 1Shaima MossamatNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones: Oxidation Reduction Nucleophilic AdditionDocument51 pagesReactions of Aldehydes and Ketones: Oxidation Reduction Nucleophilic AdditionmacybnzNo ratings yet
- Exercises in Organic Synthesis Based on Synthetic DrugsFrom EverandExercises in Organic Synthesis Based on Synthetic DrugsNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 @stereochemistry PDFDocument5 pagesTutorial 1 @stereochemistry PDFMoulindu Kundu50% (2)
- Synthesis Review - Undergraduate Organic Synthesis GuideDocument19 pagesSynthesis Review - Undergraduate Organic Synthesis GuidePhạm Thị Thùy NhiênNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2016 ExamsDocument20 pagesChemistry 2016 ExamsHoàng MinhNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Cmpds AnskeyDocument6 pagesAromatic Cmpds AnskeyAaron LeeNo ratings yet
- Intro To Organic ChemDocument91 pagesIntro To Organic ChemMiguel Marquez GelacioNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry TestDocument1 pageOrganic Chemistry Testron971No ratings yet
- OrganicChemistryChapter5 PDFDocument19 pagesOrganicChemistryChapter5 PDFJuliet Tatiana CumbeNo ratings yet
- CARBONYL CONDENSATION REACTIONS 2 (10 Mei 2013)Document34 pagesCARBONYL CONDENSATION REACTIONS 2 (10 Mei 2013)Mammy Nya AllyaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IIDocument7 pagesOrganic Chemistry IIRoberto SIlvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 10 PDFKelsi Kyla PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document11 pagesLecture 1Fang GaoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Final Exam - Questions OnlyDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry Final Exam - Questions OnlybrookNo ratings yet
- Class-XII (Chemistry) Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Objective Type QuestionsDocument9 pagesClass-XII (Chemistry) Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Objective Type QuestionsPranav DhimanNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry I - Practice Exercise: Alkene Reactions and MechanismsDocument9 pagesOrganic Chemistry I - Practice Exercise: Alkene Reactions and MechanismsElliot JamesNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halide-Jeemain - Guru PDFDocument37 pagesAlkyl Halide-Jeemain - Guru PDFUma JadounNo ratings yet
- Alkanes McqsDocument2 pagesAlkanes McqsMuhammad Ahtisham AsifNo ratings yet
- 12B Alcohol 2Document11 pages12B Alcohol 2Kasun RatnayakeNo ratings yet
- ICSE Chemistry Board Paper19 PDFDocument9 pagesICSE Chemistry Board Paper19 PDFPrajakta DigheNo ratings yet
- Complete Course Organic ChemistrDocument11 pagesComplete Course Organic Chemistrmanash-12No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry (Alkyl Had., Stereo., Aromat.) (160 Items)Document17 pagesOrganic Chemistry (Alkyl Had., Stereo., Aromat.) (160 Items)S AdiaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry & Numerical MCQ Test 3 - Makox MCQsDocument5 pagesAnalytical Chemistry & Numerical MCQ Test 3 - Makox MCQsنونه الحنونةNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Alkene ReactivityDocument23 pagesChapter 8 - Alkene ReactivitySimran DhunnaNo ratings yet
- ReagentsDocument5 pagesReagentsSomu Yashawant ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- 2013 Organic Chemistry Exam First YearDocument7 pages2013 Organic Chemistry Exam First YearAnonymous oqlnO8eNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - MCQs Test - 1Document3 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers - MCQs Test - 1Prasant Kumar100% (1)
- Excel JEE Booster (3A, 3B) Chemistrty Alcohol Phenol and EtherDocument21 pagesExcel JEE Booster (3A, 3B) Chemistrty Alcohol Phenol and Ethersourav gargNo ratings yet
- Organic Functional Group Analysis: International Series of Monographs on Analytical Chemistry, Volume 8From EverandOrganic Functional Group Analysis: International Series of Monographs on Analytical Chemistry, Volume 8No ratings yet