Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basics, Maintenance, and Diagnostics 27
Uploaded by
imcoolmailme2Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basics, Maintenance, and Diagnostics 27
Uploaded by
imcoolmailme2Copyright:
Available Formats
Transformers:
Basics, Maintenance, and Diagnostics
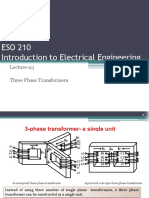
Note that, in the shell form transformers, (see figure 7) the magnetic
flux, external to the coils on both left and right extremes, has complete
magnetic paths for stray and zero sequence flux to return to the coils.
In the core form, it can easily be seen from the figure that, on both left
and right extremes, there are no return paths. This means that the flux
must use external tank walls and the insulating medium for return
paths. This increases core losses and decreases overall efficiency and
shows why most large transformers are built as shell form units.
2.5 Core Losses
Since magnetic lines of force in a transformer are constantly changing
in value and direction, heat is developed because of the hysteresis of
the magnetic material (friction of the molecules). This heat must be
removed; therefore, it represents an energy loss of the transformer.
High temperatures in a transformer will drastically shorten the life of
insulating materials used in the windings and structures. For every
8 degrees Celsius (C) temperature rise, life of the transformer is cut
by one-half; therefore, maintenance of cooling systems is critical.
Losses of energy, which appears as heat due both to hysteresis and to
eddy currents in the magnetic path, is known as core losses. Since
these losses are due to alternating magnetic fields, they occur in a
transformer whenever the primary is energized, even though no load is
on the secondary winding.
2.6 Copper Losses
There is some loss of energy in a transformer due to resistance of the
primary winding to the magnetizing current, even when no load is
connected to the transformer. This loss appears as heat generated in
the winding and must also be removed by the cooling system. When a
load is connected to a transformer and electrical currents exist in both
primary and secondary windings, further losses of electrical energy
occur. These losses, due to resistance of the windings, are called
copper losses (or the I2R losses).
13
You might also like
- TransformersDocument6 pagesTransformersTowfiqNo ratings yet
- How To Minimize Iron Losses in TransformerDocument7 pagesHow To Minimize Iron Losses in TransformerijsretNo ratings yet
- Transformers: Shell TypeDocument5 pagesTransformers: Shell TypeMeghanath AdkonkarNo ratings yet
- Training Module Manufacture TransformerDocument91 pagesTraining Module Manufacture TransformerSanjeev Kadian100% (2)
- PROJECT WORK SubstationDocument91 pagesPROJECT WORK SubstationSai Royals100% (1)
- How To Minimize Iron Losses in Transformer: ENG - Bassam AL - GhramDocument11 pagesHow To Minimize Iron Losses in Transformer: ENG - Bassam AL - GhramosamaNo ratings yet
- First Tests of Bi-Y T-FDocument8 pagesFirst Tests of Bi-Y T-FEBENo ratings yet
- To Study The Open Circuit/Core Losses of Single Phase TransformerDocument5 pagesTo Study The Open Circuit/Core Losses of Single Phase TransformerTanzeel UR RehmanNo ratings yet
- Contents:: 1 5 2 Working Principle 6 3 Construction 7 4 Types of Transformers 8Document12 pagesContents:: 1 5 2 Working Principle 6 3 Construction 7 4 Types of Transformers 8Abhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding AbstractDocument5 pagesArc Welding AbstractotuozegarbaNo ratings yet
- Center For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electromechanical Systems LabDocument11 pagesCenter For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electromechanical Systems LabIrfan HaiderNo ratings yet
- 2008 Vlach OsDocument51 pages2008 Vlach Osanurag_jay12464No ratings yet
- Evaluation Study of Performance Analysis & Characteristics of Amorphous Core Transformer For Electrical Distribution SystemDocument7 pagesEvaluation Study of Performance Analysis & Characteristics of Amorphous Core Transformer For Electrical Distribution SystemSamuel AdamuNo ratings yet
- Small Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsFrom EverandSmall Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsNo ratings yet
- Predicting Temperature Rise of Ferrite Cored TransformersDocument5 pagesPredicting Temperature Rise of Ferrite Cored TransformersPhạm Văn TưởngNo ratings yet
- C !" # $%&C'C (') C) ') C) + 'CDocument8 pagesC !" # $%&C'C (') C) ') C) + 'COmar QasmiNo ratings yet
- Unit IIIDocument11 pagesUnit IIIAshok BNo ratings yet
- Electric Arc Furnace Transformer Secondary Circuit CalculationsDocument13 pagesElectric Arc Furnace Transformer Secondary Circuit CalculationsikamelyaastutiNo ratings yet
- Transformer EfficiencyDocument12 pagesTransformer EfficiencyhaysomaNo ratings yet
- Loss Reduction in Distribution TransformersDocument37 pagesLoss Reduction in Distribution Transformerstapas_kbNo ratings yet
- AAAdddd 1Document3 pagesAAAdddd 1Anonymous ufMAGXcskMNo ratings yet
- Project Bhel 2Document12 pagesProject Bhel 2jatt_yankyNo ratings yet
- TractionDocument6 pagesTractionPrashant KoliNo ratings yet
- TransformersDocument9 pagesTransformersumerNo ratings yet
- EE Presentation1Document11 pagesEE Presentation1Shubhranil GharaNo ratings yet
- Enercon Finals Assignment 5Document18 pagesEnercon Finals Assignment 5Ezekiel Brizuela100% (2)
- MMAWDocument21 pagesMMAWAkash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current ElectricityDocument34 pagesAlternating Current Electricityahmadhassan1364No ratings yet
- Experiment No.7 Transformers: Engr. Conrado QuinalayoDocument9 pagesExperiment No.7 Transformers: Engr. Conrado QuinalayoJaloyd MacalalagNo ratings yet
- Transformer LossesDocument10 pagesTransformer LossesSagarikaRoutNo ratings yet
- Transformers - Three Phase TransformersDocument25 pagesTransformers - Three Phase TransformersDeepakDeep100% (1)
- Failure, Causes and Analysis of Magnetic Circuit in Power TransformerDocument8 pagesFailure, Causes and Analysis of Magnetic Circuit in Power TransformerreevamandaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Cooling Method1Document12 pagesTransformer Cooling Method1Gideon MoyoNo ratings yet
- Power TransformersDocument62 pagesPower Transformersmoka ahmedNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument12 pagesPhysicsAyushNo ratings yet
- Superconducting Magnetic Energy StorageDocument7 pagesSuperconducting Magnetic Energy StorageAnton Fatoni100% (1)
- Basic Construction of TransformerDocument17 pagesBasic Construction of TransformerRudra DeviNo ratings yet
- Types of Power Losses in Transformers? How Can We Reduce Eddy Current and Hysteresis Losses?Document10 pagesTypes of Power Losses in Transformers? How Can We Reduce Eddy Current and Hysteresis Losses?legasuNo ratings yet
- Auto-Transformer Design - A Practical Handbook for Manufacturers, Contractors and WiremenFrom EverandAuto-Transformer Design - A Practical Handbook for Manufacturers, Contractors and WiremenRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- 5.4.2 - Induction and Dielectric Heating 1Document27 pages5.4.2 - Induction and Dielectric Heating 1Milan AcharyaNo ratings yet
- DCAC Q4 TransformersDocument2 pagesDCAC Q4 TransformersShane De VillaNo ratings yet
- 1.list Out Trouble Shooting Techniques For Transformer TransformerDocument30 pages1.list Out Trouble Shooting Techniques For Transformer Transformerrohith mukkamalaNo ratings yet
- Transformer Maintenance: ContentDocument71 pagesTransformer Maintenance: ContentGnanavel GNo ratings yet
- Automotive Applications of EMPT PDFDocument7 pagesAutomotive Applications of EMPT PDFmohamad zareNo ratings yet
- Transformers SWDocument7 pagesTransformers SWBryan FerrolinoNo ratings yet
- EEPC108 Module 1Document52 pagesEEPC108 Module 1Elizabeth GomezNo ratings yet
- Direct Current Generators and Motor AssignmentDocument9 pagesDirect Current Generators and Motor AssignmentThirdy SanchezNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument117 pagesUnit IIThangam MaheshNo ratings yet
- Ology: Pusa Institute of TechnDocument33 pagesOlogy: Pusa Institute of TechnDeepesh KNo ratings yet
- Technological Institute of The Philippines Cubao, Quezon CityDocument18 pagesTechnological Institute of The Philippines Cubao, Quezon CityJohn Raven Pajes EngalanNo ratings yet
- Em 1 Unit IvDocument49 pagesEm 1 Unit Ivckissyou04No ratings yet
- TransformerDocument17 pagesTransformerAbragam Siyon SIngNo ratings yet
- Protecting The Leads of A Powered Magnet That Is Protected With Diodes and ResistorsDocument4 pagesProtecting The Leads of A Powered Magnet That Is Protected With Diodes and ResistorsdabalejoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument25 pagesElectromagnetic Inductionbalasubramanian979No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - BeeieDocument47 pagesUnit 2 - BeeieKarthick Sivakumar ChellamuthuNo ratings yet
- DC Machines (Part1)Document22 pagesDC Machines (Part1)Narayana NagapuriNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines 2 MARKSDocument9 pagesElectrical Machines 2 MARKSdtselvanNo ratings yet
- Inductor and Flyback Transformer DesignDocument20 pagesInductor and Flyback Transformer Designbmmostefa100% (1)
- Chapter - One Transformer DesignDocument21 pagesChapter - One Transformer Designgebretensaymamu11No ratings yet
- Broadband Over Power Line-3364Document5 pagesBroadband Over Power Line-3364imcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Accuracy Limit Factor of Current TransformerDocument1 pageAccuracy Limit Factor of Current Transformerimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Over Reach of Distance RelayDocument2 pagesOver Reach of Distance Relayimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Powerline Communications-Final PDFDocument23 pagesPowerline Communications-Final PDFimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Calculation of Multiplication Factor of Energy MetersDocument3 pagesCalculation of Multiplication Factor of Energy Metersimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Accuracy Limit Factor of Current TransformerDocument1 pageAccuracy Limit Factor of Current Transformerimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Over Reach of Distance RelayDocument2 pagesOver Reach of Distance Relayimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Critical-Power Automatic Transfer Systems - Design and ApplicationDocument18 pagesCritical-Power Automatic Transfer Systems - Design and ApplicationRazvan Mares100% (1)
- ACSR Rail - 954MCM - RAIL954-ACSR - Nassau National CableDocument2 pagesACSR Rail - 954MCM - RAIL954-ACSR - Nassau National Cableimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Cable SizingDocument2 pagesCable SizingMohammed ThoufeeqNo ratings yet
- IEEMAJournal Guide 0Document1 pageIEEMAJournal Guide 0imcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Low Resistance Testing PDFDocument19 pagesLow Resistance Testing PDFAaqib MujtabaNo ratings yet
- GisDocument1 pageGisimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- 02 Oliver Nenadovic 1Document1 page02 Oliver Nenadovic 1imcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- 18 NTDocument1 page18 NTimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- 11 Starting The Construction Work 120Document1 page11 Starting The Construction Work 120imcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- 1 The Development of Construction ProceduresDocument1 page1 The Development of Construction Procedureskkppkk1No ratings yet
- Excavation Working Space Pipelines Earthwork Construction Concrete BrickworkDocument1 pageExcavation Working Space Pipelines Earthwork Construction Concrete Brickworkimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- 1.2 The Most Widely Used Contracts For ConstructionDocument1 page1.2 The Most Widely Used Contracts For Constructionkkppkk1No ratings yet
- 18 Earthworks and Pipelines 225Document1 page18 Earthworks and Pipelines 225imcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- 15 EntDocument1 page15 Entimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Concrete Production Plant Power Generators and Compressors Extra Land Main OfficesDocument1 pageConcrete Production Plant Power Generators and Compressors Extra Land Main Officesimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- 3 Payment Arrangements, Risks and Project Cost Estimating 29Document1 page3 Payment Arrangements, Risks and Project Cost Estimating 29imcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Qualification Attached To Tenders Checking Tenders: 7 The Contractor's Site Organization 80Document1 pageQualification Attached To Tenders Checking Tenders: 7 The Contractor's Site Organization 80imcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- 5 Preparing Contract Documents 50Document1 page5 Preparing Contract Documents 50imcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- 5 Preparing Contract Documents 50Document1 page5 Preparing Contract Documents 50imcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Applications of Optical Technology in The Telecommunication NetworksDocument1 pageApplications of Optical Technology in The Telecommunication Networksimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Able of Ontents: Chapter 1 - Optical Fibres CharacteristicsDocument1 pageAble of Ontents: Chapter 1 - Optical Fibres Characteristicsimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- Preface Xiii Acknowledgements XivDocument1 pagePreface Xiii Acknowledgements Xivimcoolmailme2No ratings yet
- The Fifth Phase: (O/E/O) Conversions Within The Optical Transport Networks (OTN) - The Two Main Reasons For The ReductionDocument1 pageThe Fifth Phase: (O/E/O) Conversions Within The Optical Transport Networks (OTN) - The Two Main Reasons For The Reductionimcoolmailme2No ratings yet