Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AntidoteDrugTool v1 2013 PDF
AntidoteDrugTool v1 2013 PDF
Uploaded by
ohsnapitsleiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AntidoteDrugTool v1 2013 PDF
AntidoteDrugTool v1 2013 PDF
Uploaded by
ohsnapitsleiCopyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacological Antidotes Table Copyright Pharmacology Weekly, Inc.
www.pharmacologyweekly.com
Drug Toxicity
Acetaminophen (APAP)
Amphetamines & derivatives
Anesthesia
Anticholinergics
Antifreeze (ethylene glycol)
Antipsychotic-Induced
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Aspirin (salicylic acid; ASA)
Benzodiazepine
Beta Blockers
Black Widow Spider Bite
Calcium Channel Blockers
Carbon monoxide (CO)
Cyanide (CN)
Antidote
N-acetylcysteine (Acetadote IV; Mucomyst)
Antipsychotics (e.g., haloperidol for dopamine antagonism);
GABA activating drugs (benzodiazepines, phenobarbital)
Dantrium (Dantrolene)
Physostigmine
Fomepizole (Antizol) or Ethanol 10% given IV
Dantrium (Dantrolene) or Bromocriptine
Note(s)
IV faster and shorter duration, but small risk of allergic reaction.
Amphetamines increase release of dopamine & norepinephrine. Treatment: Block dopamine
receptors; suppress the CNS from over stimulation.
Interferes with Ca++ release via Ryr receptor on sarcoplasmic reticulum; muscle relaxation.
Must be on cardiac monitor. Get ECG first.
Fomepizole is a competitive inhibitor of alcohol dehydrogenase & toxic metabolites.
Interferes with Ca++ release via Ryr receptor on sarcoplasmic reticulum; muscle relaxation.
Alkalization of urine +/- Dialysis
Flumazenil (Romazicon)
Glucagon; High dose insulin/glucose; +/- Cardiac pacing
Benzodiazepines (if seizures)
Black Widow Spider Antivenin (Latrodectus Mactans)
Calcium chloride or gluconate; +/- glucagon; +/- dopamine (if
hypotensive)
Oxygen via non-rebreather mask; hyperbaric oxygen
Amyl Nitrate, sodium nitrite, then Sodium Thiosulfate
Hydroxocobalamin (Cyanokit; a hydroxylated form of B12)
Cause ionization of ASA thereby causing ion trapping for renal elimination.
Caution rapid and/or overcorrection can cause seizure.
Glucagon can increase myocardial contractility, pulse, and AV conduction.
Digoxin
Ethylene glycol (Antifreeze)
Heparin (UFH)
Hydrofluoric acid
Iron (Fe)
Isoniazid (INH)
Isopropyl alcohol
Lead (Pb)
Digoxin Immune Fab (Digibind)
Fomepizole (Antizol)
Protamine sulfate
Calcium gel
Deferoxamine (Desferal)
Pyridoxine (vitamin B6)
Hemodialysis
Succimer (Chemet); DMSA (Meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid)
Low Molecular Weight Heparins
Mercury (Hg)
Methanol (Windshield Wiper
Fluid, Sterno, Paint Solvent)
Methotrexate
Neuromuscular Blockers (Nondepolarizing Agents)
Nitrates
Opioids
Organophosphates/Pesticides
Protamine sulfate
Succimer (Chemet); DMSA (Meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid)
Fomepizole (Antizol) or Ethanol 10% given IV
Snake Bite (Rattle Snake)
Sulfonylureas (SU)
Thrombolytics
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCA)
Valproic acid
Warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven)
Leucovorin
Edrophonium (Enlon), neostigmine (Prostigmin)
Methylene blue
Naloxone (Narcan)
Atropine +/- pralidoxime (2-PAM; Protopam)
Body decontamination
Crotalidae polyvalent immune Fab Ovine (CroFab)
Octreotide (Sandostatin)
Aminocaproic acid; tranexamic acid; aprotinin
Sodium bicarbonate
Naloxone +/- Dialysis +/- L-carnitine
Vitamin K (Phytonadione; Mephyton)
Can see target lesion. Venom neutralizing antibodies (equine). Can be given up to 90 hrs after bite.
Verify not digoxin toxicity as hypercalcemia can worsen it.
CO causes lactic acidosis. If pregnant give longer treatment due to presence of fetal Hgb.
CN causes lactic acidosis. Amyl nitrate induces a methemoglobin in RBC to combine CN, Na
thiosulfate conversion of CN to thiocyanate for renal elimination. Each hydroxocobalamin
molecule binds to one CN molecule to form cyanocobalamin for renal clearance.
Fab portions only of antibodies generated from sheep that bind to digoxin.
Fomepizole is a competitive inhibitor of alcohol dehydrogenase & oxalic acid formation.
Neutralizes heparin. Caution as it can act as an anticoagulant as well.
Mixture of 1 amp Ca gluconate with 2-3 packs of Surgilube.
Chelates with iron from ferritin & hemosiderin (not transferrin or Hgb) to make water soluble.
Replenishes reductions in vitamin B6.
Forms acetone & risk for coma. No anion gap seen, but does osmolar gap.
Can see basophilic stippling on histology. Chelates with lead to form water soluble chelates for
urinary excretion. SE: possible bone marrow suppression. Not indicated for prophylaxis.
60-75% effective; requires staggered dosing.
May chelate with Hg. Not approved for Hg toxicity. Can also try penicillamine.
Fomepizole is a competitive inhibitor of alcohol dehydrogenase & formic acid formation (optic
nerve damage/blindness). Sterno is a chafing fuel or portable fires in the foodservice industry.
FH4 derivative that bypasses dihydrofolate reductase being inhibited by methotrexate.
Cholinesterase inhibitors increase acetylcholine levels at NMJ. Non-depolarizing agents
(atracuronium, mivacurium, pancuronium, rocuronium, tubocurarine)
Goal methemoglobin <20%; less effective in G6PD.
Except meperidine induced seizures.
Atropine antagonizes muscarinic receptors (anticholinergic effect). 2-PAM attempts to reactivate
acetylcholinesterase that was inactivated by phosphorylation.
IgG antibody that neutralizes venom toxins. Best used within 6 hours of bite.
Block/suppress insulin release due to SU and/or glucose.
Inhibit plasminogen activation; inhibits plasmin (aprotinin).
Monitor ECG and ABG; if seizures give benzodiazepines.
VPA metabolites can induce NH3+ & GABA (naloxone may displace from receptor).
IV associated with > side effects; avoid unnecessary over correction; monitor H/H, INR.
Version: 1.2013. Developed & Reviewed by: Anthony J. Busti, MD, PharmD, FNLA, FAHA; Gregory McKeever, MD; Medical Director. Please check www.pharmacologyweekly.com for current version and disclaimer.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Naplex KatDocument21 pagesNaplex KatShan Shani100% (5)
- 7896 - Super NAPLEX Review PDFDocument72 pages7896 - Super NAPLEX Review PDFFrancis Leonardes100% (9)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- MSDS - Mobil Heavy Duty Sca Precharged 50/50 PredilutedDocument11 pagesMSDS - Mobil Heavy Duty Sca Precharged 50/50 Predilutedobedot100% (1)
- Antidote Chart: N-Acetylcysteine, NAC (Mucomyst) PO: Loading Dose: 140mg/kg PO: NauseaDocument11 pagesAntidote Chart: N-Acetylcysteine, NAC (Mucomyst) PO: Loading Dose: 140mg/kg PO: NauseaTapioca PearlNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ExpDocument4 pagesChemistry ExplovehopeNo ratings yet
- Uttar Pradesh Voluntary Action NetworkDocument3 pagesUttar Pradesh Voluntary Action NetworklovehopeNo ratings yet
- Attachment C454ea4cDocument32 pagesAttachment C454ea4clovehopeNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Science 2014Document24 pagesPharmaceutical Science 2014lovehope100% (1)
- Academic Sciences: Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical ResearchDocument4 pagesAcademic Sciences: Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical ResearchlovehopeNo ratings yet
- A C A D e M I C S C I e N C e SDocument5 pagesA C A D e M I C S C I e N C e SlovehopeNo ratings yet
- 2014 - 13 - Article 5Document4 pages2014 - 13 - Article 5lovehopeNo ratings yet
- Exp't 42: Two Easy Diels-Alder PuzzlesDocument5 pagesExp't 42: Two Easy Diels-Alder Puzzleslovehope0% (1)
- Introduction of PharmacologyDocument10 pagesIntroduction of PharmacologylovehopeNo ratings yet
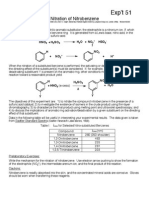
- Exp't 51: Nitration of NitrobenzeneDocument4 pagesExp't 51: Nitration of NitrobenzenelovehopeNo ratings yet
- Exp't 61: 1,4-Di-T-Butylbenzene Via Friedel-Crafts AlkylationDocument6 pagesExp't 61: 1,4-Di-T-Butylbenzene Via Friedel-Crafts AlkylationlovehopeNo ratings yet
- Exp 17Document4 pagesExp 17lovehopeNo ratings yet
- Exp 11Document4 pagesExp 11lovehopeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Diuretic Drugs: Instructor: Lee, Hon-CheungDocument12 pagesPharmacology of Diuretic Drugs: Instructor: Lee, Hon-CheunglovehopeNo ratings yet
- Exp't 13: Phase-Transfer-Catalyzed Alkylation of Diethyl MalonateDocument5 pagesExp't 13: Phase-Transfer-Catalyzed Alkylation of Diethyl MalonatelovehopeNo ratings yet
- Exp't 41: The Reaction of Maleic Anhydride and CycloheptatrieneDocument5 pagesExp't 41: The Reaction of Maleic Anhydride and CycloheptatrienelovehopeNo ratings yet
- Pre-Matric SC Scholarship 2014-2015 (10) Name of The State/ UT .. District . Name of The Institution Total No of Beneficiaries Academic YearDocument5 pagesPre-Matric SC Scholarship 2014-2015 (10) Name of The State/ UT .. District . Name of The Institution Total No of Beneficiaries Academic YearlovehopeNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Evaluation of Solid Dispersion of Terbinafine HydrochlorideDocument7 pagesPreparation and Evaluation of Solid Dispersion of Terbinafine HydrochloridelovehopeNo ratings yet
- Exp't. 206: An NMR Study of Enzyme ActivityDocument2 pagesExp't. 206: An NMR Study of Enzyme ActivitylovehopeNo ratings yet
- Tablets: Unit IiiDocument43 pagesTablets: Unit Iiilovehope100% (2)
- 3rd Sem HB SyllabusDocument6 pages3rd Sem HB SyllabuslovehopeNo ratings yet
- The Conservation Orbital: of SymmetryDocument6 pagesThe Conservation Orbital: of SymmetrylovehopeNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii: Topical AgentsDocument26 pagesUnit-Iii: Topical AgentslovehopeNo ratings yet
- Immobilized Enzyme Systems: Enzyme Immobilization: To Restrict Enzyme Mobility in A Fixed SpaceDocument17 pagesImmobilized Enzyme Systems: Enzyme Immobilization: To Restrict Enzyme Mobility in A Fixed SpacelovehopeNo ratings yet
- Cosmetics Baby CareDocument36 pagesCosmetics Baby Carelovehope100% (1)
- Student Tox LectureDocument49 pagesStudent Tox Lecturelenin_villaltaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Practice Worksheet 1Document25 pagesEnzymes Practice Worksheet 1Divyanshi VikramNo ratings yet
- MPC Antidote List 2016Document2 pagesMPC Antidote List 2016Vin BitzNo ratings yet
- Forensic Medicine AIIMS May 2001 To November 2019 First EditionDocument153 pagesForensic Medicine AIIMS May 2001 To November 2019 First EditionLaura VelásquezNo ratings yet
- 50 Drugs: Every Emergency Physician Should KnowDocument52 pages50 Drugs: Every Emergency Physician Should KnowMohamed Abu ElgheetNo ratings yet
- Antidote Chart 2012 PDFDocument3 pagesAntidote Chart 2012 PDFRommel IrabagonNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology FirecrackerDocument37 pagesPharmacology FirecrackerRehan Usman100% (1)
- MSDS Prestone Antifreeze CoolantDocument6 pagesMSDS Prestone Antifreeze CoolantAna ZieglerNo ratings yet
- ToxicologyDocument197 pagesToxicologyRichelle Dianne Ramos-Giang100% (6)
- TOXICOLOGY MCQsDocument9 pagesTOXICOLOGY MCQsSanjiv Sharma100% (1)
- Module 4 Toxicology MBJDocument95 pagesModule 4 Toxicology MBJAmiel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Antidote - Chart - 20141014 (Poison Control System) PDFDocument5 pagesAntidote - Chart - 20141014 (Poison Control System) PDFMichael Freudiger100% (1)
- Methanol Information 2 PDFDocument5 pagesMethanol Information 2 PDFPark RangerNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Product Name: Mobil Brake Fluid Dot 4Document14 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Product Name: Mobil Brake Fluid Dot 4MichaelNo ratings yet
- Toxic Alcohols - High Yields NEJMDocument21 pagesToxic Alcohols - High Yields NEJMDr. Shanojan Thiyagalingam, FRCPC FACPNo ratings yet
- تجميعات Pharmacology - 1397-11-30-22-05Document6 pagesتجميعات Pharmacology - 1397-11-30-22-05Mohammed ShaddadNo ratings yet
- Antidotes 2 List 2011Document2 pagesAntidotes 2 List 2011Alpesh ValaNo ratings yet
- Varcarolis Foundations of Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing - Ebook - A Clinical Approach 8th EditionDocument1 pageVarcarolis Foundations of Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing - Ebook - A Clinical Approach 8th Editionsophia onuNo ratings yet
- Pharma SuperexamDocument72 pagesPharma SuperexamVelasco JohnNo ratings yet
- Prestone Antifreeze MSDSDocument8 pagesPrestone Antifreeze MSDSJoseNo ratings yet
- Extracorporeal Removal of Poisons and Toxins: Joshua David King, Moritz H. Kern, and Bernard G. JaarDocument8 pagesExtracorporeal Removal of Poisons and Toxins: Joshua David King, Moritz H. Kern, and Bernard G. JaarArdiana FirdausNo ratings yet
- DOWSIL™ 982-H Curing Agent Black SDSDocument21 pagesDOWSIL™ 982-H Curing Agent Black SDSAquatic studentNo ratings yet
- PRESTone AnticongelanteDocument8 pagesPRESTone AnticongelanteegarciachNo ratings yet
- Methanol ToxicityDocument75 pagesMethanol ToxicitySyNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. IdentificationDocument12 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. Identificationanon_444174592No ratings yet
- AntidoteDocument2 pagesAntidoteZeeia MendozaNo ratings yet