Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Osa Zone
Osa Zone
Uploaded by
mallik7890 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageh
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenth
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageOsa Zone
Osa Zone
Uploaded by
mallik789h
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
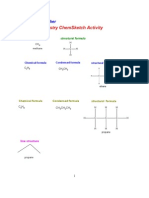
Osazone Formation
Phenylhydrazine (C6H5NHNH2) reacts with carbons #1 and #2 of
reducing sugars to form derivatives called osazones. The formation of
these distinctive crystalline derivatives is useful for comparing the
structures of sugars. Glucose and fructose react as shown below:
H
C
OH
HO
OH
OH
C6H5NHNH2
NNHC6H5
OH
HO
HO
OH
OH
CH2OH
C6H5NHNH2
CH2OH
NNHC6H5
NNHC6H5
NNHC6H5
HO
OH
OH
OH
OH
C6H5NHNH2
CH2OH
CH2OH
D-glucose
osazone
CH2OH
CH2OH
NNHC6H5
HO
HO
OH
OH
OH
OH
CH2OH
D-fructose
C6H5NHNH2
CH2OH
C6H5NHNH2
NNHC6H5
HO
NNHC6H5
NNHC6H5
HO
OH
OH
OH
OH
CH2OH
C6H5NHNH2
CH2OH
osazone
Identical osazones are obtained from D-glucose and D-fructose.
This demonstrates that carbons #3 through #6 of D-glucose and
D-fructose molecules are identical. The same osazone is also obtained
from D-mannose. This indicates that carbons #3 through #6 of the
D-mannose molecule are the same as those of D-glucose and D-fructose
molecules. In fact, D-mannose differs from D-glucose only in the
configuration of the H and OH groups on carbon #2.
You might also like
- 2 CarbohydratesDocument54 pages2 CarbohydratesoecologieNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of CarbohydratesDocument66 pagesChemistry of CarbohydratesPraveen VundrajavarapuNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates 9Document26 pagesCarbohydrates 9Prakash Amruth Raj ChNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Test - ReportDocument12 pagesCarbohydrates Test - Reportscorp198167% (6)
- Carbohydrates PresentationDocument60 pagesCarbohydrates PresentationRaagas, ChristianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Phenol (Aromatic Alcohol) Alcohol SPDocument18 pagesChapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Phenol (Aromatic Alcohol) Alcohol SPKriti Tyagi100% (2)
- Biochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingFrom EverandBiochemistry Applied to Beer Brewing - General Chemistry of the Raw Materials of Malting and BrewingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- LecturerDocument22 pagesLectureratef.salman.grNo ratings yet
- 07 Carbohydrate LabDocument9 pages07 Carbohydrate LabCrizielle GarciaNo ratings yet
- BSC MLT ClassDocument38 pagesBSC MLT ClassBhojNo ratings yet
- 1 ChoDocument38 pages1 ChoFauzan FasnidNo ratings yet
- Karbohidrat JupeDocument47 pagesKarbohidrat JupeRayanda AdiputraNo ratings yet
- COLORIMETRIC IDENTIFICATION OF UNKNOWN SUGARS-مضغوط PDFDocument12 pagesCOLORIMETRIC IDENTIFICATION OF UNKNOWN SUGARS-مضغوط PDFHassan mohamad Al-bayateNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Carbohydrates TPDocument19 pagesLecture 5 Carbohydrates TPIrene DuttaNo ratings yet
- Karbohidrat Struktur Dan Fungsi: Dian Riana Ningsih, Msi Prodi Kimia MipaDocument47 pagesKarbohidrat Struktur Dan Fungsi: Dian Riana Ningsih, Msi Prodi Kimia MipaNathanael UlrichsternNo ratings yet
- Introductory Biochemistry: CarbohydratesDocument68 pagesIntroductory Biochemistry: CarbohydratesMahrukh SaeedNo ratings yet
- Glucose - Preparation, Properties, Uses & Structures .Document6 pagesGlucose - Preparation, Properties, Uses & Structures .Oyester pearlNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Structure and NomenclatureDocument60 pagesCarbohydrates Structure and NomenclatureNikka Mia AbadiesNo ratings yet
- Reaction of CarbohydrateDocument8 pagesReaction of CarbohydrateWaseem AjmalNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 CarbohydrateDocument17 pagesCHAPTER 5 CarbohydrateFirdaus ShabuddinNo ratings yet
- Principles of Biochemistry (Carbohydrates)Document32 pagesPrinciples of Biochemistry (Carbohydrates)Sohaib NazirNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules Game Changer 3 DecDocument121 pagesBiomolecules Game Changer 3 DecpiyaliNo ratings yet
- 2 CarbohydratesDocument49 pages2 CarbohydratesVishwanath SinduvadiNo ratings yet
- The Citric Acid Cycle II and The Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument38 pagesThe Citric Acid Cycle II and The Pentose Phosphate Pathwayghai_85No ratings yet
- C1 Carbohydrates Part2 Cyclic FormDocument27 pagesC1 Carbohydrates Part2 Cyclic FormAlliana Denice VicencioNo ratings yet
- 12 CARBOHYDRATES Reactions of MonosaccharidesDocument21 pages12 CARBOHYDRATES Reactions of MonosaccharidesRebecca CrossNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculesDocument16 pagesBio Moleculesnoorunnisa0184No ratings yet
- 13 DPP Thnote+19c-19e Dpps+Ans+SolDocument56 pages13 DPP Thnote+19c-19e Dpps+Ans+SolVaibhav SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Glycosaminoglycans: (Mucopolysaccharides)Document50 pagesGlycosaminoglycans: (Mucopolysaccharides)AvinashNo ratings yet
- Convert Fischer To HaworthDocument3 pagesConvert Fischer To HaworthDoris GrimaldiNo ratings yet
- ProjectionDocument3 pagesProjectionkaliegh4204No ratings yet
- Carob Hydrates SummaryDocument17 pagesCarob Hydrates Summaryalizay91No ratings yet
- Lecture3 BiochemistryDocument59 pagesLecture3 BiochemistryEssam HassanNo ratings yet
- Unit-14 Biomolecules 2023Document22 pagesUnit-14 Biomolecules 2023jagannathanNo ratings yet
- Dr.H.Mohammad Hanafi, Mbbs (Syd.) .MS.: Fakultas Kedokteran UnairDocument48 pagesDr.H.Mohammad Hanafi, Mbbs (Syd.) .MS.: Fakultas Kedokteran UnairahmustofaNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis PDFDocument2 pagesGlycolysis PDFunknownxemNo ratings yet
- DokumenDocument2 pagesDokumenELSA OKTAVIANI SOPYANNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument39 pagesBiological Macromoleculesapi-337296800No ratings yet
- Glycoproteins ProteoglycansDocument7 pagesGlycoproteins Proteoglycans43357No ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry Hydroxy Compound PDFDocument71 pagesMatriculation Chemistry Hydroxy Compound PDFiki292No ratings yet
- Organic ChemDocument116 pagesOrganic ChemNidhi Sisodia100% (1)
- Carbohydrates: Biochemistry For Allied Mecdical CoursesDocument41 pagesCarbohydrates: Biochemistry For Allied Mecdical CoursesFelica Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chuoi Phan Ung Ve AminDocument2 pagesChuoi Phan Ung Ve AminNguyễn LyNo ratings yet
- AS Unit 1: Basic Biology and Cell Organisation 1.1 Syllabus Objectives AssessedDocument26 pagesAS Unit 1: Basic Biology and Cell Organisation 1.1 Syllabus Objectives AssessedZoé LennonNo ratings yet
- BT301 Tutorial-3 SolutionsDocument12 pagesBT301 Tutorial-3 SolutionsShivaani EswaranNo ratings yet
- 1 ChoDocument79 pages1 ChoFrance Jan First SaplacoNo ratings yet
- Module 11 Carbohydrates Lecture 29 Carbohydrates I: C H O + 6O 6CO 6H O Energy Oxidation Photosynthesis + + GlucoseDocument5 pagesModule 11 Carbohydrates Lecture 29 Carbohydrates I: C H O + 6O 6CO 6H O Energy Oxidation Photosynthesis + + GlucoseRajiv KalsiNo ratings yet
- CarbohydrateDocument39 pagesCarbohydrateAkila AkinsNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Agitha R. Menon PGT AECS, IndoreDocument19 pagesBiomolecules: Agitha R. Menon PGT AECS, Indoreshivanigangwar69No ratings yet
- Carbohydrates PDFDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates PDFChristelle Marie Aquino Beroña100% (1)
- Booher Chem Sketch Activity 1Document13 pagesBooher Chem Sketch Activity 1c_booher9561No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Chemistry BMC 3Document65 pagesCarbohydrate Chemistry BMC 3sarahwassel2015No ratings yet
- Glycolysis: Glucose Is Converted To PyruvateDocument21 pagesGlycolysis: Glucose Is Converted To PyruvateFrogWarriorNo ratings yet
- TEST-1 ALCOHOL Physical PropertiesDocument5 pagesTEST-1 ALCOHOL Physical PropertiesFableNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument26 pagesBIOMOLECULESVicky VigneshNo ratings yet
- Amino Polymer 1Document58 pagesAmino Polymer 1Siddharth ShahNo ratings yet
- Nano Physical and Thermochemical Parameters Investigation of Essential Oils Ginger (Zingiberene and Gingerol)Document20 pagesNano Physical and Thermochemical Parameters Investigation of Essential Oils Ginger (Zingiberene and Gingerol)mallik789No ratings yet
- RT 201 KrauseDocument45 pagesRT 201 Krausemallik789No ratings yet
- Tate Olicies in Rief: Sex and HIV EducationDocument5 pagesTate Olicies in Rief: Sex and HIV Educationmallik789No ratings yet
- IOSTEXV Anastacio& MarinhoDocument11 pagesIOSTEXV Anastacio& Marinhomallik789No ratings yet
- Development and Validation Dietary Methodology For N-Nitroso CompoundsDocument25 pagesDevelopment and Validation Dietary Methodology For N-Nitroso Compoundsmallik789No ratings yet
- Benzoat - KalamaDocument7 pagesBenzoat - KalamaPham Minh DuyNo ratings yet
- Go To Hell by MadhubabuDocument48 pagesGo To Hell by Madhubabumallik789100% (1)
- 36 Sydney Mangham.: Lecturer in Botany, Armstrong College, Newcastle-on-Tyne, in The University of Durham.Document6 pages36 Sydney Mangham.: Lecturer in Botany, Armstrong College, Newcastle-on-Tyne, in The University of Durham.mallik789No ratings yet