Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Household Water-Treatment Systems
Household Water-Treatment Systems
Uploaded by
toanvmpetrologx0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageSlow sand filtration is the most effective household water treatment system for removing various contaminants. It can highly effectively remove bacteria, amoebas, guinea-worm, cercaria, iron, manganese, fluoride, organic matter, and turbidity. Proper use is important as untreated water can remain contaminated otherwise. Coagulation, flocculation and settlement is also effective at removing many contaminants through the addition of chemicals to attract and remove particles. Storage and aeration are moderately effective methods that improve water quality through sedimentation and oxidization of chemicals.
Original Description:
Some techniques for household treating water
Original Title
Household Water-treatment Systems
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSlow sand filtration is the most effective household water treatment system for removing various contaminants. It can highly effectively remove bacteria, amoebas, guinea-worm, cercaria, iron, manganese, fluoride, organic matter, and turbidity. Proper use is important as untreated water can remain contaminated otherwise. Coagulation, flocculation and settlement is also effective at removing many contaminants through the addition of chemicals to attract and remove particles. Storage and aeration are moderately effective methods that improve water quality through sedimentation and oxidization of chemicals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageHousehold Water-Treatment Systems
Household Water-Treatment Systems
Uploaded by
toanvmpetrologxSlow sand filtration is the most effective household water treatment system for removing various contaminants. It can highly effectively remove bacteria, amoebas, guinea-worm, cercaria, iron, manganese, fluoride, organic matter, and turbidity. Proper use is important as untreated water can remain contaminated otherwise. Coagulation, flocculation and settlement is also effective at removing many contaminants through the addition of chemicals to attract and remove particles. Storage and aeration are moderately effective methods that improve water quality through sedimentation and oxidization of chemicals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
LINKING TECHNOLOGY CHOICE WITH OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE
72
TABLE 6.1 HOUSEHOLD WATER-TREATMENT SYSTEMS AND THEIR EFFECTIVENESSa
Effectiveness over factors that affect water quality
Treatment system
Straining through fine cloth
Consists in pouring raw water
through a piece of fine, clean,
cotton cloth to remove some
of the suspended solids.
Aeration
Oxidizes iron (Fe) and manganese (Mn). Good aeration of
the water is also important for
slow, sand filtration to be
effective, especially if there is
not enough oxygen in the
surface water. Water can easily
be aerated by shaking it in a
vessel, or by allowing it to
trickle through perforated trays
containing small stones.
Storage/pre-settlement
Storing water for only one day
can eliminate some bacteria,
but it should be stored for 48
hours to eliminate cercaria (snail
larvae). The longer the water is
stored, the more the suspended
solids and pathogens will settle
to the bottom of the container.
The top water can then be used
after sedimentation.
Coagulation, flocculation
and settlement
In coagulation, a liquid coagulant, such as aluminium sulfate,
is added to the water to attract
suspended particles. The water
is then gently stirred to allow the
particles to come together and
form larger particles (flocculation), which can then be
removed by sedimentation,
settlement or filtration. The
amount of coagulant needed
will depend on the nature of the
contaminating chemical
compounds and solids.
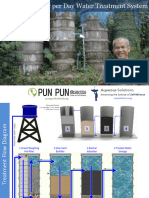
Slow sand filtration
Water passes slowly downwards
through a bed of fine sand at a
steady rate. The water should
not be too turbid, otherwise the
filter will get clogged. Pathogens are naturally removed in
the top layer where a biological
film builds up. A potential
problem is that some households do not use this technology
effectively and the water can
remain contaminated.
Bacteria,
amoebas
Guineaworm
Cercaria
Fe, Mn
Fluoride
Arsenic
Salts
Odour,
taste
Organic
matter
Turbidity
Adapted from: Skinner & Shaw (1998).
The treatments were categorized as being: of no effect, or of unknown effectiveness (); of little effect (); moderately effective
(); highly effective ().
You might also like
- Environment Management System ManualDocument5 pagesEnvironment Management System ManualtoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Salt Water Converted To Purified Drinking Water by Using Pedal PowerDocument44 pagesSalt Water Converted To Purified Drinking Water by Using Pedal PowerUNITED CADD100% (1)
- Water Treatment ProcessDocument20 pagesWater Treatment Processadib1991No ratings yet
- CHE 262 Chemical Processes and Sustainability: Prepared By: Mohd Shahrul Nizam Bin SallehDocument24 pagesCHE 262 Chemical Processes and Sustainability: Prepared By: Mohd Shahrul Nizam Bin SallehMohd Shahrul Nizam SallehNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment ProcessDocument17 pagesWater Treatment ProcessCarel De Jager100% (1)
- Sand Filter Design PDFDocument14 pagesSand Filter Design PDFWONG TS63% (8)
- Conventional Water TreatmentDocument21 pagesConventional Water TreatmentGani AbdilahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - FiltrationDocument22 pagesLesson 6 - FiltrationZar Chi100% (1)
- Water Treatment & MethodsDocument39 pagesWater Treatment & MethodsHaydar TaşNo ratings yet
- Household Water Treatment MethodsDocument2 pagesHousehold Water Treatment Methodstony frankNo ratings yet
- Pe Project Class 11Document19 pagesPe Project Class 11Kalp patniNo ratings yet
- Report On Sedimentation, Coagulation and Filtration: Name-Section - Semester - Roll NoDocument8 pagesReport On Sedimentation, Coagulation and Filtration: Name-Section - Semester - Roll NoArghyadip SarkarNo ratings yet
- Direct From The Tap: Water Treatment StepsDocument3 pagesDirect From The Tap: Water Treatment Stepsswami22No ratings yet
- Direct From The Tap: Water Treatment StepsDocument3 pagesDirect From The Tap: Water Treatment Stepsswami22No ratings yet
- Water Treatment SystemsDocument12 pagesWater Treatment Systemskim alfonsoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Assighnment: Submitted By-: Mrs. Deepshikha MamDocument24 pagesChemistry Assighnment: Submitted By-: Mrs. Deepshikha MamRaviVasdevNo ratings yet
- Conventional Water Distribution SystemDocument41 pagesConventional Water Distribution SystemTRISHIA JOYCENo ratings yet
- Water Purification AssignmentDocument2 pagesWater Purification AssignmentKhynan Rhyss VicenteNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Processes and Treatment Units: Process of Treating Water by Plain SedimentationDocument6 pagesWater Treatment Processes and Treatment Units: Process of Treating Water by Plain SedimentationStanley Scott ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Properties of WaterDocument16 pagesLesson 2 Properties of WaterJunnaz BalacuitNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument18 pagesChemistry ProjectAni78% (9)
- Water TreatmentDocument12 pagesWater TreatmentPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- A Modern Treatment PlantDocument3 pagesA Modern Treatment Plantcharvie benzNo ratings yet
- Water Conditioning Processes 1. Distillation: Distilled Water Herbicides PesticidesDocument6 pagesWater Conditioning Processes 1. Distillation: Distilled Water Herbicides PesticidesClintNo ratings yet
- 2022 EU 2 Module 2 Designing Building Water Systems Part 2Document43 pages2022 EU 2 Module 2 Designing Building Water Systems Part 2BryanHarold BrooNo ratings yet
- Group 08Document11 pagesGroup 08Sihle TolikiNo ratings yet
- LN - Water Purity and TreatmentDocument2 pagesLN - Water Purity and Treatmentmichealshodeinde994No ratings yet
- Water Treatment ProcessDocument3 pagesWater Treatment ProcessPalak BafnaNo ratings yet
- Health Effects Associated With Turbidity in Drinking WaterDocument3 pagesHealth Effects Associated With Turbidity in Drinking WaterKate CordialNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 DCC 40152Document27 pagesTopic 3 DCC 40152Sham AzrulNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument20 pagesChapter ThreeKasozi Bateesa ShafickNo ratings yet
- SEDIMENTATIONDocument4 pagesSEDIMENTATIONニール シルベラNo ratings yet
- Dec 307 Enviromental EngineeringDocument7 pagesDec 307 Enviromental Engineeringutachi93No ratings yet
- Types of Water SupplyDocument8 pagesTypes of Water SupplyMardiyya SuleimanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 WATER TREATMENT - Section 1Document41 pagesCHAPTER 3 WATER TREATMENT - Section 1Mbali MagagulaNo ratings yet
- Top 7 Methods of Water TreatmentDocument2 pagesTop 7 Methods of Water Treatmentpedjamt-1No ratings yet
- WaterDocument17 pagesWaterKennethNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Plant 1 3Document16 pagesWater Treatment Plant 1 3Shuvadip RoyNo ratings yet
- IGNTU Econtent 677113707754 M.SC EnvironmentalScience 2 PallaviDas EnvironmentalPollutionandControlTechnique I 5Document56 pagesIGNTU Econtent 677113707754 M.SC EnvironmentalScience 2 PallaviDas EnvironmentalPollutionandControlTechnique I 5vsumedhaNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Poster CompleteDocument1 pageWater Treatment Poster Completedangerous0100% (2)
- Water Purification Is A Process of Removing Undesirable ChemicalsDocument15 pagesWater Purification Is A Process of Removing Undesirable ChemicalsJatinChadhaNo ratings yet
- CPP. Microproject PDF 2022Document11 pagesCPP. Microproject PDF 2022Prathmesh ManusmareNo ratings yet
- Water PortabilityDocument4 pagesWater PortabilityMegha Nair PillaiNo ratings yet
- WTP IndoDocument1 pageWTP IndotasyaNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Process - Kenali Alam JuruteraDocument63 pagesWater Treatment Process - Kenali Alam JuruteraRaja Norazilla Raja YunusNo ratings yet
- Report of WTPDocument14 pagesReport of WTPnishantNo ratings yet
- Water PurificationDocument11 pagesWater Purificationsonu HalderNo ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument2 pagesWater TreatmentArren Joyce Jagna LannaoNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Processes: 1. SofteningDocument2 pagesWater Treatment Processes: 1. SofteningecthhNo ratings yet
- Assignment Water Supply (Individual)Document24 pagesAssignment Water Supply (Individual)eryky21No ratings yet
- 2000LPD English 2022Document11 pages2000LPD English 2022terabytecrNo ratings yet
- Report of WTPDocument14 pagesReport of WTPnishantNo ratings yet
- How Is Water TreatedDocument8 pagesHow Is Water Treatedjugal ranaNo ratings yet
- The Water Treatment ProcessDocument11 pagesThe Water Treatment ProcessRAMTINNo ratings yet
- MF2178 PDFDocument6 pagesMF2178 PDFKhawar NehalNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Process123Document4 pagesWater Treatment Process123Creator UnknownNo ratings yet
- Bio AADocument2 pagesBio AAMokshitha Reddy YanamalNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment ProcessesDocument55 pagesWater Treatment ProcessesJohn Carlo AbalaNo ratings yet
- 7 PDFDocument6 pages7 PDFMithun ChandranNo ratings yet
- Water PurificationDocument12 pagesWater PurificationRoseNavyaNo ratings yet
- The Enabling Environment in PakistanDocument1 pageThe Enabling Environment in PakistantoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Example of Calculating Molecular MassDocument1 pageExample of Calculating Molecular MasstoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Prefixes Used in The SI SystemDocument1 pagePrefixes Used in The SI SystemtoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- The Importance of ChemistryDocument1 pageThe Importance of ChemistrytoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Some Physical PropertiesDocument1 pageMeasurement of Some Physical PropertiestoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Molecular MassDocument1 pageHow To Calculate Molecular MasstoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Density and TemepraturesDocument1 pageMeasurement of Density and TemepraturestoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Flow Totalization of LiquidDocument1 pageFlow Totalization of LiquidtoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Reference On Properties of Various Southern Diesel BlendsDocument2 pagesReference On Properties of Various Southern Diesel BlendstoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Clausen Weir Rule For Wate Measurement UtahDocument1 pageClausen Weir Rule For Wate Measurement UtahtoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- 3.3.1 Waveforms: Waveforms Are A Kind of Graph. Graphs Have An X-Axis, Which RunsDocument1 page3.3.1 Waveforms: Waveforms Are A Kind of Graph. Graphs Have An X-Axis, Which RunstoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Overshot Gates For Water MeasurementDocument1 pageOvershot Gates For Water MeasurementtoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- English Studying TipsDocument3 pagesEnglish Studying TipstoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extraction OsunDocument1 pageSolvent Extraction OsuntoanvmpetrologxNo ratings yet