Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Platelets
Uploaded by
PrasanaBathumalai0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views1 pagePlatelets, also called thrombocytes, are cell fragments produced by the bone marrow that aid in blood clotting. Megakaryocytes in the bone marrow break apart to release between 1,000-3,000 platelets each. Platelets circulate in the bloodstream for around 9-10 days, after which they are removed by the spleen if old or damaged. A normal platelet count is 150,000-450,000 per microliter, with lower counts considered thrombocytopenic and higher counts thrombocytotic. When blood vessels are damaged, platelets secrete enzymes and thromboplastin that trigger coagulation and formation of a fibrin mesh to form clots and prevent excessive blood loss.
Original Description:
biology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPlatelets, also called thrombocytes, are cell fragments produced by the bone marrow that aid in blood clotting. Megakaryocytes in the bone marrow break apart to release between 1,000-3,000 platelets each. Platelets circulate in the bloodstream for around 9-10 days, after which they are removed by the spleen if old or damaged. A normal platelet count is 150,000-450,000 per microliter, with lower counts considered thrombocytopenic and higher counts thrombocytotic. When blood vessels are damaged, platelets secrete enzymes and thromboplastin that trigger coagulation and formation of a fibrin mesh to form clots and prevent excessive blood loss.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views1 pagePlatelets
Uploaded by
PrasanaBathumalaiPlatelets, also called thrombocytes, are cell fragments produced by the bone marrow that aid in blood clotting. Megakaryocytes in the bone marrow break apart to release between 1,000-3,000 platelets each. Platelets circulate in the bloodstream for around 9-10 days, after which they are removed by the spleen if old or damaged. A normal platelet count is 150,000-450,000 per microliter, with lower counts considered thrombocytopenic and higher counts thrombocytotic. When blood vessels are damaged, platelets secrete enzymes and thromboplastin that trigger coagulation and formation of a fibrin mesh to form clots and prevent excessive blood loss.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Platelets
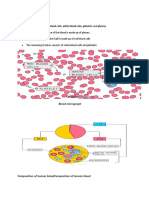
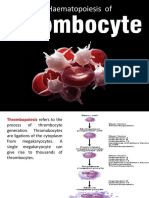
Platelets is called thrombocytes smallest cell in blood
The primary function is to aid in the blood clotting process
It is produced from the bone marrow, the large bone marrow is called
MEGAKARYOCTES
Megakaryoctes are huge cell that break into fragment to form platelets
These cell fragment have no nucleus but due contain structures called
granules
Megakaryoctes can produced anywhere from 1000 to 3000 platelets. Platelets
can circulated in blood stream about 9 to 10 days
They become old or damaged, they removed from circulation by the spleen.
Normal platelets range 150000 to 450000 platelets per micro liter of blood
If more 450 000 more - thrombocytosis
If less than 150 000 thrombocytopenia
Blood clotting
Excessive loss in blood is prevented from the cut blood vessels by the formation of
clots. This process is called coagulation
Damaged platelets secrete thromboplastin or throbokinase
Thromokinase is an enzyme that change prothrombine ( present in blood) in
the presence of calcium ion
Fibrin form thread like structure that form a sticky substances at the
damaged portion of the blood vessel
This the network does not allowed to pass through and this plasma which
lacks the fibrinogen is called serum
The mass that is formed at the cut become denser and it is called clot
Normal coagulation required vitamin k and it is followed by clot reaction
( tightening of the solution of the clot) and untimely fibrinolysis ( dissolution
of the blood)
A clotting in an unbroken blood vessel is called thrombosis. Thrombi that
move from the site of the origin is called embolus.
You might also like
- Lecture Notes On Renal Physiology For MBBSDocument129 pagesLecture Notes On Renal Physiology For MBBSNayyer Khan83% (6)
- PlateletsDocument21 pagesPlateletsSana Fatima0% (1)
- Thrombopoiesis and Megakaryopoiesis: BY Dr. Etu-Efeotor T. PDocument22 pagesThrombopoiesis and Megakaryopoiesis: BY Dr. Etu-Efeotor T. PPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Haemostasis MechanismDocument15 pagesHaemostasis MechanismThakur KanchanNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates By: Tarek Khaleefa Alwaan. Supervised By: Dr. MustafaDocument9 pagesCarbohydrates By: Tarek Khaleefa Alwaan. Supervised By: Dr. MustafaAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- Platelets: By: Tarek Khaleefa Alwaan. Supervised ByDocument9 pagesPlatelets: By: Tarek Khaleefa Alwaan. Supervised ByAhmed AliNo ratings yet
- 1.3 The Mechanism of Blood ClottingDocument10 pages1.3 The Mechanism of Blood ClottingReakhd Bt KhdNo ratings yet
- CH 15 BloodDocument6 pagesCH 15 Bloodsann1992No ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System 2Document21 pagesThe Cardiovascular System 2aboody62621No ratings yet
- HemostasisDocument9 pagesHemostasisJared Khoo Er Hau100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Blood and Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Blood and Cardiovascular SystemCharise LigoresNo ratings yet
- Darah: Dr. Yetty Machrina Bagian Fisiologi FK UsuDocument44 pagesDarah: Dr. Yetty Machrina Bagian Fisiologi FK UsuMyst AngelNo ratings yet
- 5149 MegakaryopoiesisDocument4 pages5149 MegakaryopoiesisCyril LumibaoNo ratings yet
- Class ADocument22 pagesClass AIdil AliNo ratings yet
- 5149 MegakaryopoiesisDocument5 pages5149 Megakaryopoiesisvishuvishu8648No ratings yet
- Hemostasis - 20230915 - 150948 - 0000Document44 pagesHemostasis - 20230915 - 150948 - 0000Lian Marie ViñasNo ratings yet
- THROMOCYTOPENIADocument5 pagesTHROMOCYTOPENIAcfgrtwifhNo ratings yet
- PlateletsDocument6 pagesPlateletsapi-550378216No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular A SystemDocument23 pagesCardiovascular A SystemRetnaning Nurani SayektiNo ratings yet
- Clotting - 05Document39 pagesClotting - 05muslemia2003No ratings yet
- 16.4B: Platelet Formation: Learning ObjectivesDocument3 pages16.4B: Platelet Formation: Learning ObjectivesBasantPdPantNo ratings yet
- grp52 DHF DseDocument17 pagesgrp52 DHF DsekcdgrvnNo ratings yet
- Blood Clotting Mechanisms and AtherosclesrosisDocument11 pagesBlood Clotting Mechanisms and AtherosclesrosisGizelle Iwo BatkoNo ratings yet
- Blood Coagulation and HaemostasisDocument76 pagesBlood Coagulation and HaemostasisArun MamachanNo ratings yet
- Aula Af 2 PDFDocument49 pagesAula Af 2 PDFtobiasmanuel179No ratings yet
- Vasoconstriction: HemostasisDocument1 pageVasoconstriction: Hemostasisclau lizNo ratings yet
- All Objectives HematologyDocument45 pagesAll Objectives HematologyNursing200980% (5)
- Blood Components PlateletsDocument3 pagesBlood Components PlateletsDavidNo ratings yet
- Underwood: Chapter 6: Thrombosis, Embolism and InfarctionDocument12 pagesUnderwood: Chapter 6: Thrombosis, Embolism and InfarctionSANo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - BloodDocument5 pagesLecture 6 - Bloodadnan yaqoobNo ratings yet
- The BloodDocument7 pagesThe BloodAnika AroviNo ratings yet
- BSM DRM p2qt6p Pages DeletedDocument70 pagesBSM DRM p2qt6p Pages DeletedLekhan KNo ratings yet
- Platelet Count by Haemocytometer 2nd Year NotesDocument21 pagesPlatelet Count by Haemocytometer 2nd Year Notesrajanti904No ratings yet
- HemostasisDocument17 pagesHemostasisHadi AdamNo ratings yet
- How Does The Blood Clot?Document1 pageHow Does The Blood Clot?Pebrian Diki PrestyaNo ratings yet
- Trombopoiesis (3) - 1Document10 pagesTrombopoiesis (3) - 1Vannisa Dwi NovianaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Blood AnatomyDocument5 pagesChapter 10 Blood AnatomyChiara Mae NiñalNo ratings yet
- Hematology L11 - ١٠٤٣٢٤Document18 pagesHematology L11 - ١٠٤٣٢٤shakib33001No ratings yet
- PlateletsDocument33 pagesPlateletsAthar Habib ShahaniNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة 5Document10 pagesالمحاضرة 5Shi no Me100% (1)
- Unit 8 The Cardiovascular System 8.3-Blood Vessels 8.4-BloodDocument20 pagesUnit 8 The Cardiovascular System 8.3-Blood Vessels 8.4-BloodSoulseekerNo ratings yet
- Written OutputDocument19 pagesWritten Outputbvietine009No ratings yet
- Edexcel As Biology Unit 1 Exam Revision NotesDocument19 pagesEdexcel As Biology Unit 1 Exam Revision Notesfockoffu100% (1)
- Blood PlateletsDocument17 pagesBlood PlateletsÉhmìđá LŷNo ratings yet
- Platelets - The Lancet 2000Document9 pagesPlatelets - The Lancet 2000bluemleinNo ratings yet
- Ijhoscr 11 319 PDFDocument9 pagesIjhoscr 11 319 PDFmgoez077No ratings yet
- Odontogenic CystsDocument6 pagesOdontogenic Cystsم.م.زينة عبد الحسينNo ratings yet
- Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)Document14 pagesBlood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)Pari JanNo ratings yet
- What Keeps The Blood Moving!Document25 pagesWhat Keeps The Blood Moving!mikeeNo ratings yet
- Biology Jan 16Document2 pagesBiology Jan 16tahjsalmonNo ratings yet
- 1-2 Hemostasis PhysiologyDocument48 pages1-2 Hemostasis PhysiologyHussein Al Saedi100% (2)
- Blood &hematologyDocument13 pagesBlood &hematologyAymen OmerNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Blood Vasculature, Megakaryocytes and PlateletsDocument31 pagesModule 1 - Blood Vasculature, Megakaryocytes and PlateletsI love dem Coffee (Migz)No ratings yet
- HEMOSTASIS Aytona PDFDocument27 pagesHEMOSTASIS Aytona PDFMae AnnNo ratings yet
- Hemostasis and ThrombosisDocument23 pagesHemostasis and ThrombosisFiqrotul Umam100% (1)
- Platelets Kel 4Document10 pagesPlatelets Kel 4U WidNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Platelet Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Platelet Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Microcirculation of Blood 101: The Next Generation of HealthcareFrom EverandMicrocirculation of Blood 101: The Next Generation of HealthcareNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to The Spleen And Its Function (What You Need To Recycle RBCs)From EverandA Simple Guide to The Spleen And Its Function (What You Need To Recycle RBCs)No ratings yet