Professional Documents
Culture Documents
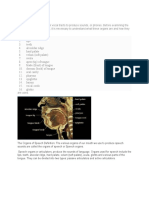
The Organs of Speech
The Organs of Speech
Uploaded by
ShaziaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Organs of Speech
The Organs of Speech
Uploaded by
ShaziaCopyright:
Available Formats
The Organs of Speech
1-nasal cavity
2-lips
3-teeth
4-aveolar ridge
5-hard palate
6-velum (soft palate)
7-uvula
8-apex (tip) of tongue
9-blade (front) of tongue
10-dorsum (back) of tongue
11-oral cavity
12-pharynx
13-epiglottis
14-larynx
15-vocal cords
16-trachea
17-esophagus
Speech organs produce the many sounds needed for language. Organs used
include the lips, teeth, tongue, alveolar ridge, hard palate, velum (soft palate), uvula
and glottis.
Speech organs - otherwise articulators - are divided into two: passive articulators
and active articulators. Passive articulators are those which remain static during
the articulation of sound. Upper lips, upper teeth, alveolar ridge, hard palate etc. are
the passive articulators. Active articulators move towards these passive articulators
to produce various speech sounds, in different manner. The most important active
articulator is tongue. Uvula, lower jaw which include lower teeth and lower lip are
the other active articulators
The Eight Parts of Human Speech Organs & Their Definitions
Human speech is one of our species' defining qualities. In order to make this
speech, eight different organs must work together.
1. Lips, Teeth, Tongue
Lips form different shapes, such as an oval, and movements in order to make
different sounds. Sounds can be formed by using the teeth to shape the lips,
in combination with the tongue, or to block air from escaping the mouth. The
tongue moves throughout the mouth and with many of the other organs, as
well as making shapes like the lips, in order to formulate speech.
2. Uvula
Where It All Happens
The uvula is used to make guttural sounds. It helps to make nasal
consonants by stopping air from moving through the nose.
3. Glottis
The glottis is used in controlling the vibration made by the vocal chords, in
order to make different sounds.
4. Alveolar Ridge
To make different sounds, known as alveolar sounds, the tongue touches the
ridges found on this organ.
5. Hard Palate
Like the alveolar ridge, the tongue touches and taps the palate when
articulating speech.
6. Velum (Soft Palate)
The movable velum can retract and elevate in order to separate the mouth
from the nasal cavity, helping to make speech less nasally. When the tongue
hits the velum, it also makes a special sound called the velar consonant.
You might also like
- Active and Passive Organs of SpeechDocument15 pagesActive and Passive Organs of SpeechТаня БродаNo ratings yet
- Traditional and Modern Approaches To SyntaxDocument55 pagesTraditional and Modern Approaches To Syntaxmardeflo87% (15)
- Place & Manner of Articulations ConsonantsDocument26 pagesPlace & Manner of Articulations Consonantsatikah100% (1)
- Sociolinguistics NotesDocument15 pagesSociolinguistics NotesRania Mounabeh100% (5)
- English Phonetics and PhonologyDocument31 pagesEnglish Phonetics and PhonologyIzzati AzmanNo ratings yet
- The Object of Study by Ferdinand de Saussure Summary (Critical Theory Third Semister)Document3 pagesThe Object of Study by Ferdinand de Saussure Summary (Critical Theory Third Semister)Nazer mirzaNo ratings yet
- Lexical RelationsDocument9 pagesLexical RelationsMei Elfrida ButarbutarNo ratings yet
- Phonological RulesDocument5 pagesPhonological RulesJasmin Cadir100% (1)
- Language ChangeDocument15 pagesLanguage ChangeKristi CooperNo ratings yet
- Dialect and Its TypesDocument2 pagesDialect and Its TypesAl Haram100% (1)
- Organs of SpeechDocument5 pagesOrgans of Speechlittle large2100% (1)
- Phonetics Phonology Full NotesDocument24 pagesPhonetics Phonology Full NotesMuralitharan Nagalingam100% (4)
- Phonemes, Phone, and AllophonesDocument6 pagesPhonemes, Phone, and AllophonesLinda Niasari100% (2)
- Language VarietyDocument2 pagesLanguage VarietyFatima Aslam100% (3)
- PhoneticsDocument20 pagesPhoneticsMohamed Tayeb SELT94% (16)
- Historical Linguistics - Genetic ClassificationDocument33 pagesHistorical Linguistics - Genetic ClassificationKhalil Brahimi100% (1)
- Semantic Assignment 1Document8 pagesSemantic Assignment 1Anggoro SasongkoNo ratings yet
- Domains of Language Use: SociolinguisticsDocument9 pagesDomains of Language Use: Sociolinguisticssajid mahmoodNo ratings yet
- Sociolinguistics Mid Term Course.Document34 pagesSociolinguistics Mid Term Course.Chishmish DollNo ratings yet
- Types of MeaningDocument4 pagesTypes of MeaningRandi Mokodaser100% (2)
- Ferdinand de SaussureDocument9 pagesFerdinand de SaussureYupi Yana MuntheNo ratings yet
- Langue and ParoleDocument2 pagesLangue and ParoleKritikaSinghNo ratings yet
- Componential Analysis and ExamplesDocument2 pagesComponential Analysis and ExamplesMar Crespo80% (5)
- Manner of ArticulationDocument15 pagesManner of ArticulationAMEEER HAMZANo ratings yet
- Inflectional MorphemesDocument7 pagesInflectional Morphemesapi-296553705100% (5)
- Language Maintenance and Language ShiftDocument19 pagesLanguage Maintenance and Language ShiftYANGUAS, NIÑA MICAELLA R.No ratings yet
- Relationship Between Language and SocietDocument3 pagesRelationship Between Language and SocietACADEMIC TOOLS100% (2)
- The Old and Middle English PeriodDocument5 pagesThe Old and Middle English PeriodNelson Aminosse Zavale100% (1)
- Characteristics of Old EnglishDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Old EnglishPushpanathan Thiru100% (1)
- Deixis & Its TypesDocument5 pagesDeixis & Its TypesAqsa100% (1)
- Language AttitudesDocument24 pagesLanguage AttitudesMuhammad Arif Al Hakim100% (1)
- Language Maintenance and ShiftDocument7 pagesLanguage Maintenance and Shiftnona100% (1)
- Allomorph and Types of AllomorphDocument6 pagesAllomorph and Types of AllomorphRizki Yulia Sari100% (4)
- What Linguistics Is NOTDocument2 pagesWhat Linguistics Is NOTFlavia Pacheco70% (10)
- Organs of SpeechDocument8 pagesOrgans of SpeechÎßhû ẞhåñdèl100% (1)
- What Are The Different Types of Antonyms in EnglishDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Different Types of Antonyms in EnglishEssam KassabNo ratings yet
- Morphological TreesDocument10 pagesMorphological TreesAnđaNo ratings yet
- Syntagmatic and Paradigmatic RelationsDocument3 pagesSyntagmatic and Paradigmatic RelationsdattarupamNo ratings yet
- Definition of LinguisticsDocument12 pagesDefinition of LinguisticsAgung PranawijayaNo ratings yet
- Problematic CasesDocument2 pagesProblematic CasesPearl67% (3)
- Speakers and CommunitiesDocument3 pagesSpeakers and CommunitiesMuhammad Imran50% (2)
- Morphological ProductivityDocument6 pagesMorphological ProductivityMuhammad KhayamNo ratings yet
- Manner of ArticulationDocument12 pagesManner of ArticulationMhonz Limbing100% (1)
- 2 - Words, Sentences, and DictionariesDocument10 pages2 - Words, Sentences, and DictionariesDian herdita setia riniNo ratings yet
- Problems in Phonemic AnalysisDocument32 pagesProblems in Phonemic AnalysisBrendon Jikal86% (7)
- Attitudes and ApplicationsDocument10 pagesAttitudes and ApplicationsArin Azkiya100% (2)
- IC AnalysisDocument16 pagesIC AnalysisSibghaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Semantic Roles - NOTESDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Semantic Roles - NOTESWaad MajidNo ratings yet
- CH 5. National Languages and Language Planning (Sociolinguistics)Document10 pagesCH 5. National Languages and Language Planning (Sociolinguistics)Priska Ginting100% (2)
- Linguistic ConflictsDocument26 pagesLinguistic Conflictsوشال VISHAL67% (3)
- Sociolingüística - Unit 1Document4 pagesSociolingüística - Unit 1Stella100% (1)
- What Linguistics Is Not PDFDocument2 pagesWhat Linguistics Is Not PDFfede37100% (1)
- StylisticsDocument17 pagesStylisticsTeodora Alexandra100% (1)
- Expected Questions of Phonetics Chapter One: Articulation and AcousticDocument17 pagesExpected Questions of Phonetics Chapter One: Articulation and Acousticالاستاذ محمد زغير100% (1)
- Formal & Functional LabelsDocument21 pagesFormal & Functional LabelsHarvinPopat100% (2)
- Eng 323 Lecture 2Document4 pagesEng 323 Lecture 2maryjames ikebunaNo ratings yet
- The Speech OrgannnDocument13 pagesThe Speech OrgannnMicka Mercado DimaanoNo ratings yet
- The Eight Parts of Human Speech Organs & Their DefinitionsDocument1 pageThe Eight Parts of Human Speech Organs & Their DefinitionsMarxlen Apostol BedolidoNo ratings yet
- PHONOLOGYDocument24 pagesPHONOLOGYAllene Salili HoncadaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Note On Speech Organ and Their Function. THR112Document18 pagesDetailed Note On Speech Organ and Their Function. THR112Samson BlessedNo ratings yet