Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flower Anatomy
Uploaded by
api-263197810Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Flower Anatomy
Uploaded by
api-263197810Copyright:
Available Formats
Flower Anatomy
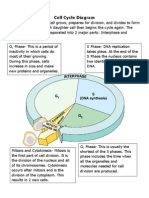
The Flower:
The flower is the reproductive unit of some plants (angiosperms). Parts of the flower include petals,
sepals, one or more carpels (the female reproductive organs), and stamens (the male reproductive
organs).
The Female Reproductive Organs:
The pistil is the collective term for the carpel(s). Each carpel includes an ovary (where the ovules are
produced; ovules are the female reproductive cells, the eggs), a style (a tube on top of the ovary),
and a stigma (which receives the pollen during fertilization).
The Male Reproductive Organs:
Stamens are the male reproductive parts of flowers. A stamen consists of an anther (which produces
pollen) and a filament. The pollen consists of the male reproductive cells; they fertilize ovules.
Fertilization:
Pollen must fertilize an ovule to produce a viable seed. This process is called pollination, and is often
aided by animals like bees, which fly from flower to flower collecting sweet nectar. As they visit
flowers, they spread pollen around, depositing it on some stigmas. After a male's pollen grains have
landed on the stigma during fertilization, pollen tubes develop within the style, burrowing down to the
ovary, where the sperm fertilizes an ovum (an egg cell), in the ovule. After fertilization, the ovule
develops into a seed in the ovary.
Types of Flowers:
Some flowers (called perfect flowers) have both male and female reproductive organs; some flowers
(called imperfect flowers) have only male reproductive organs or only female reproductive organs.
Some plants have both male and female flowers, while other have males on one plant and females
on another. Complete flowers have stamens, a pistil, petals, and sepals. Incomplete flowers lack one
of these parts.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Biome PosterDocument1 pageBiome Posterapi-263197810No ratings yet
- ProjectDocument3 pagesProjectapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Biomes Chart Grad PrepDocument1 pageBiomes Chart Grad Prepapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Dihybrid Cross Practice IIIDocument1 pageDihybrid Cross Practice IIIapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Kingdom Circle DirectionsDocument1 pageKingdom Circle Directionsapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Pedigree Charts - NotesDocument2 pagesPedigree Charts - Notesapi-263197810No ratings yet
- The Six Kingdoms of LifeDocument17 pagesThe Six Kingdoms of Lifeapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Biomes InformationDocument15 pagesBiomes Informationapi-26319781050% (2)
- Non-Mendelian Inheritance PracticeDocument5 pagesNon-Mendelian Inheritance Practiceapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Evidence For Evolution SlidesDocument11 pagesEvidence For Evolution Slidesapi-2631978100% (1)
- Genetics With A Smile CompleteDocument4 pagesGenetics With A Smile Completeapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle Diagram & Importance of Chromosomes inDocument2 pagesCell Cycle Diagram & Importance of Chromosomes inapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Mouse Cloning Lab QuestionsDocument1 pageMouse Cloning Lab Questionsapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Pedigree PracticeDocument2 pagesPedigree Practiceapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Mla Sample PaperDocument11 pagesMla Sample Paperapi-246856658No ratings yet
- 2c Biotechnology Worksheet 2Document2 pages2c Biotechnology Worksheet 2api-263197810No ratings yet
- Karyotyping Simulation ProductDocument2 pagesKaryotyping Simulation Productapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Dna Replication Foldable InstructionsDocument1 pageDna Replication Foldable Instructionsapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument1 pageCell Cycleapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Comparing Mitosis and MeiosisDocument1 pageComparing Mitosis and Meiosisapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis V Respiration FoldableDocument1 pagePhotosynthesis V Respiration Foldableapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Illustrating Dna StructureDocument2 pagesIllustrating Dna Structureapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Mutations Practice - KeyDocument3 pagesMutations Practice - Keyapi-263197810No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)