Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Substitution Notes For Students
Uploaded by
api-2185117410 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views2 pages1. Alcohols can undergo substitution reactions with reagents like Lucas reagent, PCl5, or SOCl2 to form chloroalkanes. Haloalkanes also undergo substitution with aqueous KOH or concentrated NH3/amines to form alcohols or amines.
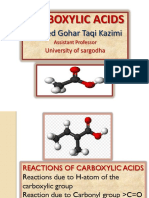
2. Acyl chlorides undergo substitution of the chloride to form carboxylic acids with water, esters with alcohols, or amides with ammonia or amines.
3. Carboxylic acids can be substituted to form acid chlorides with reagents like SOCl2 or PCl5, esters with alcohols, or amides with ammonia or amines in the presence
Original Description:
Original Title
substitution notes for students
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Alcohols can undergo substitution reactions with reagents like Lucas reagent, PCl5, or SOCl2 to form chloroalkanes. Haloalkanes also undergo substitution with aqueous KOH or concentrated NH3/amines to form alcohols or amines.
2. Acyl chlorides undergo substitution of the chloride to form carboxylic acids with water, esters with alcohols, or amides with ammonia or amines.
3. Carboxylic acids can be substituted to form acid chlorides with reagents like SOCl2 or PCl5, esters with alcohols, or amides with ammonia or amines in the presence
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views2 pagesSubstitution Notes For Students
Uploaded by
api-2185117411. Alcohols can undergo substitution reactions with reagents like Lucas reagent, PCl5, or SOCl2 to form chloroalkanes. Haloalkanes also undergo substitution with aqueous KOH or concentrated NH3/amines to form alcohols or amines.
2. Acyl chlorides undergo substitution of the chloride to form carboxylic acids with water, esters with alcohols, or amides with ammonia or amines.
3. Carboxylic acids can be substituted to form acid chlorides with reagents like SOCl2 or PCl5, esters with alcohols, or amides with ammonia or amines in the presence
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Substitution reactions (plain substitution, condensation, hydrolysis, esterification)
1. Alcohols, by Lucas reagent (3 and 2) to form a chloroalkane by or PCl5/PCl3/
SOCl2.
H3C
CH CH3
concHCl
/ ZnCl
2
OH
Lucas reagent
CH3CH2CH2OH + PCl5
2. Haloalkanes, using aqueous KOH and alcoholic/concentrated NH3/amine
Br
CH3
CH3
+KOH (aq)
CH3CH2Cl + NH3 (conc)
CH3CH2Cl + CH3NH2 (conc)
3. Acyl chlorides can react by substitution of the Cl to form
Carboxylic acids, RCOOH
esters, RCO2R
amides, RCONH2
a) CH3COCl + H2O
b) CH3COCl + CH3OH
c) CH3COCl + 2NH3
+Br
4. Carboxylic acids can react by substitution of the OH to form
acid chlorides, RCOCl (SOCl2, PCl5, PCl3)
esters, RCO2R (alcohols)
amides, RCONH2 (amine/ammonia)
a)
O
H3C
PCl 5
C
OH
b)
O
H3C
cH+
C
OH
c)
CH3OH
heat
Using ammonia AND HEAT (2 step reaction)
heat
CH3CH2CO2H + NH3
CH3CH2CO2H + NH3
d) Using amines to form Nsubstituted amides
heat
CH3CH2COOH + 2CH3NH2
CH3CH2COOH + 2CH3NH2
You might also like
- Refrigeration CyclesDocument29 pagesRefrigeration CyclesJoulie Jonsi100% (1)
- Summary of Important Organic ReactionsDocument41 pagesSummary of Important Organic ReactionsKathyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document37 pagesChapter 12Biotechnology IIUM Kuantan100% (2)
- Drug MetabolismDocument52 pagesDrug MetabolismUsman AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Guentner Subcooling EN PDFDocument18 pagesGuentner Subcooling EN PDFNotlim MarulandaNo ratings yet
- Instructions: CHE 314 - Heat Transfer Final Exam (Fall 2018), Dec. 18, 9:00am-11:00am: PavilionDocument8 pagesInstructions: CHE 314 - Heat Transfer Final Exam (Fall 2018), Dec. 18, 9:00am-11:00am: PavilionAkib ImtihanNo ratings yet
- A, K&CDocument45 pagesA, K&CDayallini Winx100% (1)
- Answers To ROH Tutorial PDFDocument12 pagesAnswers To ROH Tutorial PDFCorvo Haosen Al-Han0% (1)
- R-Cooh, R-Co H,: À Ant À VinegarDocument43 pagesR-Cooh, R-Co H,: À Ant À VinegarArvin MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid 2Document13 pagesCarboxylic Acid 2Junaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Phenol (Aromatic Alcohol) Alcohol SPDocument18 pagesChapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Phenol (Aromatic Alcohol) Alcohol SPKriti Tyagi100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry 2Document2 pagesOrganic Chemistry 2nila95No ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Revision SlideDocument51 pagesCarboxylic Acid Revision Slidejohn nashNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsDocument22 pagesAldehydes Ketones Carboxylic AcidsvenkithebossNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 12Document20 pages12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 12sangam patraNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon 4Document35 pagesHydrocarbon 4AjayNo ratings yet
- Flow Charts in Organic ChemistryDocument16 pagesFlow Charts in Organic ChemistryJessie McCartney85% (27)
- 3 Functional Groups Alcohols:: Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. KingDocument27 pages3 Functional Groups Alcohols:: Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. KingHuấnĐìnhNguyễnNo ratings yet
- Alcohols 2Document15 pagesAlcohols 2Junaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument37 pagesCarboxylic Acidaman2611994_1920111580% (5)
- Alcohols and EthersDocument51 pagesAlcohols and EthersnanaNo ratings yet
- Lec - EnolDocument46 pagesLec - EnolZamzam Siti MultazamNo ratings yet
- 10.4 Hydroxy Compounds Alcohols: Learning OutcomesDocument10 pages10.4 Hydroxy Compounds Alcohols: Learning OutcomesSaqib HussainNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument17 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsSohamNo ratings yet
- Alcohols 1630993189Document56 pagesAlcohols 1630993189Sahisa MahatNo ratings yet
- ALKANOLSDocument25 pagesALKANOLSKoki KingNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohol: Oxidation ReductionDocument18 pagesReactions of Alcohol: Oxidation ReductioncikguhafidzuddinNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Ether EpoxideDocument31 pagesAlcohol Ether EpoxideANISTHESIAHYUNI BINTI DURMAN FKJNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids NotesDocument74 pagesAldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Notessamay gujratiNo ratings yet
- Alcohols: Which of The Structures Is/are Classified As Phenols?Document7 pagesAlcohols: Which of The Structures Is/are Classified As Phenols?Kaviraj SinghNo ratings yet
- C10K Carbonyl Chemistry EmailDocument37 pagesC10K Carbonyl Chemistry EmailMatthew яeject'z BennettNo ratings yet
- I - Asam KarboksilatDocument45 pagesI - Asam KarboksilatAku Big Bos DayuNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons NotesDocument13 pagesHydrocarbons NotesShivansh Pundir100% (1)
- Carboxylic AcidDocument21 pagesCarboxylic AcidShalsabila NHNo ratings yet
- Pdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument159 pagesPdf-Haloalkanes and HaloarenesOmkar Singh Shekhawat100% (2)
- Alkene Alkyne PDFDocument45 pagesAlkene Alkyne PDFKartikeya AryaNo ratings yet
- HaloalkeneDocument20 pagesHaloalkeneRashmi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document30 pagesChapter 7Apichat Junsod100% (4)
- Carboxylic Acids:: R-Cooh, R-Co HDocument29 pagesCarboxylic Acids:: R-Cooh, R-Co HRao Wazim AkramNo ratings yet
- Organic 6 CDocument26 pagesOrganic 6 CDr.Rajarshi PatelNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Hydrocarbons Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocument20 pagesJEE Main Hydrocarbons Revision Notes - Free PDF Downloadpurple youNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt 19 20 XII Che Study Package 4 Level 1 Chapter 10Document36 pagesCLS Aipmt 19 20 XII Che Study Package 4 Level 1 Chapter 10Utkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- 7 Unit - 2 - Mod - 1 - Carboxylic - Acids - and - Derivatives PDFDocument8 pages7 Unit - 2 - Mod - 1 - Carboxylic - Acids - and - Derivatives PDFKrisNo ratings yet
- Hydroxy CompoundsDocument7 pagesHydroxy CompoundsahumanbeinginearthNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes KetonesDocument51 pagesAldehydes Ketonesadarsh mohanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6, 7 Halohydrocarbon, Alcohol, PhenolDocument89 pagesChapter 6, 7 Halohydrocarbon, Alcohol, PhenolGan Suk Ling100% (1)
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives NewDocument18 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Newxinying94No ratings yet
- 00 Perkenalan Ilmu KimiaDocument26 pages00 Perkenalan Ilmu Kimiaꓰꓡꓡꓰꓠ-ꓓꓰꓖꓰꓠꓰꓣꓰꓢꓢ.No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones For IitjeeDocument65 pagesAldehydes and Ketones For Iitjeevarundhall1994No ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and DerivativesDocument7 pagesCarboxylic Acids and DerivativesahumanbeinginearthNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes Short AnsDocument2 pagesAldehydes Short AnsMOHAMED HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties:-: Cacl CH Oh Cacl CH Oh MGCL Choh MgclchohDocument8 pagesPhysical Properties:-: Cacl CH Oh Cacl CH Oh MGCL Choh MgclchohA BeheraNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon LatestDocument23 pagesHydrocarbon LatestHimanshuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ALCOHOLDocument65 pagesChapter 1 ALCOHOLNURUL AINUN MUHAMMAD NOR100% (1)
- Alcohols, Ethers and PhenolsDocument45 pagesAlcohols, Ethers and Phenolsshivam08No ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds Xi Xii Study MaterialsDocument171 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Xi Xii Study MaterialsCristiano Hamdiansyah SempadianNo ratings yet
- 202 Practice FinalDocument4 pages202 Practice FinalElaineNo ratings yet
- Ligand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsFrom EverandLigand Platforms in Homogenous Catalytic Reactions with Metals: Practice and Applications for Green Organic TransformationsNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry Research TaskDocument4 pagesChemistry Research Taskapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Entropy Notes and Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesEntropy Notes and Exam Questionsapi-218511741100% (1)
- 2 5 Marking ScheduleDocument6 pages2 5 Marking Scheduleapi-218511741No ratings yet
- IUPAC HandoutDocument9 pagesIUPAC HandoutjanellamaikaNo ratings yet
- Eslwriting Video Worksheet CosmeticsDocument5 pagesEslwriting Video Worksheet Cosmeticsapi-2185117410% (1)
- Level 2 Basic Facts Worksheet AnswersDocument9 pagesLevel 2 Basic Facts Worksheet Answersapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Quantitative Chem Notes Titrations OnlyDocument18 pagesQuantitative Chem Notes Titrations Onlyapi-218511741No ratings yet
- First Spontaneous Reactions WorksheetDocument2 pagesFirst Spontaneous Reactions Worksheetapi-2185117410% (1)
- On WorksheetDocument2 pagesOn Worksheetapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Iron - Thiocyanate EquilibriumDocument7 pagesIron - Thiocyanate Equilibriumapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Opticalisomerism 09Document2 pagesOpticalisomerism 09api-218511741No ratings yet
- Oxidation of Organic Compounds WorksheetDocument3 pagesOxidation of Organic Compounds Worksheetapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Fats and Oils NotesDocument1 pageFats and Oils Notesapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Esterification ExperimentDocument2 pagesEsterification Experimentapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Names and Structures Small Test 2Document1 pageNames and Structures Small Test 2api-218511741No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones ExperimentDocument2 pagesAldehydes and Ketones Experimentapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Organic Names and Formula QuestionsDocument1 pageOrganic Names and Formula Questionsapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Organic Names and Formula Answers OnlyDocument1 pageOrganic Names and Formula Answers Onlyapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document17 pagesChapter 05Huan Lin100% (1)
- Unidense and UniloaderDocument5 pagesUnidense and Uniloaderarunkumar23101No ratings yet
- Me8391 Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageMe8391 Engineering ThermodynamicsAiam PandianNo ratings yet
- Chemical Changes and Reaction WorksheetDocument2 pagesChemical Changes and Reaction WorksheetriddhiNo ratings yet
- A Procedure To Obtain The Effective Nuclear Charge From The Atomic Spectrum of SodiumDocument3 pagesA Procedure To Obtain The Effective Nuclear Charge From The Atomic Spectrum of SodiumBenjamín Marc Ridgway de SassouNo ratings yet
- SEM Lab ManualDocument11 pagesSEM Lab ManualTan Hui HengNo ratings yet
- Magnesium: Current and Alternative Production Routes: August 2010Document12 pagesMagnesium: Current and Alternative Production Routes: August 2010Salem GarrabNo ratings yet
- Wollastonite IJSRET - Paper TemplateDocument4 pagesWollastonite IJSRET - Paper TemplateChidananda GNo ratings yet
- Advances in Functionalized Nanoparticles Based Drilling Inhibitors For Oil ProductionDocument12 pagesAdvances in Functionalized Nanoparticles Based Drilling Inhibitors For Oil ProductionMario Valentino DioNo ratings yet
- Complex and Protin BindingDocument11 pagesComplex and Protin BindingdhananjaylandgeNo ratings yet
- New AQA ELC Science Component 4: Chemistry in Our WorldDocument2 pagesNew AQA ELC Science Component 4: Chemistry in Our WorldChris HarrisNo ratings yet
- Artigo Macauba PCADocument14 pagesArtigo Macauba PCAjuventude JuventudePIBFNo ratings yet
- Creatinine: Kinetic MethodDocument2 pagesCreatinine: Kinetic MethodVenura VishwajithNo ratings yet
- Lipid Analysis: Melisa Intan BarlianaDocument38 pagesLipid Analysis: Melisa Intan BarlianaChantique Maharani0% (1)
- Advanced Separation ProcessesDocument33 pagesAdvanced Separation Processesعمار ياسر50% (2)
- EAMCET-QR-Chemistry-Jr Chem-2.Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument13 pagesEAMCET-QR-Chemistry-Jr Chem-2.Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Propertiespvnchem100% (1)
- Module 6-7Document2 pagesModule 6-7Duchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- Chen 1994Document6 pagesChen 1994ZhalaNo ratings yet
- Cyanexpert 130: Application SheetsDocument55 pagesCyanexpert 130: Application Sheets林圣贺No ratings yet
- Heat - Thermodynamics Virtual Lab - Physical Sciences - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual LabDocument1 pageHeat - Thermodynamics Virtual Lab - Physical Sciences - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual LabjeroldscdNo ratings yet
- Role of RDF in SDGsDocument16 pagesRole of RDF in SDGsANo ratings yet
- Chemcad KilnDocument9 pagesChemcad Kilningbarragan87No ratings yet
- FFPMDocument171 pagesFFPMGulyam Maribasappa Rajendra PrasadNo ratings yet
- Science 5-1st QUARTER-DISTRICT-SUMMATIVE-ASSESSMENT-TESTDocument4 pagesScience 5-1st QUARTER-DISTRICT-SUMMATIVE-ASSESSMENT-TESTMayien Tatoy JubanNo ratings yet
- Summary Cube Test As of 07052019 (Nehemiah Wall)Document6 pagesSummary Cube Test As of 07052019 (Nehemiah Wall)Mohd Musa HashimNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document30 pagesCH 7Eman AlbastawyNo ratings yet