Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alginate: Anionic Polysaccharide Cell Walls Brown Algae Gum
Uploaded by
Rizky Ds0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pagetest
Original Title
7. Alginate
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenttest
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageAlginate: Anionic Polysaccharide Cell Walls Brown Algae Gum
Uploaded by
Rizky Dstest
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Blandina FT5(14212019)
Food Processing Tech.
Alginate
Alginic acid, also called algin or alginate, is an anionic polysaccharide distributed
widely in the cell walls of brown algae, where through
binding with water it forms a viscous gum. In extracted
form it absorbs water quickly; it is capable of absorbing
200-300 times its own weight in water. Its color ranges
from white to yellowish-brown. It is sold in filamentous,
granular or powdered forms.
Alginates are refined from brown seaweeds. A wide variety
of
brown seaweeds of
the
phylum Phaeophyceae are
harvested throughout the world to be converted into the
raw material commonly known as sodium alginate.
Sodium alginate has a wide use across a wide variety of
industries including food, textile printing & pharmaceutical.
Dental impression material utilizes alginate as its means of
gelling. Alginate is both food and skin safe.
Alginates from different species of brown seaweed often
have variations in their chemical structure, resulting in
different physical properties. For example, some may yield
an alginate that gives a strong gel, another weaker gel; one
may readily give a cream/white alginate, another may give
that only with difficulty and is best used for technical
applications where color does not matter.
One of the product use sodium alginate is alginate beads
(calcium Alginate) which created through the addition of aqueous calcium chloride to
aqueous sodium alginate. It is a water-insoluble, gelatinous substance.
This usually use for beverage, appetizers, dessert and
topping which already added by coloring or flavor. Beside
that it can also use as enzyme package when through
catalytic reaction, so the enzyme are easily take back
again after reaction with substrate.
You might also like
- SeaweedDocument150 pagesSeaweedصالحة باوزير100% (2)
- The Flight of The BumblebeeDocument2 pagesThe Flight of The BumblebeeEmanuele Bracchi100% (1)
- Suppository 121004132503 Phpapp01Document60 pagesSuppository 121004132503 Phpapp01نور الهدىNo ratings yet
- Thickeners and EmulsifiersDocument31 pagesThickeners and EmulsifiersVanshika Srivastava 17IFT017No ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature and Studies: On The Development of Kamias-Katmon ProductsDocument24 pagesReview of Related Literature and Studies: On The Development of Kamias-Katmon ProductsKimNo ratings yet
- Agar ExtractionDocument11 pagesAgar ExtractionGibran Muhammad Tri RahmawanNo ratings yet
- Economic Importance of AlgaeDocument49 pagesEconomic Importance of Algaesantanu rana100% (1)
- Alginat de SodiuDocument3 pagesAlginat de SodiuRoxana NegruNo ratings yet
- Economic Importance of Algae 1Document13 pagesEconomic Importance of Algae 1yamuna veniNo ratings yet
- Algae in Our LifeDocument7 pagesAlgae in Our LifesureshNo ratings yet
- Sodium AlginateDocument1 pageSodium AlginateCyril Amar SencilNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Formulation: Preparation of SuppositoryDocument52 pagesIntroduction and Formulation: Preparation of SuppositoryImam BisriNo ratings yet
- Effect of Alcohol On Gellan GumDocument2 pagesEffect of Alcohol On Gellan GumajaykhortNo ratings yet
- AgarDocument8 pagesAgarPiyush RathourNo ratings yet
- Adulterants Used in Carbohydrates CognosyDocument8 pagesAdulterants Used in Carbohydrates CognosyTanmay WalunjNo ratings yet
- Alginatos DaniscoDocument4 pagesAlginatos DaniscoPaul AgudeloNo ratings yet
- 6 AgarDocument3 pages6 AgarANUMAY PANDANo ratings yet
- Algae WorksheetDocument2 pagesAlgae WorksheetNobleMathewsNo ratings yet
- Alginates PDFDocument20 pagesAlginates PDFliaNo ratings yet
- Alginates PDFDocument20 pagesAlginates PDFDaniel Antonio Aguilera BullaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Uses of AlgaeDocument22 pagesLesson 5 - Uses of AlgaeIonela ConstandacheNo ratings yet
- Alginate Fiber SpeechDocument6 pagesAlginate Fiber SpeechTawfiq Hossain KhanNo ratings yet
- Economic Importance of AlgaeDocument9 pagesEconomic Importance of AlgaeYedhu KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Economic Importance - AlgaeDocument39 pagesEconomic Importance - AlgaeSteveNo ratings yet
- (9 MABINI) Group 2 Presentation-WPS OfficeDocument52 pages(9 MABINI) Group 2 Presentation-WPS OfficeRussel LabusanNo ratings yet
- Aureobasidium: Characteristics of The GenusDocument5 pagesAureobasidium: Characteristics of The GenusIcha ChairunNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Aids From Natural SourcesDocument36 pagesPharmaceutical Aids From Natural SourcesHarish Kakrani100% (7)
- GelatinDocument18 pagesGelatinAiman MeerNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Economic Imp. of AlgaeDocument5 pagesModule 1 Economic Imp. of AlgaeNimya BabuNo ratings yet
- Agar AgarDocument9 pagesAgar AgarDieudonné TerteongNo ratings yet
- FarmakognosiDocument13 pagesFarmakognosiDewi MagistasariNo ratings yet
- Catalog AlphaseaweedDocument17 pagesCatalog AlphaseaweedSonia Oktavia MargaretaNo ratings yet
- Week 14Document3 pagesWeek 14Lebanan Aprille MarieNo ratings yet
- Thickening and Gelling AgentsDocument10 pagesThickening and Gelling AgentsHemasriNo ratings yet
- Research On ColloidsDocument4 pagesResearch On ColloidsJunyvil TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy PDFDocument206 pagesPharmacognosy PDFJunelle CostesNo ratings yet
- Discuss On The Topic Alage Are Harmful and BeneficialDocument8 pagesDiscuss On The Topic Alage Are Harmful and Beneficialeunice osei owusuNo ratings yet
- Guso (Eucheuma SP.) Ice Cream Enhanced With Blue TernateDocument10 pagesGuso (Eucheuma SP.) Ice Cream Enhanced With Blue TernateMamta AgarwalNo ratings yet
- CarrageenanDocument7 pagesCarrageenanpdekraaijNo ratings yet
- Alland Robert Technical+Paper+Fibres Size+small4Document6 pagesAlland Robert Technical+Paper+Fibres Size+small4Elli SiosonNo ratings yet
- Lect 5 Inulin & DextrinDocument5 pagesLect 5 Inulin & Dextrinahsanonweb1983100% (1)
- Functions and Uses of Different SeaweedsDocument11 pagesFunctions and Uses of Different Seaweedsbabyln oronanNo ratings yet
- EMMANUEL KIPKOECH (Autosaved) .DocxaDocument8 pagesEMMANUEL KIPKOECH (Autosaved) .DocxaEdward MuiruriNo ratings yet
- UNIT IV - Bitters N SweetnersDocument30 pagesUNIT IV - Bitters N Sweetnersshweta tyagiNo ratings yet
- Development of Aquatic Functional FeedDocument3 pagesDevelopment of Aquatic Functional FeedAung Thu PhyoNo ratings yet
- Kelps AS Commercial Algae: Seminar On Phycology (Bom 101)Document10 pagesKelps AS Commercial Algae: Seminar On Phycology (Bom 101)shemphang mawrieNo ratings yet
- Ashvini Finance Cash Flow Statment For Narmada Gilatines, JabalpurDocument43 pagesAshvini Finance Cash Flow Statment For Narmada Gilatines, JabalpurAshwani KhatriNo ratings yet
- Jojs MS Id 555579Document7 pagesJojs MS Id 555579Ve LinNo ratings yet
- AMPALAYADocument6 pagesAMPALAYACamille SudarioNo ratings yet
- Economic Importance of AlgaeDocument53 pagesEconomic Importance of Algaesiddharthsharma0212No ratings yet
- Gelatin PDFDocument11 pagesGelatin PDFumn581No ratings yet
- Acharya N. G. Ranga Agricultural UniversityDocument7 pagesAcharya N. G. Ranga Agricultural UniversityPhanisreeNo ratings yet
- Assignment Gelatin PDFDocument17 pagesAssignment Gelatin PDFWayMeen Pang0% (1)
- Jurnal Internasional Uji KatalaseDocument13 pagesJurnal Internasional Uji KatalaseIka Dewi AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Plant Gums PDFDocument5 pagesPlant Gums PDFmanoj_rkl_07100% (1)
- The Use of Aloe Vera in Shelf Life Extension of Fresh FruitsDocument4 pagesThe Use of Aloe Vera in Shelf Life Extension of Fresh FruitsKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Research in PhysicsDocument9 pagesResearch in PhysicsMyla Riza Sintones NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Tekpang HalalDocument12 pagesTekpang HalalNindya SulistyaniNo ratings yet
- Adeyemo & Onilude, 2014Document7 pagesAdeyemo & Onilude, 2014Neeraj VermaNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Purpose: Something HereDocument7 pages1.1. Purpose: Something HereRizky DsNo ratings yet
- COS 495 - Lecture 5 Autonomous Robot Navigation: Instructor: Chris Clark Semester: Fall 2011Document30 pagesCOS 495 - Lecture 5 Autonomous Robot Navigation: Instructor: Chris Clark Semester: Fall 2011flv_91No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - System Engineering - Neural Network Based Path Planning For Mecanum Wheeled Omni Directional RobotDocument12 pagesAssignment 1 - System Engineering - Neural Network Based Path Planning For Mecanum Wheeled Omni Directional RobotRizky DsNo ratings yet
- 56789Document23 pages56789Rizky DsNo ratings yet
- Teamviewer ManualDocument76 pagesTeamviewer ManualRehab WahshNo ratings yet
- Suspension System: Presented By: Enzo Oestanto Mochammad Rizky DiprasetyaDocument10 pagesSuspension System: Presented By: Enzo Oestanto Mochammad Rizky DiprasetyaRizky DsNo ratings yet
- PAPERDocument5 pagesPAPERRizky DsNo ratings yet
- Managing and Specifying Microcontroller Projects: Harold ConveyDocument78 pagesManaging and Specifying Microcontroller Projects: Harold ConveyRizky DsNo ratings yet
- Modelling Electromagnetic Suspension Force Using Measured Inductance-Airgap DataDocument4 pagesModelling Electromagnetic Suspension Force Using Measured Inductance-Airgap DataRizky DsNo ratings yet
- Uni SushiDocument2 pagesUni SushiRizky DsNo ratings yet
- Modelling Electromagnetic Suspension Force Using Measured Inductance-Airgap DataDocument4 pagesModelling Electromagnetic Suspension Force Using Measured Inductance-Airgap DataRizky DsNo ratings yet
- Tugas Eleng JumatDocument7 pagesTugas Eleng JumatRizky DsNo ratings yet
- Thesis Mochammad Rizky DiprasetyaDocument125 pagesThesis Mochammad Rizky DiprasetyaRizky DsNo ratings yet
- SL GsDocument80 pagesSL GsRizky DsNo ratings yet
- Thesis Prototype SOP v1Document1 pageThesis Prototype SOP v1Rizky DsNo ratings yet
- Beer and Its Production - NewaDocument13 pagesBeer and Its Production - NewaRizky DsNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 (MT) - Quiz 1a - SolutionDocument5 pagesPhysics 2 (MT) - Quiz 1a - SolutionRizky DsNo ratings yet
- Lirik Run Devil RunDocument2 pagesLirik Run Devil RunRizky DsNo ratings yet
- MicroC2 eCh09L05AssemProgTimersDocument32 pagesMicroC2 eCh09L05AssemProgTimersRizky DsNo ratings yet
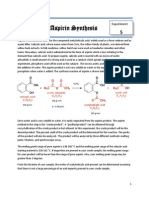
- Exp 5 - AspirinF11Document5 pagesExp 5 - AspirinF11Rizky DsNo ratings yet
- FXCM Micro New To Forex GuideDocument27 pagesFXCM Micro New To Forex GuideRizky DsNo ratings yet
- Lecture05 - Electric Current and DC CircuitDocument31 pagesLecture05 - Electric Current and DC CircuitRizky DsNo ratings yet
- Lirik Blue TomorrowDocument2 pagesLirik Blue TomorrowRizky DsNo ratings yet