Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sphenoid Bone Description
Uploaded by
Georgina CarterOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sphenoid Bone Description
Uploaded by
Georgina CarterCopyright:
Available Formats
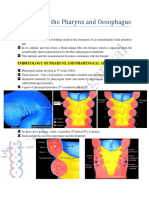
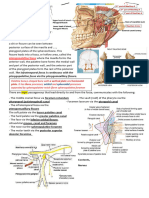
Landmarks and features of the Sphenoid bone
The sphenoid bone is a bat or butterfly shaped bone (coming from the
Greek word sphenoeides meaning wedge-shaped) that articulates
with both cranial and facial bones, including the occipital, temporal,
parietal, and frontal bones in the cranium and the zygomatic, palatine,
maxilla, and vomer facial bones. The sphenoid has lesser and greater
wings; the greater wings extend laterally from the body while the
lesser wings extend on the anterior surface from the body. From the
inside of the skull, you can see that the body of the sphenoid is
grooved by the pituitary fossa (sella turcica) that is bordered by the
dorsum sellae inferiorly and the tuberculum sellae superiorly. The optic
groove runs superior to the body and contains the optic canal, which is
also within the lesser wing of the sphenoid. The lesser wing of the
sphenoid forms part of the floor of the anterior cranial fossa, and its
medial end is the anterior clinoid process. Between the greater wing
and the lesser wing of the sphenoid is the superior orbital fissure, and
within the greater wing of the sphenoid one can see the foramen
rotundum, foramen ovale, and foramen spinosum. The greater wing of
the sphenoid can be seen on the lateral view of the skull, on the floor
of the temporal fossa.
Anteriorly the foramen rotundum opens into the pterygopalatine fossa.
The pterygopalatine fossa is a hidden region of the skull and can only
be seen from the side, in a fissure between the lateral pterygoid plate
and the maxilla. The sphenoid is also composed of two pterygoid
processes each with two pterygoid plates, the medial pterygoid plate
and the lateral pterygoid plate. The pterygoid plates are attachment
sites for muscles that move the mandible. The medial pterygoid plate
had a pterygoid hamulus inferiorly and a scaphoid fossa superiorly.
Within the body of the sphenoid there are two sphenoidal air sinuses
that are separated by a septum, usually off the midline. The basi
sphenoid articulates with the basi occipate, the articulation fuses at
about 15 years of age. The sphenoid has a spine that can be seen in
the infratemporal fossa.
You might also like
- Anatomy of The HeadDocument24 pagesAnatomy of The HeadAbdul Nasifh Bn Hamsa100% (1)
- The Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormFrom EverandThe Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Block Based LearningDocument12 pagesBlock Based LearningRevathi DadamNo ratings yet
- Found 903118732 4683Document2 pagesFound 903118732 4683Bogdan Robert CNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Cranial Base: SeminarDocument34 pagesGrowth and Development of Cranial Base: SeminarMNSNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Human Anatomy Dr. Mohammed WasnanDocument12 pagesLecture 4 Human Anatomy Dr. Mohammed Wasnanspo9equtabaNo ratings yet
- The Bones in The Neurocranium: David Terfera Shereen Jegtvig Clinical Anatomy For DummiesDocument25 pagesThe Bones in The Neurocranium: David Terfera Shereen Jegtvig Clinical Anatomy For DummiesFrozen Pandora MahayaNo ratings yet
- Sphenoid BoneDocument76 pagesSphenoid BoneLALITH SAI KNo ratings yet
- The Endoskeleton of Birds.Document29 pagesThe Endoskeleton of Birds.Ian LasarianoNo ratings yet
- Lec 6 Anatomy First StageDocument36 pagesLec 6 Anatomy First Stagespo9equtabaNo ratings yet
- ЧерепDocument34 pagesЧерепbekafop813No ratings yet
- 06 Lec 11 12 Anatomy First YearDocument13 pages06 Lec 11 12 Anatomy First YearS:M:ENo ratings yet
- Skeletal System4Document1 pageSkeletal System4Elisha DienteNo ratings yet
- Middle Cranial FossaDocument5 pagesMiddle Cranial Fossaalexandra663No ratings yet
- Anatomy 2-1 - Lecture One (HEAD & NECK)Document21 pagesAnatomy 2-1 - Lecture One (HEAD & NECK)Abod AbodNo ratings yet
- Cavities of The Neuro and ViscerocraniumDocument79 pagesCavities of The Neuro and ViscerocraniumSchönberger AlbertNo ratings yet
- Bones and Cartilages of The Head and NeckDocument27 pagesBones and Cartilages of The Head and Neckyachiru121100% (1)
- Lecture Medskull - ModofiedDocument88 pagesLecture Medskull - ModofiedNikolai SamaniegoNo ratings yet
- ანატომია ზეპირიDocument22 pagesანატომია ზეპირიmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Anatomy First YearDocument8 pagesLecture 7 Anatomy First Yearspo9equtabaNo ratings yet
- Axial Skeleton ScriptDocument4 pagesAxial Skeleton ScriptMichaelVincentLimNo ratings yet
- Basic anatomy and respiratory system overviewDocument10 pagesBasic anatomy and respiratory system overviewRick DasNo ratings yet
- Pharynx Anatomy - Overview, Gross Anatomy, Microscopic AnatomyDocument9 pagesPharynx Anatomy - Overview, Gross Anatomy, Microscopic AnatomyCarmen-BadeaNo ratings yet
- The Cranial BoneDocument13 pagesThe Cranial BoneSondos HarbiehNo ratings yet
- The Orbit and Eye: Anatomy and FunctionsDocument12 pagesThe Orbit and Eye: Anatomy and FunctionsOjambo FlaviaNo ratings yet
- Axial Skeleton Second LectureDocument23 pagesAxial Skeleton Second LectureRichard BidalNo ratings yet
- Anatomia - Prof. Ibrahim Behluli PDFDocument222 pagesAnatomia - Prof. Ibrahim Behluli PDFRinor Mujaj100% (10)
- Interior of SkullDocument11 pagesInterior of SkullUnaiza Siraj100% (1)
- Found 903128372 4535Document2 pagesFound 903128372 4535Bogdan Robert CNo ratings yet
- The Axial Skeleton: Structure and FunctionDocument18 pagesThe Axial Skeleton: Structure and FunctionRaiza Abegail RoxasNo ratings yet
- A Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)From EverandA Guide for the Dissection of the Dogfish (Squalus Acanthias)No ratings yet
- Anatomy of the Pharynx and Oesophagus EmbryologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy of the Pharynx and Oesophagus EmbryologyBkas GrgNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of the Pharynx and Oesophagus EmbryologyDocument12 pagesAnatomy of the Pharynx and Oesophagus EmbryologyArjun SainiNo ratings yet
- Pterygd and OrbitDocument10 pagesPterygd and OrbitAmbg GhalyNo ratings yet
- Skull BonesDocument79 pagesSkull BonesJennifer FirestoneNo ratings yet
- Anatomia TemporalDocument17 pagesAnatomia TemporalClaudia HeiderNo ratings yet
- Anterior and Posterior Petrosectomy Seminar 13 Jan 2021 DR Abhinav 2Document76 pagesAnterior and Posterior Petrosectomy Seminar 13 Jan 2021 DR Abhinav 2Tamajyoti GhoshNo ratings yet
- Temporal Bone RadioantomyDocument43 pagesTemporal Bone RadioantomyRavindra MuzaldaNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy - 9Document2 pagesGeneral Anatomy - 9ayaaqassimalmodafarNo ratings yet
- The SkullDocument28 pagesThe SkullAyethNo ratings yet
- Skull VaultDocument31 pagesSkull VaultMEME KA GHANTANo ratings yet
- Chapter 139 Anatomy of The Skull Base Temporal Bone External Ear and Middle Ear Larry G Duckert - CompressDocument12 pagesChapter 139 Anatomy of The Skull Base Temporal Bone External Ear and Middle Ear Larry G Duckert - CompressWudieNo ratings yet
- AnaphylabDocument5 pagesAnaphylabAnne Denise ArenasNo ratings yet
- The Foramen Magnum: Albert L. Rhoton, JR., M.DDocument39 pagesThe Foramen Magnum: Albert L. Rhoton, JR., M.Dbodeadumitru9261100% (1)
- THE HUMAN SKELETONDocument24 pagesTHE HUMAN SKELETONIza ShaNo ratings yet
- 28 Temporal Bone (Done)Document7 pages28 Temporal Bone (Done)Ayah HyasatNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Solomon Adane (MSC.)Document43 pagesPrepared By: Solomon Adane (MSC.)AmanuelNo ratings yet
- Skull Bones GuideDocument17 pagesSkull Bones Guideمدونة الأحترافNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument15 pagesAnatomyAdeleye John AdebolaNo ratings yet
- 02 SkullDocument19 pages02 Skullapi-19641337No ratings yet
- Head and NeckDocument63 pagesHead and Neckbayenn100% (1)
- KOSTI GLAVE - DETALJAN PREGLED ANATOMIJE LOBANJE I KOSTIJU LICADocument30 pagesKOSTI GLAVE - DETALJAN PREGLED ANATOMIJE LOBANJE I KOSTIJU LICAJohn PaulisNo ratings yet
- Telencephalon - General OrganizationDocument23 pagesTelencephalon - General OrganizationMirko BelanNo ratings yet
- Calvaria: Bones of The CalvariaDocument4 pagesCalvaria: Bones of The CalvariaAnnisa SafiraNo ratings yet
- 2020 03 13 PW5 TRHN - Frontal and Orbital RegionDocument25 pages2020 03 13 PW5 TRHN - Frontal and Orbital Regionmohammad ahmedNo ratings yet
- Bones of The CraniumDocument15 pagesBones of The Craniumhosam ahmedNo ratings yet
- Canals, Fissures, and Foramina of Cranial Bones: Orbital RegionDocument7 pagesCanals, Fissures, and Foramina of Cranial Bones: Orbital RegionGhaidaa SadeqNo ratings yet
- A New Species of Heteromyid Rodent from the Middle Oligocene of Northeast Colorado with Remarks on the SkullFrom EverandA New Species of Heteromyid Rodent from the Middle Oligocene of Northeast Colorado with Remarks on the SkullNo ratings yet