Professional Documents
Culture Documents
11 Commonly-Performed Tests For Urinalysis
Uploaded by
bluetealOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
11 Commonly-Performed Tests For Urinalysis
Uploaded by
bluetealCopyright:
Available Formats
11 commonly-performed tests for urinalysis
1. pH
Measure of acid-base balance in urine
Can be affected by certain treatments or diet
Normal pH: 5.5-6.5
High pH: vegetarian diet
Low pH: starvation (fats metabolism produces acidic ketone bodies)
2. Specific gravity
Measure the osmolality of urine
Shows how well the kidneys balance the amount of water in urine
High SG: dehydration
Low SG: kidney problems (glomerular nephritis or diabetes insipidus. Unable to
concentrate urine)
3. Total proteins
Normally not found in urine
Conditions like haemolysis, pregnancy and certain diseases (chronic renal failure, UT
inflammation) cause proteinuria
Chronic renal failure cause increase in blood pressure due to damaged glomerulus
4. Blood
Not found in urine normally
Presence indicate menses, kidney injury, obstruction of urine formation/excretion
5. Haemoglobin
Used to detect hemoglobin in the urine (hemoglobinuria)
Presence indicates blood in urine (hematuria) which is not normal
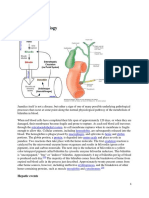
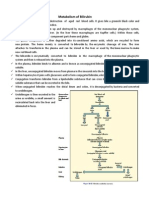
6. Bilirubin
Waste product from the breakdown of haemoglobin
Not present in urine normally
Presence indicates haemolytic anaemia or liver disease where bilirubin leak back into
bloodstream and excreted in urine
Pre-hepatic
o Increase in bilirubin-brought to liver for conjugation-brought to small intestineincrease in urobillinogen
Hepatic
o Bilirubin leak into bloodstream-brought to liver-decrease in urobillinogen
Post-hepatic
o Breakdown of Hb release Haem- converted to bilirubin-accumulate in livercannot be brought to small intestine-enter kindeys-increase levels in urine
7. Urobillinogen
Formed from bilirubin in intestines with small amounts being absorbed into bloodstream
Normally present in urine in low concentrations
Positive results indicates liver disease
8.
Leukocytes
Produce esterase that can be detected by dipstick
Not found in urine normally
Presence indicates infection (UTI) or kidney disease
9. Glucose
Little or no glucose found in urine normally
Presence (glucosuria) indicates diabetes mellitus or kidney damage/disease
Diabetes cause increase in glucose levels that exceed threshold of kidneys. Spill
into urine
10. Ketones
Intermediate products of fat metabolism
Not found in urine normally
Presence indicates starvation, malfunction in carbohydrate utilization, or insufficient
insulin (diabetic patients)
Insufficient insulin=no glucose to be converted into energy for cellular aerobic
glycolysis
11. Nitrites
Presence indicates UTI or sample contamination
Many Gram-negative bacteria can convert nitrate to nitrite
You might also like
- Med Geeks Clinical Lab GuideDocument17 pagesMed Geeks Clinical Lab GuideHuy Hoang100% (1)
- 15 Coned CCRN GastrointestinalDocument21 pages15 Coned CCRN GastrointestinalAkbar TaufikNo ratings yet
- Clinical Lab Guide: by MedgeeksDocument17 pagesClinical Lab Guide: by MedgeeksHuy HoangNo ratings yet
- Urine AND Feces: Prepared By: Group 5Document37 pagesUrine AND Feces: Prepared By: Group 5Chantal RaymondsNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandLiver Cirrhosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis PDFDocument56 pagesUrinalysis PDFTio AjhaNo ratings yet
- Urine Analysis PracticalDocument53 pagesUrine Analysis PracticalMubasharAbrar100% (2)
- Fatty Liver Diet Cookbook: Triumph Over FLD and Hepatic Steatosis with Scrumptious Low-Fat Recipes, Harness Your Metabolism, and Embrace a Swell-Free Life Naturally [II EDITION]From EverandFatty Liver Diet Cookbook: Triumph Over FLD and Hepatic Steatosis with Scrumptious Low-Fat Recipes, Harness Your Metabolism, and Embrace a Swell-Free Life Naturally [II EDITION]Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (7)
- Clinical Significance of Bilirubin in Liver Function TestsDocument24 pagesClinical Significance of Bilirubin in Liver Function TestsAbdulsalam JumaiNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis TableDocument9 pagesUrinalysis TableMegNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests (Sem)Document6 pagesLiver Function Tests (Sem)Francisco NiegasNo ratings yet
- Total Protein Albumin + Globulins (Ig, Complements, Fibrinogen, A1-Antrypsin Etc)Document4 pagesTotal Protein Albumin + Globulins (Ig, Complements, Fibrinogen, A1-Antrypsin Etc)bryan chan100% (1)
- Urine AnalysisDocument69 pagesUrine Analysisvinay0717100% (3)
- Lets Get Started - Urinalysis PDFDocument3 pagesLets Get Started - Urinalysis PDFSatya PramanaNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument29 pagesJaundiceMurali TiarasanNo ratings yet
- Clin Path Trans 3.05 Urinalysis (2b)Document6 pagesClin Path Trans 3.05 Urinalysis (2b)Reymart FernandezNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary System Functions of The Liver IncludeDocument19 pagesHepatobiliary System Functions of The Liver IncludeRacha MougharbelNo ratings yet
- Liver Disease Study GuideDocument11 pagesLiver Disease Study GuideLauren OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Presentation JaundiceDocument49 pagesPresentation JaundiceVinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- Jaundice in Adults: Manifestations of Liver DiseaseDocument5 pagesJaundice in Adults: Manifestations of Liver DiseaseClarithq LengguNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Hepato-Biliary SystemDocument30 pagesDiseases of Hepato-Biliary SystemRupak PandeyNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument4 pagesJaundiceShubhamNo ratings yet
- Liver Funection TestDocument33 pagesLiver Funection TestDjdjjd SiisusNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary Diseases 3Document28 pagesHepatobiliary Diseases 3AmirahNo ratings yet
- Pathological Urine: Physical Examination of UrineDocument8 pagesPathological Urine: Physical Examination of UrineOLUWASEGUN K AfolabiNo ratings yet
- Hepatic CirrhosisDocument12 pagesHepatic CirrhosisFaye Mie VelascoNo ratings yet
- Liver MarkersDocument4 pagesLiver MarkerslucaNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis 2Document6 pagesUrinalysis 2Reygie MataNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis Pre LabDocument6 pagesUrinalysis Pre LabbobbyNo ratings yet
- Urine AnalysisDocument53 pagesUrine AnalysisMaath KhalidNo ratings yet
- Jaundice 121213125330 Phpapp01Document29 pagesJaundice 121213125330 Phpapp01ARUSHI ARVINDNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Abnormal Urine NotesDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Abnormal Urine Notesahteshammirji575No ratings yet
- Metabolism of BilirubinDocument3 pagesMetabolism of BilirubinEris Abdul Aziz100% (1)
- Bile Production - Constituents - TeachMePhysiologyDocument2 pagesBile Production - Constituents - TeachMePhysiologynotesom44No ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of JaundiceDocument4 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of JaundiceVirag PatilNo ratings yet
- Reagent StripDocument7 pagesReagent Stripromerodion71No ratings yet
- Liver Panel: EM 6203 Dr. K. AikenheadDocument24 pagesLiver Panel: EM 6203 Dr. K. AikenheadCrystal Lynn Keener SciariniNo ratings yet
- Jaundice: Prepared By: Ozhen ArasDocument29 pagesJaundice: Prepared By: Ozhen ArasAzizul HalidNo ratings yet
- Urine Examination New-1Document81 pagesUrine Examination New-1H GondaliyaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - The LiverDocument66 pagesPathophysiology - The LiverMichelle BilayaNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests - Level II Students - 17 June 2008Document10 pagesLiver Function Tests - Level II Students - 17 June 2008safemindNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On - Jaundice NewDocument50 pagesCase Presentation On - Jaundice NewSara NoorNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of The Liver: GlossaryDocument21 pagesCirrhosis of The Liver: GlossaryNophNo ratings yet
- UrinalysisDocument4 pagesUrinalysisNur Ain Che Muda100% (1)
- Analysis of Abnormal UrineDocument12 pagesAnalysis of Abnormal Urinesingonstrings365No ratings yet
- JAUNDICE Group Work. FinalDocument27 pagesJAUNDICE Group Work. FinalNambuye Midyero AhmedNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis Diagnostic Test and Differential DiagnosisDocument21 pagesViral Hepatitis Diagnostic Test and Differential DiagnosisNedeln AudleyNo ratings yet
- Urine Analysis Lab ConDocument13 pagesUrine Analysis Lab ConChristineAla63% (8)
- Chemical Examination of UrineDocument46 pagesChemical Examination of UrineH GondaliyaNo ratings yet
- BilirubinDocument2 pagesBilirubinZukhruful MuzakkieNo ratings yet
- Lect. 8Document30 pagesLect. 8jayNo ratings yet
- Biochem FecalysisDocument5 pagesBiochem FecalysisDonna DominnoNo ratings yet
- UrineDocument17 pagesUrinealynne_pascua8530No ratings yet
- MedSurg NotesDocument21 pagesMedSurg NotesShanny BNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology 3-6 UrinalysisDocument3 pagesClinical Pathology 3-6 UrinalysisAndrew KalawNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument4 pagesJaundiceAbo Omar Ahmed100% (1)
- Urea/ Ammonia Tests: Primary Liver Function TestsDocument6 pagesUrea/ Ammonia Tests: Primary Liver Function TestsMemory MahwendaNo ratings yet
- Liver PathologyDocument35 pagesLiver Pathologynhgwdwffp2No ratings yet
- Estu LBM 2Document12 pagesEstu LBM 2Roby SandeiaNo ratings yet







![Fatty Liver Diet Cookbook: Triumph Over FLD and Hepatic Steatosis with Scrumptious Low-Fat Recipes, Harness Your Metabolism, and Embrace a Swell-Free Life Naturally [II EDITION]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/598276019/149x198/1b7a1779c0/1711328726?v=1)