Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vehicle Propulsion by Pulse-Jet Engine
Uploaded by
Chiranjeevi Dakshina Murthy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views11 pagesnice ppt
Original Title
Vehicle Propulsion by Pulse-jet Engine
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentnice ppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views11 pagesVehicle Propulsion by Pulse-Jet Engine
Uploaded by
Chiranjeevi Dakshina Murthynice ppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
VEHICLE PROPULSION BY PULSE JET
ENGINE
UNDER THE GUIDANCE OF PROF.K.BALA SHOWRY
PRINCIPAL
M.TECH,PH.D
V C A D MURTHY(345)
A V RAVITEJA(348)
S RAJESH GOUD(339)
BHUVAN CHAND(306)
What is Project PulseJet?
Type ofjet enginewhere combustion occurs inpulses.
Pulse jet engines have few or nomoving parts.
They are capable of running statically.
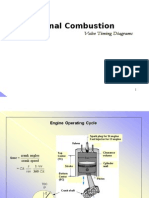
WORKING PRINCIPLE
Operation similar to modern reciprocating engine.
Defined cycles : suction of air/fuel mixture, compression, ignition
and exhaust.
First stage : ignition of a fuel/air charge
Cumbustion/ power stage:Hot gases expand rapidly, increasing
the pressure greater than atmospheric pressure.
partial vacuum is formed behind the rapidly
escaping exhaust gases.
This
draws fresh fuel/air mixture into the engine.
At
the same time, a small proportion of exhaust
gases lose momentum due to pressure difference.
This
piston of hot gases compresses the fresh
charge and ignites it.
LOCKWOOD HILLER DESIGN
COMBUSTION CYCLE
CUT OPEN FIGURES
THERMODYNAMIC CYCLE
TheLenoir cycleis an idealized thermodynamic cycleoften
used to model
apulse-jet engine.
Comprises of 3 cycles:
Heat added at constant
volume.
Adiabatic Expansion.
Exhaust of the hot gasses
at a constant pressure.
FUEL
Runs on most commercially available fuels.
Liquid fuels need to be pumped and vapourized.
Gaseous fuels fed from the cylinder under pressure and the fuel
flow regulation also easy.
Use of a gaseous fuel would facilitate direct injection without
vaporization.
Propane is usually preferred due to its high energy density (50
MJ/kg).
PJ ENGINE AFTER ROLLING
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Otto CycleDocument16 pagesOtto CycleSwati MadanNo ratings yet
- The Petrol Engine: A Text-book dealing with the Principles of Design and Construction, with a Special Chapter on the Two-stroke EngineFrom EverandThe Petrol Engine: A Text-book dealing with the Principles of Design and Construction, with a Special Chapter on the Two-stroke EngineNo ratings yet
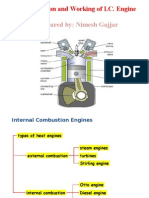
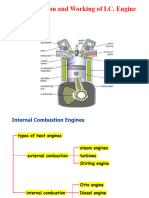
- Prepared By: Nimesh Gajjar: Construction and Working of I.C. EngineDocument68 pagesPrepared By: Nimesh Gajjar: Construction and Working of I.C. EngineTanpaNamaNo ratings yet
- Basic of EngineDocument68 pagesBasic of EngineJoshNo ratings yet
- 4 Stroke Petrol EngineDocument11 pages4 Stroke Petrol EngineAnkit Joshi50% (4)
- Four-stroke engine basicsDocument8 pagesFour-stroke engine basicsVamsidhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- ICE EngineDocument102 pagesICE EngineyanNo ratings yet
- 2 Stroke 4 StrokeDocument32 pages2 Stroke 4 StrokeCyrus TaclobNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Tumble Motion in Engines Through SimulationDocument8 pagesAnalyzing Tumble Motion in Engines Through SimulationLorant BordasNo ratings yet
- Ic Engines: Four Stroke Cycle Diesel EnginesDocument11 pagesIc Engines: Four Stroke Cycle Diesel Enginesmechjobs4meNo ratings yet
- Indivual Report ME372Document10 pagesIndivual Report ME372محمد MqNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: SOLOMON RAJA: Construction and Working of I.C. EngineDocument68 pagesPrepared By: SOLOMON RAJA: Construction and Working of I.C. EnginesolomonrajarNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine Fundamentals GuideDocument23 pagesDiesel Engine Fundamentals GuideAjaykuamrNo ratings yet
- Introduction and HistotricalDocument44 pagesIntroduction and HistotricalTesfahun TegegneNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine - FundamentalDocument20 pagesDiesel Engine - FundamentalSoumen BhattaNo ratings yet
- En601 Foundation For Energy EngineeringDocument10 pagesEn601 Foundation For Energy EngineeringJAMI PRUDHVI RAJNo ratings yet
- Diesel CycleDocument7 pagesDiesel CycleRehman MansuriNo ratings yet
- Hot Bulb EngineDocument12 pagesHot Bulb EngineRoberto Ortega MicalizziNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document8 pagesLesson 2Polaris PenidoNo ratings yet
- Project Title Proposed Research Research Domain Field of ResearchDocument11 pagesProject Title Proposed Research Research Domain Field of ResearchAffan ChoudhryNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education Certificate: Mechanical Engineering of Marathwada Mitra Mandal'sDocument16 pagesMaharashtra State Board of Technical Education Certificate: Mechanical Engineering of Marathwada Mitra Mandal's190 208 Rahul DhaneshwarNo ratings yet
- List of Experiments: Lab In-Charge Hod MeDocument41 pagesList of Experiments: Lab In-Charge Hod MeAshiq HussainNo ratings yet
- Four-Stroke Diesel Engine CyclesDocument10 pagesFour-Stroke Diesel Engine Cyclesmechjobs4meNo ratings yet
- Selair Selkirk Reciprocating EnginesDocument19 pagesSelair Selkirk Reciprocating EnginesErico Antonio TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- LV06 - Engines - Issue 1Document72 pagesLV06 - Engines - Issue 1Valentin Silvan Valentin SilvanNo ratings yet
- A Six Stroke EngineDocument7 pagesA Six Stroke EngineOmar MetwallyNo ratings yet
- THERMO BS II NotesDocument8 pagesTHERMO BS II Notesm.waseemNo ratings yet
- Working of SI & CI Engines (2S & 4S) : Power Unit (Engine)Document12 pagesWorking of SI & CI Engines (2S & 4S) : Power Unit (Engine)Satish BheleNo ratings yet
- 2stroke Engine Vs 4 Stroke EngineDocument7 pages2stroke Engine Vs 4 Stroke EngineEmmanuvalBabyKizhakkelNo ratings yet
- 1514285118329-Notes ALP InductionDocument97 pages1514285118329-Notes ALP InductionKhirod SahuNo ratings yet
- Heat Engine DesignDocument25 pagesHeat Engine DesignEamonn McStravickNo ratings yet
- 4 Stroke EngineDocument6 pages4 Stroke Engineasra 10100% (2)
- Internal Combustion Engines: LecturDocument30 pagesInternal Combustion Engines: LecturPuneet GargNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 B Ic EnginesDocument47 pagesUnit 1 B Ic Enginesoliyad teferiNo ratings yet
- Knocking (Also Called Knock, Detonation, Spark Knock, Pinging or Pinking) in SparkDocument5 pagesKnocking (Also Called Knock, Detonation, Spark Knock, Pinging or Pinking) in SparkRobert HolemsNo ratings yet
- Two Stroke Engine: 1. Swedish SaabDocument6 pagesTwo Stroke Engine: 1. Swedish SaabGilbert Escolano AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Actual CyclesDocument19 pagesActual CyclessunilbagadeNo ratings yet
- Difference Between 2 Stroke and 4 Stroke EnginesDocument4 pagesDifference Between 2 Stroke and 4 Stroke EnginesTakrama MichaelNo ratings yet
- Compact Steam Power Plant: DescriptionDocument13 pagesCompact Steam Power Plant: Descriptionnawaz_engr1892No ratings yet
- Basic Mech Civil EnggDocument94 pagesBasic Mech Civil EnggVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- 4-Stroke Petrol Engine History & DesignDocument19 pages4-Stroke Petrol Engine History & Designvivek8194No ratings yet
- Suction/Intake Stroke: Guledew, Aaron B BSIT-2Document2 pagesSuction/Intake Stroke: Guledew, Aaron B BSIT-2Jagabi Aeron Jay GuledewNo ratings yet
- Reciprocating Engines Section BDocument45 pagesReciprocating Engines Section BJuly TadeNo ratings yet
- Edexcel HNC/D Plant and Process Principles Outcome 4 - Power Supply Equipment Tutorial 1 - Diesel EnginesDocument9 pagesEdexcel HNC/D Plant and Process Principles Outcome 4 - Power Supply Equipment Tutorial 1 - Diesel EnginescataiceNo ratings yet
- Le2 Basic Components and Working PrinciplesDocument46 pagesLe2 Basic Components and Working Principlessaichandrasekhar_dNo ratings yet
- POWERPLANT1 PPT 9 Diesel Cycle and Brayton CycleDocument31 pagesPOWERPLANT1 PPT 9 Diesel Cycle and Brayton CycleRicky AntonioNo ratings yet
- Types of EnginesDocument24 pagesTypes of EnginesTimothy Del ValleNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart: Otto CycleDocument5 pagesFlow Chart: Otto CycleTanisha ThomasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Reciprocating Engine TheoryDocument36 pagesLecture 1 - Reciprocating Engine TheoryIan WhitingNo ratings yet
- Four Stroke EnginesDocument5 pagesFour Stroke EnginesPacumio ClaretteNo ratings yet
- Dual CycleDocument3 pagesDual CycleHazel AdoNo ratings yet
- I C Engine Lab ManualDocument46 pagesI C Engine Lab Manualمحمد رأفتNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction: 1.1 Ic EngineDocument54 pagesChapter 1 Introduction: 1.1 Ic Engineavanish SinghNo ratings yet
- Split-Cycle Engine RevolutionDocument14 pagesSplit-Cycle Engine RevolutionSameer Patil0% (1)
- Piston Engine Principles and ConstructionDocument276 pagesPiston Engine Principles and ConstructionLaith LaithNo ratings yet
- Darul Hikmah University Agricultural College Farm Machinery LectureDocument20 pagesDarul Hikmah University Agricultural College Farm Machinery Lecturehusni ahmedNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Vehicles and Systems Unit 3A Aircraft PowerplantsDocument81 pagesAerospace Vehicles and Systems Unit 3A Aircraft Powerplantsshashi1810No ratings yet
- Eight Verses in Praise of Krishna by Adi ShankaraDocument7 pagesEight Verses in Praise of Krishna by Adi ShankaraChiranjeevi Dakshina MurthyNo ratings yet
- Cover LetterDocument2 pagesCover LetterChiranjeevi Dakshina MurthyNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations ManagementDocument284 pagesProduction and Operations Managementsnehal.deshmukh89% (28)
- AvengersDocument1 pageAvengersChiranjeevi Dakshina MurthyNo ratings yet
- Plant Layout and Material HandlingDocument2 pagesPlant Layout and Material Handlingsasi0823No ratings yet
- Mechanical SyllabusDocument113 pagesMechanical SyllabusChiranjeevi Dakshina MurthyNo ratings yet
- AldepDocument10 pagesAldepSankalp BhatiyaNo ratings yet
- Build A LockwoodDocument16 pagesBuild A LockwoodkokiskoNo ratings yet
- Arizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksFrom EverandArizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- New York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksFrom EverandNew York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksNo ratings yet
- The Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptFrom EverandThe Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- South Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptFrom EverandSouth Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Naples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoFrom EverandNaples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Japanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensFrom EverandJapanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensNo ratings yet