Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medical Uses: Deficiency
Uploaded by
Dr. MNV KiranbabuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Medical Uses: Deficiency
Uploaded by
Dr. MNV KiranbabuCopyright:
Available Formats
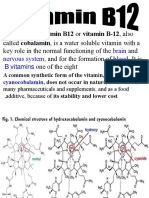
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, vitamin B12 or vitamin B-12, also called cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin with a
key role in the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and for the formation of blood.
Deficiency[edit]
Main article: Vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency can potentially cause severe and irreversible damage, especially to the brain
and nervous system. At levels only slightly lower than normal, a range of symptoms such
as fatigue, depression, and poor memory may be experienced.[2]
Vitamin B12 deficiency can also cause symptoms of mania and psychosis.[29][30]
Medical uses[edit]
Vitamin B12 is used to treat vitamin B12 deficiency, cyanide poisoning, and hereditary deficiency of
transcobalamin II.[10] It is given as part of the Schilling test for detecting pernicious anemia.[10]
For cyanide poisoning, a large amount of hydroxocobalamin may be given intravenously and
sometimes in combination with sodium thiosulfate.[11] The mechanism of action is straightforward: the
hydroxycobalamin hydroxide ligand is displaced by the toxic cyanide ion, and the resulting harmless
B12 complex is excreted in urine. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration approved (in
2006) the use of hydroxocobalamin for acute treatment of cyanide poisoning. [12]
High vitamin B12 level in elderly individuals may protect against brain atrophy or shrinkage associated
with Alzheimer's disease and impaired cognitive function.[13]
High-dose administration of Vitamin B12 has been additionally validated to stimulate the activity of the
body's TH1 suppressor T-Cells, which then down-regulates the over-production of the allergen
antibody IgE in allergic individuals.[14]
Vitamin B12 has extremely low toxicity, and even taking enormous doses does not appear to be
harmful to healthy individuals
Vitamin B12 supplements are effective for preventing deficiencies, especially in vegetarians, and are
often marketed as weight loss supplements. However, no scientific studies have shown that B 12 is
effective for weight loss
dietary reference intake for an adult ranges from 2 to 3 g per day (US),[15] and 1.5 g per day (UK).
[16]
But according to a new study,[17] the DRI should be 4 to 7 g per day. The Center for Food Safety
and Applied Nutrition recommends 6 g per day,
Vitamin B12 is believed to be safe when used orally in amounts that do not exceed the recommended
dietary allowance (RDA). There have been studies that showed no adverse consequences of doses
above the RDA.
You might also like
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandVitamin B12 Deficiency, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Vitamin B12 Boots Energy and Cures FatigueDocument9 pagesVitamin B12 Boots Energy and Cures FatiguecantodelcisneNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 - Essential For Healthy Blood, Brain, and Dna: Homocysteine and Cardiovascular DiseaseDocument3 pagesVitamin B12 - Essential For Healthy Blood, Brain, and Dna: Homocysteine and Cardiovascular Diseaseizeldien5870No ratings yet
- Maitri ChakraDocument1 pageMaitri ChakraDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12Document16 pagesVitamin B12sadaq84No ratings yet
- Vitamin B12Document17 pagesVitamin B12madhujayarajNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B 12Document3 pagesVitamin B 12reshma1977No ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 PDFDocument22 pagesVitamin B12 PDFjcoppala4476No ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 DeficiencyDocument12 pagesVitamin B12 DeficiencyMagazin HdPNo ratings yet
- Micronutrient: Vitamin B-12 Micronutrient: Vitamin B-12: Presented by Abby Christensen Presented by Abby ChristensenDocument12 pagesMicronutrient: Vitamin B-12 Micronutrient: Vitamin B-12: Presented by Abby Christensen Presented by Abby ChristensenAbby ChristensenNo ratings yet
- Dietary Supplement Fact Sheet - Vitamin B12 - Health Professional Fact SheetDocument14 pagesDietary Supplement Fact Sheet - Vitamin B12 - Health Professional Fact SheetSwastikaMishraNo ratings yet
- Nutri b12Document3 pagesNutri b12gupblrNo ratings yet
- Vitamin b12 Cobalamin and Parkinsons DiseaseDocument4 pagesVitamin b12 Cobalamin and Parkinsons DiseaseSupermanNo ratings yet
- Elgar, 2022Document17 pagesElgar, 2022Caoimhe O'BrienNo ratings yet
- 11/supplement-Guide-Vitamin-B12 Vitamin B-12 (Cobalamin)Document2 pages11/supplement-Guide-Vitamin-B12 Vitamin B-12 (Cobalamin)Tafta Na E'iNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 - CobalaminDocument12 pagesVitamin B12 - CobalamincloogisNo ratings yet
- Benifits of Vitamin B12Document1 pageBenifits of Vitamin B12ChakNo ratings yet
- Chronic Vitamin B DeficiencyDocument4 pagesChronic Vitamin B DeficiencyxtinebadzNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 DeficiencyDocument6 pagesVitamin B12 DeficiencyDzuljuniaf JaafarNo ratings yet
- Makalah MateriDocument17 pagesMakalah MateriRuwindaNo ratings yet
- The Four Stages of Vitamin B12 DeficiencyDocument11 pagesThe Four Stages of Vitamin B12 Deficiencyzlautarevic-1No ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 ReviewDocument12 pagesVitamin B12 ReviewMunyaradzi Nhambure100% (1)
- b12 VitDocument9 pagesb12 VitAurelian Ionel CostinNo ratings yet
- Vitamin b12 Tissue Regeneration PDFDocument9 pagesVitamin b12 Tissue Regeneration PDFochichornia381314No ratings yet
- HEMATOLOGYDocument1 pageHEMATOLOGYDaniela Jean DiolataNo ratings yet
- RegistroDocument46 pagesRegistroTikTokrineNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Vitamin B12 Anemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Vitamin B12 Anemia, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- B12 DeficiencyDocument11 pagesB12 DeficiencysoniapalmaNo ratings yet
- Diphyllobothrium Latum (FishDocument3 pagesDiphyllobothrium Latum (FishSabrina TolentinoNo ratings yet
- HemaDocument2 pagesHemaKarshey Alagad ObutNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Vitamin b12Document10 pagesResearch Paper On Vitamin b12gz7y9w0s100% (1)
- DRUG STUDY EldersDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY EldersChrizley Shawn DeroniaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin b12 Production - ParulDocument20 pagesVitamin b12 Production - Parulanon-90455980% (5)
- Vitamina b12Document3 pagesVitamina b12Raluca Elena Raluca ElenaNo ratings yet
- B12 Deficiency PDFDocument11 pagesB12 Deficiency PDFDuarte Nuno DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Water Solu Able VitaminsDocument4 pagesBiochemistry Water Solu Able Vitaminsartventoure projectNo ratings yet
- b12 130816041332 Phpapp02Document15 pagesb12 130816041332 Phpapp02botanokaNo ratings yet
- B VitaminsDocument4 pagesB Vitaminsulylope0% (1)
- Folinext Nutritional Supplement Tablet 10 Tab StripDocument7 pagesFolinext Nutritional Supplement Tablet 10 Tab StripSai PkNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12Document18 pagesVitamin B12Kimberly A. S. SmithNo ratings yet
- Animal Nutrition and FeedingDocument16 pagesAnimal Nutrition and Feedingmarianette balucasNo ratings yet
- Test Result Test Name Unit: Ms. Jahanzaibbanoo Faruk PatelDocument2 pagesTest Result Test Name Unit: Ms. Jahanzaibbanoo Faruk PatelJahan Faruk PatelNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency AnemiaDocument4 pagesVitamin B12 Deficiency AnemiaAnonymous 2rNFWzNo ratings yet
- Vitamin C NotesDocument3 pagesVitamin C NotesGabriela NovoaNo ratings yet
- R.G. VermaDocument16 pagesR.G. VermaMohit ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Research Paper - Depression and Vitamin B12Document7 pagesResearch Paper - Depression and Vitamin B12AarohiNo ratings yet
- Potential Role of Vitamin D For The Management of Depression and AnxietyDocument19 pagesPotential Role of Vitamin D For The Management of Depression and Anxietyjolios85No ratings yet
- Vitamin D Deficiency in Childhood - A Review of Current Guidelines On Diagnosis and ManagementDocument7 pagesVitamin D Deficiency in Childhood - A Review of Current Guidelines On Diagnosis and Managementcoolarun86No ratings yet
- The Role of Vitamin D Deficiency in TheDocument8 pagesThe Role of Vitamin D Deficiency in ThefitrianugrahaNo ratings yet
- VitaminB12 ConsumerDocument3 pagesVitaminB12 ConsumerpatgarettNo ratings yet
- Vegetarian Lifestyle and Monitoring of Vitamin B-12 StatusDocument13 pagesVegetarian Lifestyle and Monitoring of Vitamin B-12 StatusDennis RotermundNo ratings yet
- Signs of Vitamin b12 DeficiencyDocument9 pagesSigns of Vitamin b12 DeficiencyMark JonesNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 DeficiencyDocument5 pagesVitamin B12 DeficiencyMustafa AlmasoudiNo ratings yet
- B12 Deficency NEJM 2013Document12 pagesB12 Deficency NEJM 2013Aída Fernanda100% (1)
- Linus Pauling Institute: Vitamin DDocument11 pagesLinus Pauling Institute: Vitamin DbqdianzNo ratings yet
- VitaminB12 Consumer PDFDocument3 pagesVitaminB12 Consumer PDFKingNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Nutrition Conscious Eating Rainbow Green Live Food CuisineDocument7 pagesSpiritual Nutrition Conscious Eating Rainbow Green Live Food CuisineJohnNo ratings yet
- Vitamin D and IodineDocument13 pagesVitamin D and IodineAreej FatimaNo ratings yet
- Nutrients: Vitamin B in Health and DiseaseDocument18 pagesNutrients: Vitamin B in Health and DiseaseSrinivas RajanalaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin B12 in Vegetarian DietsDocument4 pagesVitamin B12 in Vegetarian DietsJesica DiazNo ratings yet
- Pernicious Anemia: A Beginner's 5-Step Guide on Managing the Condition Through Diet and Vitamin B12 SupplementationFrom EverandPernicious Anemia: A Beginner's 5-Step Guide on Managing the Condition Through Diet and Vitamin B12 SupplementationNo ratings yet
- Examples: Analyzing AlgorithmsDocument3 pagesExamples: Analyzing AlgorithmsDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Kala Chakra Dasha Set-UpDocument1 pageKala Chakra Dasha Set-UpDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1Dr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- m1 IntroDocument13 pagesm1 Introapoorva96No ratings yet
- Jaimini Chara Dasha: (Method of Raghavabhatta & Nrisimhasuri)Document1 pageJaimini Chara Dasha: (Method of Raghavabhatta & Nrisimhasuri)Dr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Kala Chakra Dasha Set-UpDocument1 pageKala Chakra Dasha Set-UpDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- 01Document5 pages01Ram AnandNo ratings yet
- Vimshottari Dasha: From........ To Dasha Lord Name Duration S.NDocument1 pageVimshottari Dasha: From........ To Dasha Lord Name Duration S.NDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- X Pdfqqweee334443Document1 pageX Pdfqqweee334443Dr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Jaimini Mandooka Dasha: (Alternate Method of Division)Document1 pageJaimini Mandooka Dasha: (Alternate Method of Division)Dr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Q 7 AasswwqqDocument1 pageQ 7 AasswwqqDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Kala Chakra Dasha-Bhuktis: Bhuktis From To Bhuktis From To Bhuktis From ToDocument1 pageKala Chakra Dasha-Bhuktis: Bhuktis From To Bhuktis From To Bhuktis From ToDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Observations From K.C.D Jeeva-Rashi and Amsha-RashiDocument1 pageObservations From K.C.D Jeeva-Rashi and Amsha-RashiDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Results of Some Important YogasDocument1 pageResults of Some Important YogasDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Observations From K.C.D Jeeva-Rashi and Amsha-RashiDocument1 pageObservations From K.C.D Jeeva-Rashi and Amsha-RashiDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Jaimini Mandooka Dasha: (Alternate Method of Division)Document1 pageJaimini Mandooka Dasha: (Alternate Method of Division)Dr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Kala Chakra Dasha-Bhuktis: Bhuktis From To Bhuktis From To Bhuktis From ToDocument1 pageKala Chakra Dasha-Bhuktis: Bhuktis From To Bhuktis From To Bhuktis From ToDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- q10 PDFDocument1 pageq10 PDFDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Q 9 DDDDocument1 pageQ 9 DDDDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Q 7 AasswwqqDocument1 pageQ 7 AasswwqqDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- JFJHGKKTKTDocument2 pagesJFJHGKKTKTDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Observations From SarvashtakavargaDocument1 pageObservations From SarvashtakavargaDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Vimshottari Dasha: From........ To Dasha Lord Name Duration S.NDocument1 pageVimshottari Dasha: From........ To Dasha Lord Name Duration S.NDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Planet Details: Astrologer: Dr. Kumara SanjayaDocument1 pagePlanet Details: Astrologer: Dr. Kumara SanjayaDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Planet Details: Astrologer: Dr. Kumara SanjayaDocument1 pagePlanet Details: Astrologer: Dr. Kumara SanjayaDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Planet Details: Astrologer: Dr. Kumara SanjayaDocument1 pagePlanet Details: Astrologer: Dr. Kumara SanjayaDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Planet Details: Astrologer: Dr. Kumara SanjayaDocument1 pagePlanet Details: Astrologer: Dr. Kumara SanjayaDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Go RaeDocument1 pageGo RaeDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet
- Planet Details: Astrologer: Dr. Kumara SanjayaDocument1 pagePlanet Details: Astrologer: Dr. Kumara SanjayaDr. MNV KiranbabuNo ratings yet