Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.1 Exercise 3 - Hess' Law
Uploaded by
Clayanne KnottCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.1 Exercise 3 - Hess' Law
Uploaded by
Clayanne KnottCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
1 EXERCISE 3 - Hess' Law
Using standard enthalpies of formation
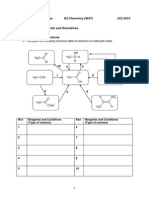
1. Given the following data:
Substance
Hf/kJmol-1
H2O(l)
-285.5
CO2(g)
-393
Ethane C2H6(g)
-83.6
Ethene C2H4(g)
+52.0
a) Write equations for the complete combustion of
i) ethane
ii) ethene
iii) hydrogen
b) Calculate the enthalpy of combustion in each case using the above data.
2. Given the following data: Hf(CH4) = -74.8 kJmol-1, Hf(CH3Cl) = -134.5 kJmol-1,
Hf(HCl) = -92.3 kJmol-1;
Calculate H for the reaction CH4(g) + Cl2(g) CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g)
3. Given the data:
4NH3(g) + 3O2(g) 2N2(g) + 6H2O(l), H = -1530kJmol-1
H2(g) + 1/2O2(g) H2O(l), H = -288 kJmol-1
Calculate the enthalpy of formation of ammonia.
4. Given the data:
Substance
Hf/kJmol-1
B2H6(g)
+31.4
B2O3(s)
-1270
C6H6(g)
+83.9
CO2(g)
-393
H2O(g)
-242
Calculate the enthalpy of combustion of gaseous diborane and gaseous benzene given
that they burn according to the following equations:
B2H6(g) + 3O2(g) B2O3(s) + 3H2O(g), C6H6(g) + 7.5O2(g) 6CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
5. When ethanol burns in oxygen under standard conditions, carbon dioxide, water and
1368 kJmol-1 of energy are produced. Calculate the enthalpy of formation of ethanol,
given that the enthalpies of formation of carbon dioxide and water are -393.7 and
-285.9 kJmol-1 respectively.
Using standard enthalpies of combustion
6. Calculate the enthalpy of formation of butane (C4H10) from the following data:
Enthalpy of combustion of graphite = -393.6 kJmol-1
Enthalpy of combustion of hydrogen = -285.9 kJmol-1
Enthalpy of combustion of butane = -2877.1 kJmol-1
7. Given the following data:
Substance
Hc/kJmol-1
CH3CH2CH2CH3
-2877
CH3CH2CH=CH2
-2717
H2
-286
Calculate H for the following reaction: CH3CH2CH=CH2 + H2 CH3CH2CH2CH3
8. Given the following data:
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(l)
CO(g) + 1/2O2(g) CO2(g)
C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g)
H2(g) + 1/2O2(g) H2O(l)
H = -890 kJmol-1
H = -284 kJmol-1
H = -393 kJmol-1
H = -286 kJmol-1
Calculate:
a) The enthalpy of formation of methane
b) The enthalpy of formation of carbon monoxide
c) The enthalpy change when methane is burned in limited oxygen to form carbon
monoxide and water.
You might also like
- Lattive EnergyDocument44 pagesLattive EnergyClarize Soo HooNo ratings yet
- Faraday's Law WorksheetDocument4 pagesFaraday's Law WorksheetBrianna MalcolmNo ratings yet
- A2 Test 11 Notes - Transition ElementsDocument11 pagesA2 Test 11 Notes - Transition Elementswill bellNo ratings yet
- IB Questionbank With ANSWERSDocument6 pagesIB Questionbank With ANSWERSRaunak Chawla100% (1)
- Topic 10 HLQDocument21 pagesTopic 10 HLQPipen 5No ratings yet
- IB DP Prescribed PracticalsDocument24 pagesIB DP Prescribed PracticalsMitul HariyaniNo ratings yet
- Until Thermal Equilibrium Is Obtained.: Loss GainDocument5 pagesUntil Thermal Equilibrium Is Obtained.: Loss GainCharls DeimoyNo ratings yet
- Cbaich, Journal Manager, 18-IASproc1969-TemperatureDependenceDocument6 pagesCbaich, Journal Manager, 18-IASproc1969-TemperatureDependencemohammedali2004No ratings yet
- UK Chemistry Olympiad Round 1 Mark Scheme 2016Document11 pagesUK Chemistry Olympiad Round 1 Mark Scheme 2016Rhan AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Answers John Green and Sadru Damji Third Edition Ibid 2008Document129 pagesChemistry Answers John Green and Sadru Damji Third Edition Ibid 2008bnkjaya-1100% (1)
- 5.3 (153 Marks) : MarkschemeDocument41 pages5.3 (153 Marks) : MarkschemeSemwezi EnockNo ratings yet
- PW-049a-Limiting Reagents-01Document5 pagesPW-049a-Limiting Reagents-01JoHan Xyth RizaldoNo ratings yet
- Born-Haber CycleDocument16 pagesBorn-Haber Cycleahmed ramadanNo ratings yet
- Chemical NomenclatureDocument7 pagesChemical NomenclatureKeith Lavin100% (1)
- Energetics: Enthalpy ChangesDocument4 pagesEnergetics: Enthalpy ChangesDr.CharinNo ratings yet
- 1 3 F Calculations Involving Gas VolumesDocument45 pages1 3 F Calculations Involving Gas VolumesForm 4BNo ratings yet
- Fill in The Table Below:: Empirical Formula WorksheetDocument2 pagesFill in The Table Below:: Empirical Formula WorksheetSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- Determination of Electrode PotentialsDocument26 pagesDetermination of Electrode PotentialsGliezl ImperialNo ratings yet
- ElecSpectra 2 UploadDocument25 pagesElecSpectra 2 UploadSarthak SinghNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Born-Haber Cycle Answer Key PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet Born-Haber Cycle Answer Key PDFBrandeice BarrettNo ratings yet
- N m05 21Document1 pageN m05 21David MathagaNo ratings yet
- H2 Chemical Kinetics and EnergeticsDocument12 pagesH2 Chemical Kinetics and EnergeticskitoniumNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry Review WorksheetqqchiuNo ratings yet
- 16 2BondEnergyDocument1 page16 2BondEnergyAhmedNo ratings yet
- 2014 Entropy Tutorial With Solution For StudentsDocument6 pages2014 Entropy Tutorial With Solution For StudentsChen ZhihaoNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding 4. Bonding: Evidence For The Existence of IonsDocument9 pagesIonic Bonding 4. Bonding: Evidence For The Existence of IonsAnastasia ErshNo ratings yet
- Rate Expression and Activation Energy: 1a. (1 Mark)Document7 pagesRate Expression and Activation Energy: 1a. (1 Mark)senna0% (1)
- HMK Reacting MassesDocument4 pagesHMK Reacting MassesloloNo ratings yet
- Acids and Derivatives TutorialDocument18 pagesAcids and Derivatives TutorialChen ZhihaoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics (Ch. 16) AP ProblemsDocument4 pagesThermodynamics (Ch. 16) AP ProblemsHasantha PereraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 07Document65 pagesChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 07Ng Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- In-Class Worksheet AnswersDocument6 pagesIn-Class Worksheet AnswersalgonzNo ratings yet
- BT2 Revision Package 2013 - AnsDocument70 pagesBT2 Revision Package 2013 - AnsSean Ng Jun JieNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibria Tutorial With AnsDocument6 pagesChemical Equilibria Tutorial With AnsDomNo ratings yet
- Ideal Heat CapacityDocument12 pagesIdeal Heat CapacityDerek Lua YongweiNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument18 pagesChemical EquilibriumCarbuncle JonesNo ratings yet
- Materials 3C04 Assignment 6 Solutions: SolutionDocument6 pagesMaterials 3C04 Assignment 6 Solutions: SolutionmacanNo ratings yet
- Energetics QuestionsDocument58 pagesEnergetics QuestionsQasim Peracha100% (1)
- Thermo Kin Ws CompleteDocument20 pagesThermo Kin Ws CompleteMohommad YawariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry A2 Summary - Nitrogen CompoundsDocument4 pagesChemistry A2 Summary - Nitrogen CompoundsFrancisca FuchsNo ratings yet
- Alkenes 2Document45 pagesAlkenes 2cikgu_amin100% (1)
- 2016 Chimie Internationala Proba Teoretica SubiectebaremeDocument51 pages2016 Chimie Internationala Proba Teoretica SubiectebaremeCristinaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of Electrochemical CellsDocument6 pagesThermodynamics of Electrochemical Cellssexycassie100% (4)
- Section 3 EnergeticsDocument47 pagesSection 3 Energeticsapi-3734333No ratings yet
- Eisermann Et Al - 1980Document15 pagesEisermann Et Al - 1980Felipe0% (1)
- Thermochemistry (Important Notes)Document2 pagesThermochemistry (Important Notes)HenrySeowNo ratings yet
- Redox Review - IB-Short QuestionsDocument8 pagesRedox Review - IB-Short QuestionsStephanie LeeNo ratings yet
- Prescribed Practicals Lab Manual 2016Document28 pagesPrescribed Practicals Lab Manual 2016rbgrossNo ratings yet
- Octahedral vs. Tetrahedral GeometriesDocument3 pagesOctahedral vs. Tetrahedral GeometriesMa'arif A. SyafiiNo ratings yet
- Mod 4 Revision Guide 10 Synthetic RoutesDocument2 pagesMod 4 Revision Guide 10 Synthetic RoutesdufraiscNo ratings yet
- Carbonyls PDFDocument10 pagesCarbonyls PDFMaheshNo ratings yet
- 10.4 Halogenoalkanes 10.4.1 Introduction To Halogenoalkane ReactivityDocument16 pages10.4 Halogenoalkanes 10.4.1 Introduction To Halogenoalkane Reactivitydiyaray100% (1)
- Structure and Bonding AnsDocument251 pagesStructure and Bonding Ansgkawsar22No ratings yet
- Chemistry Set 9Document21 pagesChemistry Set 9s_adhyaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem ReactionsDocument7 pagesOrganic Chem ReactionsTeo Jia Ming NickolasNo ratings yet
- Chem Last Min NotesDocument2 pagesChem Last Min NoteslegitmanofmenNo ratings yet
- As Tute 1 September 2016Document2 pagesAs Tute 1 September 2016Piyumi ObeyesekeraNo ratings yet
- Homework Enthalpy CalculationsDocument2 pagesHomework Enthalpy CalculationsErnur Teginbaev100% (1)
- Topic 2 - ThermochemistryDocument4 pagesTopic 2 - ThermochemistryMutasimNo ratings yet