Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tektronix sg-505 PDF
Uploaded by
plasmapete0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
191 views82 pagesOriginal Title
tektronix_sg-505.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
191 views82 pagesTektronix sg-505 PDF
Uploaded by
plasmapeteCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 82
Tektronix, Inc.
P.O. Box 500
Beaverton, Oregon
070.2823.00
Product Group 75
97077
Tektronix
COMMITTED TO EXCELLENCE
PLEASE CHECK FOR CHANGE INFORMATION
AT THE REAR OF THIS MANUAL.
SG 505
OSCILLATOR
WITH OPTION 01
Francais Deutsch Bae
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
Serial Number
First Printing OCT 1979
Revised MAR 1986
Gopyrignt © 1979 Tektronix, tne. All rights reserved.
‘Contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any
form without the written permission of Tektronix, Inc
Products of Tektronix. Inc. and its subsidiaries are covered
by US. ang foreign patents and/or pending patents.
TEKTRONIX, TEK, SCOPE-MOBILE, and
istered trademarks of Tektronix, Ine
are reg-
Printedin U.S.A. Specification and price change privileges
are reserved,
Copyright © 1979 TEKTRONIX INC, Tour droite éeervés
LLecantenude ce manuel ne peut etre reproduit sous quelque for-
se que oe rot sane accord de Tektronix Ine.
‘Tous let produits TEKTRONIX sont bravetds US et Exranger et
ler logotypes TEKTRONIX, TEK SCOPE MOBILE, Gay sont
posts
Imprimé aux USA, TEKTRONIX se rétrve le droite mosiier
‘arecteristiques et pr cans le cadre de développementstechno-
Tosiques.
Copyright © 1979 durch Tektronix, inc. Alle Rechte vorbr
hnaltan. Der Inhalt Gieser Publixation ‘dar! onne Genehmigur,
von Tektronix, Inc. nicht weitergegeben werden,
Produkte von Tekironix. Inc. und seinen Tochtergeselischaiten
sind durch US- und Auslandspatente und/oder schwebende
Patente abgedeckt.
TekrmoN, Te SCOFE-MOBILE una GH sna gesonozte
Gedruckt in U.S.A Spozitikations- und Preisanderungen
bleiben vorbehalten
C SOMA T 2 b= Dad, REN.
KTRONIX, TEK, SCOPE-MOBILE.
GST? haar atone er.
BM TERE, HRI FS CRETE
aranat,
INSTRUMENT SERIAL NUMBERS.
Each instrument has a serial number on a panel insert, tag,
‘or stamped on the chassis. The first number or letter
designates the country of manufacture. The last five digits
of the serial number are assigned sequentially and are
unique to each instrument. Those manufactured in the
United States have six unique digits. The country of
manufacture is identified as follows:
18000000
400000
200000
300000
700000
Tektronix, inc., Beaverton, Oregon, USA
Tektronix Guernsey, Ltd., Channel Isiands
Tektronix United Kingdom, Ltd., London
Sony/Tektronix, Japan
‘Tektronix Holland, NV, Heerenveen,
‘The Netherlands
8G 505
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Uist of llustrations:
List of Tables i
Operators Satety Summary . .
Servicing Safety Summary
OPERATORS PART
Section 1 SPECIFICATION
Introduction
Perlormance Conditions .
Electrical Characteristics,
Front Panel .
ear Interface
Miscellaneous ae
Environmental ..... 0.6.05
Physical Characteristics...
ENGLISH VERSION
Section 2. OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS.
Installation instructions
Preparation tor Use
Repackacing information
Controls and Connectors.
‘Operators Familiarization
General Operating information
Cutout Connections
Frequency Selection
Output Level Selection
intermodulation Test Signal
Rear Interface Signals
FRENCH VERSION
Chapitre 2 INSTRUCTIONS D'UTILISATION
Mise enroute...
Opérations prétiminsi
Instructions dexpéaition
Commandes et connecteurs =
Sélection de la fréquence...
REV A OCT 1960
Page
ve
4
ve
13
+3
v4
4
at
at
22
22
ad
a4
24
ad
pa
aa
a
Page
Sélection du niveau de sortie 22
Bornes de sortie 22
Utilisation de Mappareil 1 22
informations ginérales d'utilisation .. 22
Connexions de sortie . 22
Sélection dela fréquence 6... 24
Sélection du niveau de sortie... 24
Signal de test d‘intermodulation (op-
tion 01) ie
Signaux déliveés sur le connecteur de
interface + 24
GERMAN VERSION
Kapitel 2. BEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG
Einbauanweisung . . . 21
Bedienungselemente und
Steckverbindungen... 0... 602004 22
Allgemeine Bedienungsanietung Ba
Ausgangssignal ... ad
Frequenzwaht - ed
Wahi des Ausgangspegels 28
Modulationstestsignal (Option 01) . 2-4
Signate an der ruckseitigen
Interfaceverdingung
Verpackungshinevatse
JAPANESE VERSION
xom Ramm
RIT 2
ZERO 2
game 2
ay hanes aee 2
2
mea
seteoom
Mipaa2e
mm aR 2
BER 2-
2
4e9-RV ab var FRED
BEBE 7 TAS
8G 505
TABLE OF CONTENTS (cont)
SERVICE PART
THE FOLLOWING SERVICING INSTRUCTIONS
ABE FOR USE BY QUALIFIED PERSONNEL ONLY.
TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY, DO NOT PER-
FORM ANY SERVICING OTHER THAN THAT CON-
TAINED IN OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS UNLESS
YOU ARE QUALIFIED TO 00 SO.
Section 3. THEORY OF OPERATION Page
lntreduetion..... a4
Phase Shift Oscillator . at
Amplitude Detector... - 06... 2. Set
Peak Detector 2. Bet
Amplitude Control seveee BH
Output Butter Amplifier... a2
Output attenuator and Butter Amplifier 22
‘Syne Driver and Syne Amplifier 32
Power Supply 92
intermodulation Test Signal (Cption O1) 3-2
Section 4 CALIBRATION PROCEDURE
Introduction... cee ad
Tost Equipment Requirements at
Partormance Check 43
Introduction... 148
Test Equipment Required ....... 43
Preparation : 43
Procedure 43
Adjustments... cece ceceee sees 418
Introduction ee 413
Test Equipment Required 43,
Preparation 413
Procedure... .eeceeesere see 418
Section 5 MAINTENANCE Page
Recalibration ... . 51
Obtaining Replacement Parts St
Cleaning instructions . . 5
Circuit Board Removal and installation S-1
Low Frequency Selection (Option 01) 5-2
Troubleshooting Aids Se
Troubleshooting Equipment 2
Static-Sensitive Components . . . 52
Section 6 OPTIONS
Section 7 REPLACEABLE ELECTRICAL PARTS
Section 8 DIAGRAMS AND CIRCUIT BOARD
ILLUSTRATIONS
Section 9 REPLACEABLE MECHANICAL PARTS
AND EXPLODED VIEW
Accessories
Change Information
e
a
42
an
B2
a3
Ba
as
oS
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS
‘SG 505 Oscillator (Option 01)
‘SG 508 installation and removal ..
Front panel controls and connectors
10 Hz aull adjustment
10 Hz harmonic distortion display
20 Hz harmonic distortion display
20 kHz harmonic distortion display
Lett side view of SG 505
NoTe
The following illustrations are located in the
diagrams foldout section at the rear of this manual
SG 505 Simplitied block diagram
Oscillator board (A10)
Troubleshooting flow chart—oscillator
Troubleshooting flow chart—power supply
IMD Option board (A11)
Agjustment locations.
Page
at
a8
43
410
410
413
8G 505
8G 505
Table
No.
1
12
oy
4
4
42
43
4
45
46
47
48
at
a2
83
ae
LIST OF TABLES
Electrical Characteristics
Miscellaneous .
Environmental.
Physical Characteristics
st of test equipment requirements
Frequeney accuracy check
Cutout fevel accuracy check
Output level step accuracy check
oval flatness check : eerie
Level flatness check 7
Harmonic correction factors... .sse ee eee eee
Factors for thd computation oe
Relative susceptibility to static discharge damage .
NOTE
The following tables are located in tne diagrams
Joldout section at the roar of this manual
Rear Interface Connector Assignments
Component reference chart
Component reterence chart
Component relerence chart
Component relerence chart
Page
1-3
4
4
4
43
45
46
“7
47
49
+10
53
®
8c 505
OPERATORS SAFETY SUMMARY
The general safety information in this part ofthe summary
is for both operating and servicing personnel. Specific
warnings and cautions will be found throughout the
manual where they apply, but may not appear in this
summary,
TERMS
In This Manual
CAUTION statements identity conditions or practices that
could resuitin damage to the equipment or other property
WAANING statemenis identify conditions or practices
that could result in personal injury or loss af life
As Marked on Equipment
CAUTION incicates @ personal injury hazard not im-
mediately accessible as one reads the marking, or a
hazard to property including the equipment itsett
DANGER indicates a personal injury hazard immediately
accessible as one reads the marking,
SYMBOLS
In This Manual
This symbol indicates where applicable
cautionary or other information is to be
found.
As Marked on Equipment
4 DANGER — High voltage.
inal
& Protective ground (earth) ter
ZX ATTENTION ~ ter to manual
AY ANOV 1973
Power Source
‘This product Is intendad to operate in a power module
connected to a power source tnat will nat apply moretnan
250 volts ems between the supply conductors or between
either supply conductor and ground. A protective ground
connection by way of the grounding conductor in the
ower cord is essential for safe operation.
Grounding the Product
‘This product is grounded through the grounding conduc-
tor of the power madule power cord. To avoid electrical
shack, plug the power cord into a properly wired recep-
tacle before connecting to the product input or outout
terminals. A protective ground connection by way of the
grounding conductor in the power cord is essential tor
safe operation,
Danger Arising From Loss of Ground
Upon oss of the protective-ground connection, all
accessible conductive parts (including knobs and con-
trols that may appoar to bo inculated) can rencer an
electric shock
Use the Proper Power Module Power Cord
Use only the power cord and connector specified for your
product.
Use only a power cord that is in good condition,
Use the Proper Fuse
To avoid tire hazard, use only the fuse of correct type,
voltage rating and current rating as specitieg in the parts
list for your product.
Refer fuse replacement to qualified service personnel
Do Not Operate in Explosive Atmospheres
To avoid explosion. do not operate this product in an
‘explosive atmosphere unless it has been specifically
certified for such operation.
vi
Do Not Operate Without Covers
To avoid personst injury, do not operate this product
without covers or panels installed, Do not apply power to
the plug-in via a plug-in extender.
8G 505
SERVICING SAFETY SUMMARY
FOR QUALIFIED SERVICE PERSONNEL ONLY
Refer also to the preceding Operators Safety Summary.
Do Not Service Alone
Do not pertorm Internal service or adjustment of this
product uniess another person capable of rendering first
aid and resuscitation is present.
Use Care When Servicing With Power On
Dangerous voltages exist at several points in this produ
To avoid personal injury, do not touch exposed connec-
tions and components while power is on.
Disconnect power before removing protective panels,
soldering, or replacing components.
Power Source
This product is intended to operate in a power module
connected o a power source that will not apply morethan
250 volts rms between the supply conductors or between
either supply conductor and ground. A protective ground
connection by way of the grounding conductor in the
power cord is essential for safe operation.
SG 505
The 8G 505 Oscitator.
viii @
Section 1—SG 505,
OPERATORS PART
SPECIFICATION
Introduction
‘The SG 505 Oscillator generates an ultraiow distortion
‘sine wave over the Irequency range from 10 Hato 100 kHz
‘hig signal can be loated or referenced to chassis ground,
The oscillator also provides a fixed amplitude ground
referenced sine wave signal at the SYNC OUT connector
that is identical in trequency to the signal {rom the
OUTPUT connector. Versions of both cutout signals are
available at the rear interface connector.
‘The Option 01 SG 505 adds an intermodulation test
signal function. This signal consists of a lower frequency
Sine wave mixeo with the selected frequency in 2&1
amplitude ratio, The lower frequency sine wave isinternal-
ly selectable tor 60 +2 of 250 Hz. The SG 506s designed
to operate in one compartment of any TM 500 Series
Power Module.
Pertormance Conditions
‘The electrical characteristics are valid only if the
‘SG 505 has been calibrated at an ambient temperature of
720°C to +30°C and is operating at an ambient tem-
perature of O°C to +50°C, unless otherwise noted,
Items listed in the Performance Requirements column
of the Electrical Characteristics are verified by completing
the Performance Check in the Calibration section of this
manual. Items listed in the Supplemental Information
Column ara not verified in this manual. They are either
explanatory notes or performance characteristics for
waich no limits are specified
Table 1-1
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Front Panel)
Characteristics
FREQUENCY
Range
bands.
Performance Requirements
40 Hz to 100 kHe in tour overtapping
‘Supplemental Information
Typically 9 Hz to 110 kHz, Nominal range
of each band is 0.90 to 11.0.
varnier Range BE % of frequency setting.
Dial Accuracy
“Ei of setting with vernier at center
Dat
Typically less than 0.019%/°C and
0.03%/hour.
‘OUTPUT LEVEL,
Calibrated Steps |
10 dBm to ~ 60d8m into 600 $ in eight
10 48 steps, £0.2 48 at 0 dBm and 1 kHz,
Step Accuracy 10.1 d8/10 GB step.
Stapility
Typlealy beter than 07 GB" and
003 devour.
Variable Range
position
REV AMAY 1980
342.2 dB to <-10 dB from calibrated
WW
Specitication—SG 505
Table 1-1 (cont)
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Front Panel)
‘Characteristics
Performance Requirements
‘Supplemental Information
OUTPUT LEVEL (cont)
Maximum Qutput
10 dBV (1 12.2 dBm) oF 3.16 V rms into
600.0.
6 Vrms unloaded
Settling Time
“= seconds to 0.2 a8 of final value,
20 Hz—100 kHz, typically <3 seconds
above 100 Hz, Worst case transient
overshoot is <3 48.
LEVEL FLATNESS
(1 ktiz reference)
10 H2—20 kHz
20 kiiz—100 xHz
40.108
£0.2 dB (exclude ~60 dB OUTPUT LEVEL,
attenuator range)
DISTORTION
(Ry 3600 9)
20 Hz—20 kHz
10 H2—20 He,
20 kH2—50 kHz.
50 kHz—100 kHz
+<0.0008% (—102 48) thd,
<0.0018% (—25 0B) thd,
+<0.0032% (—90 48) thd
Refer to Butfered Main Qutput toad
Impecance limitation under Electrical
‘Characteristics (Rear interface)
Typleally <0.0009%
ouTPuT |
Impedance | 800.0 2%, Floating or grounded through approxi=
| mately 30 9. Output impedance coos
not change with OUTPUT ON/OFF
selection
De Onset { “1% of output ac ms voltage
Maximum Floating
Voltage
£30 V peak. (0.01 uF between output
common and chassis ground in floating
mode.)
Line Related Common
Mode Output Voltage
In Floating Mode
Typically <50 mV ems into an open
circuit.
‘SYNC OUTPUT ‘Sine wave with same frequency
Signal ae aint ‘Thd Is typically <2% and phase shift
200 mires 420% sine wave to 20KHz, from OUTPUT ts typically < 5°
at least 120 mv at 100 KHz, 20 He to 20 kta
Impedance | 1 KA, E10%, ground referenced and
Isolated trom main output
12 EV JUN 1981
Table 1-1 (cont)
Specitication—SG 505
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Front Panel)
Characteristics
| Pertormance Requirements
Supplemental information
INTERMOO TEST SIGNAL)
(Optional)
Signal
[Lf sine wave mixed with normal oscillator
output in a 4 (0.1) to 1 amplitude ratio.
SYNC OUT signal is #f component only,
Lt Freauency
Level
Rasidual ima
Tintarnally selectable 60 Hz (2% )or
|250 Hz (2%)
[Composite peak-to-peak output is within
| £0.2 68 of the normal oscilator mode
|eine wave outout.
Typically <0.0005% from 25 KHz to
10 kHz and <0.001% from 10 kHz
10 20 kHz,
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Rear Intertace)
Characteristics
Performance Requirements
‘Supplemental Information
Buffered Main Outout
Syne Output
Ping 25A and 264 (common). Unity gain
| putferea version of the actual output
signal from front panel connector.
Pin 26A is electrically connected to front
panei OUTPUT common. To prevent poss-
ible instrument damage, do not float
output in excess of #30 V peak. Output
impedance is approximately 800 0. To
prevent degradation in oscillator dis-
tortion at the front panel, the rear
Interface load impedance must be =1 kA.
This output is inteded to provide an
ac signal level reference for gain
measurements, Th is typically <0,03%,
Pins 278 and 288 (ground). Approximately
200 mV rms sine wave identical to front
pane! SYNC output signal, Output
Impedance is approximately $0 2
and always ground referenced
Table 1-2
MISCELLANEOUS.
Characteristics
Powor Consumption
Calioration interval
Warm-up Time
Pertormance Requirements
Supplemental Information
6 VA or less.
1000 hours or 6 months,
30 minutes,
REV JAN 1983
13
‘Specitication—SG 505
Table 1-3
ENVIRONMENTAL”
Characteristics
Description
‘Meets MIL-T-268008, class 5
Temperature
Operating oct +50°C
Non-Operating 85°C to +75°C
Humidity 30.35% AH for 5 daye cycled to 60°C. Exceeds MiL-T-288008, class 5
aititude : Exceeds MIL-T-260008, class 2
Operating 4.6 kr (15,000 11,
Non-operating 15 km {50,000 ft).
Vibration (0.36 mm (0.015") 10 Hz to 65 He, ‘Meets or exceeds MiL-T-288008,
75 minutes” ‘class §, with exception in certain
power modules.”
‘Shock | 30g (1/2 sine), 11 ms, 1 shocks Meets or exceeds MIL-T-288008,
Bench Handling
Electrical Discharge
45° of 4” oF equilibrium, whichever
occurs first
Mo. MIL-STO 461/462.
20 KV maximum,
class 5, with exception in certain
power modules
‘Meets MIL=T-288008, claas 3.
Meets MIL-T-288008, class 3.
(Charge applied to each pro-
truding area of the product under
test except the output terminals,
‘Transportation®
Vibration
Package Drop
“with power module except where noted.
25 mm (1°) at 270 ¢pm for 1 hour.
40 drops from 91 cm (3 fy.
* 128 mm (0.01!) 10 Ha to 55 Hz in TM 207, 144 5U3, TM 508, TM 300,
20 g's (V2 sine), 14 ms, 18 shocks In TM 501, TM 503, TM 504, TH 506.
“yout power module
Table 1-4
‘Qualified under Navonal Sate
Transit Association Preshipment
Test Procedures 1A-B-1 and 1A-B-2.
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(Charactorises
Description
Finish
Plastic-aluminum laminate front panel
Net Weight
Overall Dimensions
1.13 kg (2.49 tbs).
{67.08 mm (2.640") W x 908.96 mm (12.140") D x 126.24 mm (4.870") H.
14
REV AOCT 1980
Section 2—SG 505
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
Preparation for Use
The SG 505 Oscillator is calibrated and ready for use
when received. it operates in any compartment of a
TM 500 series power module. Refer to the power module
struction manual for line voltage requirements and
power module operation. A list of standard accessories
and part numbers) is located in the back of this manual
‘The SG 505 Option 01 instrument has an intermodula-
tion test function that mixes a 60 Hz or 250 Hz sine wave
with any selected frequency at the OUTPUT connector.
The SG $05 contains an internal jumper that may be
positioned to cnange themixed 60 Hz sina wave to 250 Ha,
‘The instrument is shioped with the jumper in the 60 Mz
position, Refer internal jumper selection to qualifies
service personnel
3 cauTion §
dAnnnnnnns
Turn the power module off before inserting or
removing the plug-in; otherwise, damage may occur
(0 the plugein circuitry.
Check to see that the plastic barriers on the inter~
‘connecting jack of the selected power module compart-
ment match the cuteuis in the SG $05 circuit board edge
Connector. Align the SG 505 chassis with the upper and
lower guidas (see Fig, 2-1) of the selected compartmen
Push the SG 505 chassis in and press firmly to seat ine
circuit board edge connector in the interconnecting |
Pull out the power switen on the power module. The
POWER indicator light on the front panel should light
soTtom
GROOVE
Fig. 2-1. SG 505 installation and removal.
24
Installation Instructions SG 505
To remove the SG 505, pull on the release latch
(located in the lower laft corner) until the interconnecting
Jack disengages and the SG 508 slides out
Repackaging Information
Wf the Tektronix instrument is shipped to a Tektronix
Service Center for service or repair, attach a tag showing
‘owner (with address) andthe name of aningividual at your
flem to contact. Include the complete instrument serial
umber anc a description of the service required.
‘Save and reuse the package in which your instrument
was shipped. I{ the original packaging is unfit for use or
not available, repackage the instrument as follows:
Surround the instrument with polyethylene sheeting to
protect the instrument finish. Obtain a carton of
corrugated cardboard of the correct carton strength
having inside dimensions of no less than six inches.
more than the instrument dimensions. Cushion the
instrument by tightly packing three inches of dunnage
oF urethane foam between carton andinstrument an al
sides, Seal the carton with shipping tape or an in-
dustrial stapier.
The carton test strength for this instrument is 200
pounds per square inch,
CONTROLS AND CONNECTORS
FREQUENCY SELECTION
@ FREQUENCY He Dit
Provides continuous frequency selection within
‘each pusnbutton selected frequency range.
@ mater Pusnbuiton
Select any one of fur reqveny anges
@ Fro vernien oa
Adjusts frequency +1% from selected frequency
OUTPUT LEVEL SELECTION
@ourrur ever 4am) ott
Selects one of sightampitudelevel steps calibrates
ina ino 2660 load
@ ourwur ever aon) CAL ois
Provides continuous amplitude adjustment above
and pelow the calibrated OUTPUT LEVEL (dm)
steps.
@ntenmo TEST sig Pushbutton (Option 01)
Pushbutton in provides a 60 Hz or 250 Hz (see
Preparation for Use) sine wave mixed with any
selected output frequency in a 4:1 amplitude ratio,
Also provides @ 60 Hz or 250 Mz sine wave at the
SYNC OUT connector.
@ owcorF Pushbutton
Connects or disconnects the signal to the OUTPUT
connector.
22
@® SNDED-FLTG Pushbutton
GNDED connects the OUTPUT connector outer
conductor (shield) to chassis ground through alow
impedance.
FLTG connects the outer conductor to ground
through a capacitor for floating operation.
OUTPUT CONNECTORS
@ oureur comector
Provides a sine wave signal at a frequency selected
by the FREQUENCY Hz dial and multiolier pusnout-
ton at an amplitude salected by the OUTPUT LEVEL
(Bm) cial (Option 01, see INTERMOD TEST SIG
Pushbutton (6)
@srwe our connector
Provides ~ 200 mV rms fixed amplitude and ground
referenced sinusoidal signal at the same frequency
as the OUTPUT signal. (Option 01, see INTERMOD
TEST SIG Pushbutton (6}).
@ scoune sinsing Post
chasse aroun
@ Release Latch
Pull to remove plug-in trom the power madule,
@ POWER Indicator
Indicator lights when power is applied to instrument
from power module,
Installation Instructions—SG 505
OPERATORS FAMILIARIZATION
General Operating Information
with the $G S05 properly installed in the power
module, allow thirty minutes warmup time or operation to
specified accuracy.
‘Output Connections
The output of the SG 505 at the OUTPUT connector is
designed to operate as 2 600 2 voltage source working
into a 600 2 load. At higher frequencies, an unterminated
for improperly terminated output may reduce amplitude
accuracy. Loads less than 600 9 may cause waveform
distortion, To ensure waveform purity, observethe follow-
ing precautions:
1. Use good quality coaxial cables and connectors,
2, Make all connections tight and as short as possible.
The signat at the SYNC OUT connector is designed for
use as an external trigger for a counter, oscilloscope, of
other device. This output is approximately 200 mV rms
with a source limpedance of 1 kA, andis always raterenc-
2d to chassis ground (even whan the main OUTPUT is
Aoating).
With the Option 01 INTERMOD TEST SIG pushbutton
in, the OUTPUT signal at the SYNC OUT connector Is.
replaced by either 60 Hz or 250 Hz (depending on the
internal jumper setting),
CAUTION §
19 avoid damage to tne SG 505 circuitry, do not
apply a voltage exceeding 30 V peek, with respect 10
chassis ground, to any front panel connector or 0
rear interlace connector pins 144-284 and 148-288,
Frequency Selection
The SG 905 produces a sine wave signal at any
eequency from 10 Hz: 100 kHz, To setthe frequency, set
tne FREQUENCY Haz dial to the desired frequency and
press the appropriate multiplier pusnbutton, The FREQ.
VERNIER dial may be used to adjust the OUTPUT.
frequency 1 percent above and delow the frequency
selected by the FREQUENCY He dial and multiplier
Sushbutton, With the FREQ YEANIER dial at the center
position, the output frequency produced is the FRE-
QUENCY He dia setting multiplied by the active multiplier
value. Signals at the OUTPUT and SYNC OUT connectors
are of the same frequency. The SYNC OUT signal can be
Used as an external signal for monitoring the OUTPUT,
24
provided no more than approximately 200 mis required
from the SYNC OUT connector.
Output Level Selection
‘The OUTPUT LEVEL dial selects eight lave! steps irom
+10 d8m to~60 dBm. The CAL control, concentric within
the OUTPUT LEVEL (aBm) cial, permits continuous,
adjustment above and below the caliorated output evel
steps. The signal at the OUTPUT connector may 02,
ground referenced or floated up to +30 V peak, using the
FLTG-GNDED pushbutton. The ON-OFF pushbutton
connects or disconnects the signal at the OUTPUT
connector.
intermodulation Test Signal (Option 01)
With the INTERMOD TEST SIG pushouttonin, a 60 Hz
oF 250 Hz sine waveis mixed with any selected frequency
at the OUTPUT connector in a 4:1 amplitude ratio. The
composite peak-to-peak amplitude is set equal to the
Peak-to-peak amplitude of the unmodulates OUTPUT,
signal. The Intermod Test Sig LF frequency sine wave is,
selectable {60 Hz or 250 Hz) by means of an internal
jumper. The SG 505is shipped with the internal jumper in,
the 60 Hz position, Refer internal frequeney selection to
gualifiec service personnel. {Information for internal
solection is provided in the Maintenance Section of this,
manual.)
In the INTERMOD TEST SiG mode, the SYNC OUT
connector provides only the 80 Hz or 250 Hz sine wave,
Rear Interface Signals
A unity gain buffered OUTPUT signal is available at
rear intertace connector pins 25A and 26A (commont.
When the rear interface OUTPUT signal is used, the reer
interface load impedance (pins 25A and 26A) must be
kA, 0 prevent OUTPUT amplitude cistortion, The ON-
OFF and FLTG-GNDED pushbuttons affect the rear
interface output signal as previously described for the
front panel OUTPUT signal
‘The signal at the front panel SYNC OUT connector is
also available atthe rearintertace connecter. pins 278 ana
288 (ground). The output imoedance at these rear inter=
face pins is approximately 50 0 and the signal is always,
referenced to ground. in an Option 01 instrument, the
INTERMOD TEST SIG pushbutton also affects the rear
Interface SYNC OUT signal as described for the front
panel SYNC OUT signal
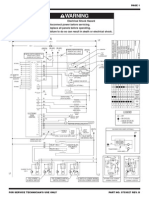
WARNING
THE FOLLOWING SERVICING INSTRUCTIONS
ARE FOR USE BY QUALIFIED PERSONNEL
ONLY. TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY, DO NOT
PERFORM ANY SERVICING OTHER THAN THAT
CONTAINED IN OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
UNLESS YOU ARE QUALIFIED TO DO SO.
REFER TO OPERATORS SAFETY SUMMARY
AND SERVICE SAFETY SUMMARY PRIOR TO
PERFORMING ANY SERVICE.
RA RB BR BA A AB EB A BEB BA BA AY
Section 3-SG 505
SERVICE PART
THEORY OF OPERATION
Introduction
This section descrives the SG 505 circuitry. The
description is divided into parts thal correspond to the
Circuit blocks shown on the block diagramin the Diagrams
section of this manual. Each of inese circuit blocks is also
outlined in gray on the circuit diagram on which it is
shown, The numbered diamond by each title of the
following description refers to the corresponding circuit
diagram number. The A10 of Atl number identities the
board assembly containing the circuit.
Phase Shit Oscitator <)> A10
The phase shift or state vatlable oscillator consists of
U1510, U1400, UT401, and associated components. Two
integrators, Ui400 and U1401, each having a 90° phase
shift, are cascaded in a logp with inverter 1510. Com
pining the phase inversion of U1510 with the two 30°
phase shifts of the integrators causes 3 360° phase shitt
necessary for oscillation, Feedback occurs from pin 6 of
U1401 to pin 2 of U1510 through F517 and A510.
The output voltage rate of change of an integrator is
proportional te tne input voltage amplituce. The integrator
timing capecitore and gain detarmine the oscillator fron
quency. The gain around tneioop isunity atthe oscillation
frequency,
Multiplier pushbuttons $1410 select the timing capac-
ors across the integrators for each frequency range. The
FREQUENCY Hr dial adjusts A520 and R520to control the
gain of the integrators, A small adjustment in the gain of
U1810, through 8810, providing a+ 1% changein requen-
ey. is accomplished by the frequency vernier dial
The signal from U1401 is routed to anetwork consisting
of Q1410, Q1411, and associated resistors and diodes.
This network composes a clamp that limits the maximum
output voltage trom U1401 to n9 greater than 3 dB above
the selected oscillator output level. Output voltage surges,
Created at initial instrument turn on, or due to switching
transiants, ara atfactively eliminated,
@
Amplitude Detector <)> ato
This circuitry provides an accurate relatively long time
constant age voltage. The output signal from 1401 is also
fed to the amplitude detector circuit U1500 (an amplitude
controlled integrator}. U1S00 compares the output of
1401 to the reference voltage (~15 V supply). The
average current through A1504 equals the current through
R500 when the output of Ur401 is 2 Vrms. The output of
[U1500 sets the input offset voltage to the peak detector,
(91600 and 1610,
Peak Detector <> Ato
This circuitry provides a fast age correction voltage.
The offset voltage from U1S00 and the ac signal from
1510 (coupled through C1603) are fedtoa peak detector
consisting of 1600. This circuitry produces anegative de
‘output voltage on the agc tine proportionaitothe negative
peak voltage of the ac signal from Ut510. Age filter
capacitors consist of combinations of C1611 and 1421
61829, and C1420, depending on the frequency range
selected. Between peaks, the agc filter capacitors charge
from positive current source Q1811. Thus, the signal et the
tage test point is a sawtooth wavoform with a fast negative
transition and a positive-going linear ramp. The network
consisting of 21502 and C1502 provides cancellation of
the fundamental frequency component of the age signal
Amplitude Control <)> aro
The amplitude of the phase shift oscillator output is
controlled by Q1801. Age voltage generated by the peak
detector and the amplitude detector controls the gate of
(1501, Components RiSTi, A1512, 81510, Ri813, C1541,
and C1510 farm a voltage divider network. This voltage
A10
‘The output signal trom Ul401 is ted through 81520,
87521, F11423, and 91518 to the output buffer amplifier
U1520. The voltage gain of U1520 is set by 1519, the
OUTPUT LEVEL (dBm) CAL control, and is variable from
about 0.3 10 3, When this control is Tully ew, the ganged
switch iS open and the buffer output amplitude is at the
Worated level set by 81423. Trimmer 91423 is internally
adjusted to set the lavel at the OUTPUT connectoi
1D dm (with $1710 in the 0 dm position)
Output Atenvator and Butler Ampltier <2> A10
‘The signal from the output butter amplifier is ted
through ON-OFF switch S1410E to output attenuator
network A1720, This network has a constant output
impedance of 600. and provides eight output levels.
‘Suiten $1710 selects the output level tap for each of the
eight output levels from +10 dBm to —60 dBm. From
51710, the signal passes to the front panel OUTPUT
connector and to the main output buffer amplifier, U1700.
Amplifier 1700 isolates the front panel OUTPUT connec-
tor from raar interface connector pin 254.
Syne Driver and Syne Ampitier <2> A10
{An optical isolator is used in this circuitry because the
SYNC OUT connector is connected to chassis ground.
‘Output from U1401 also passesthrough U1200tothe base
‘of 21300, Transistor Q1301 produces a de bias current
[necessary to operate the LED in the linear region) which
iscombined with the ac current atthe oscillator frequency.
‘Syne Level Adjustment A1301 sets the gain of 1200 for an
output of 200 mV ims at the SYNC OUT connector. The
‘currant through the LED section of optical isolator U1300
‘varies the intensity of emitted light. This light intensity
Controls the current through the transistor section of the
‘optical isolator. The sync amplifier, consisting of 1900,
1201, and A1200, converts the output current from U1300,
tovoltage. The output of 21900 is coupled through RvzUs
to the front panel SYNC OUT connector and through
21202 to rear interface connector pin 278.
Power Supply a10
Power is supplied to the SG $05 from the 25 V ac
floating winding of the power module. The 25 ac is
applied to the primary winding of T1220. Each of the two
secondary windings supplies 25 V ac, whichis rectitiad by
beridge rectifiers CAI119 and CRI114 and flitered by
©1212 and C1211
“The two series pass transistors in the power module
and UN101A and U11018 regulate the +15 V and —18
32
supply voltages. Resistors A1208 and 1205 divide the
HSV to +82 V at pin 5 of Ut101B. Operational ampiifier
U11018 compares the voltage at pin § with the +82
reference voltage at pin6, suoplied by VA1201. The output
‘of U1101B drives the series pass transistor in the power
module, If the voltage at pin § of UT101B moves below
8.2 V, the output of U11018 goes more negative, causing
more base currant flaw in the PNP series pass transistor.
This raises the +15 to ine level where U11078 can
function, Resistor 1207 and C1200 decouple the +18 v
used in the output amplifier.
‘The —18 V supply tracks tne +15 V supply. Operational
amplifier UTTOTA compares the voltage at pin 3 to ine
floating ground potential at pin 2. The voltage at the
junetion of the voltage divider A1102 and R1101 is OV ih
the +15 V and 15 V supply voltages are correct. If the
15 ¥ supply voltage moves toward ground, the output of
UT101A goes more positive, causing increased base
current and conduction in the NPN series pass transistor
which causes the ~15 V to go more negative. FET Q1110
provides base current to the PNP series pass transistor at
instrument turn on.
Current limit for tne +15 V supply is provided by
RII, CR1112, and A1120. The maximum output for
each supply is 200 mA. At this current the series pass
transistor base voltage is 1.4 more negative than
(ground. If the output of U1101B attempts to crive tne
transistor base voltage more negative than ~1.4V, tne
current limiting diodes conduct, clamping the base at
1.4, The base to emitter voltage of tne series pass
transistor is limited by the voltage drop across R1120. The
negative current limit operates in a similar manner.
Interiodulation Test Signal (Option 01) <> A1t
Cption 01 instruments include an intermodulation test
signal that mixes a 60 Hz or 250 Hz sine wave with tne
Selected frequency in 4:1 amplitude ratio (four partsiow
frequency to one part selected frequency). The circuit
contains a Wein-pridge oscillator composed of U1 100 and
associated components, To select a 60 Hz output at
U1100, jumper P1700 is removed from the circuit. The
oscillator frequency is set to 60Hz by C1100, C1200,
R102, and A113. With the jumper positioned across
J1100, resistors R107 and Fi1104 are added tothe circuit
‘changing the Ieequency to 250 Hz.
A peak datector consisting of CRI110 and Q1110
controls the gain of the oscillator by adjusting the voltage
at the gate of QI111. Resistor At211 is an internat
adjustment that sets the amplitude of the signal trom
ut109,
REV AMAY 1980
Section 4—SG 505
CALIBRATION PROCEDURE
Introduction
‘This section consists of a Performance Check and an
Agjustments pracedure, The Performance Check verifies
the electrical specifications listed under Performance
Requirements in the Specifications section of this manual.
‘The Adjustments pracedure describes a sequential ac-
justment of internal controls should it be necessary to
estore the instrument performance to the electrical
specifications listed in the Specifications section.
Tektronix, ine, provides complete instrument repair
lang celioration at local Field Service Centers and at the
Factory Service Center, Contact your local Tektronix Field
Office or representative for further information.
Test Equipment Requirements
Below is a list of equipment required to perform the
Performance Check and Adjustments procedure. Other
equipment may be substituted wnen suitable, Tolerances
that are specified in the Performance Check anc Ad-
justments procecure apply to the instrument under ‘est
‘and do not include test equipment errr.
Table 41
UST OF TEST EQUIPMENT REQUIREMENTS
‘Application
/ Pertormance Performance | Adjustments
Description Requirements Check Step step, Example
Tha 500 Series Power ‘Allstepe | Allstops | TEKTRONIX TM 503,
Module TM 504, oF TM 508
Gaunter 0.1 He resolution at 1.2.18 1 | TEKTRONIX 0c 504
100 kHz Digital Counter’
Calibration Fixture | 80 dB notch at 10 Hz, 3.4.5.6, 2 | TEKTRONIX 087-0938-00
| 20 2; 60 48 notch at 78,810 Calibration Fixture!
|. 20 kHz, 50 kHz, 100 KH2.
wide Band Fs Eos from25Heio | 8.4.6.7. 2.3 | Hewiett Packard 34030
Voltmeter 300 kH2. 0.6% trom 10 Hz | 10, 17 True ims Vortmeter
10.25 He.
Aims Voltmeter | 20.2% at 1 kee 3,6, 10.11 2.3. | TEKTRONIX OM 501A
Digital Multimeter?
Oscilloscope: 5.8.9.1 4 | TeEKTRONIX 77048
or 7603 Oseitoscope
Vertical Amplifier General purpose, Banc- 2 | TexTRONIx TAISA
width, 10 MHz vertical Amplitior
Differential Comparator | Comparison voltage, 6 V 58 TEKTRONIX 713,
Amplifier overload capability | Ditferentiat Comparator
50 mv/civ gain
Time Base General purpose, 5.8.12 ¢ | TERTRONIX T8508
10 us/div sweep rate
REV AMAY 1960
| Time Base
at
Calibration Procedure—SG 505
Table 4-1 (cont)
‘Application
Performance Performance | Adjustments
Description Requirements Check Step Step
Spectrum Analyzer 102 resolution: 80 48 | s | TEKTRONIX 7L8/L3
aynamic range; ~60 38 | Spectrum Analyzer
reterence level i
Differential Amaliier | Gain of 10,100, 1000 488 TERTAONIK AM 502
|. outost swing >10'¥ | Ditterertiat Amplifier
Tea comia cables | 509 Ailsteas | Al'sieps [-Tektronix Part
with male bne | No. 012-0057-01
Tea Extender Cabie Ail sieps | Tektronix Part
No, 067-0648-02
Bne T Adaptor 0 | | Tektronix Part
| No. 103-0030-00
Termination 300) 3 Tektronix Part
No, 011-0048-01
Tea. comiat cable | 50, 18 inch 3.4.5.6 2 | Tektronix Part
a9 | No, 912-0078-00
“ther ms wotmeter may be used for these steps listed in commen
‘The numbers in Table 4-1 columns refer to the Perfor- @ Cheek Distortion
mance Check ar Adjustment Stapin which the equioment
S used. The following list indexes the steos for each 10, Check Outout impedance
procedure
11, Cheek Syne Out Amplitude
Perlormance Check steps: 12, Chock intermodulation Test Signal Ratio (Oation
1. Check Frequency Accuracy a
18. Check Intermodulstion Test Signal Frequency
2, Check Frequency Vernier Range
Check Output Level Accuracy
4, Check Output Leval Step Accuracy
5, Check Output Level Stop Accuracy (alternative
method}
6. Check Output Levet Variable Range
7, Check Level Flatness
8, Check Level Flatness (alternative method)
42
(Option 01)
Adjustment Procedure steps:
1
2
Adjust Frequency He Dial
Adjust Output Level Amplitude
Adjust Sync Out Amplitude
Adjust intermodulation Test Signal Ratio (Option
on
Calibration Procedure—SG 505
Performance Check
PERFORMANCE CHECK
Introduction
‘This procedure checks the electrical characteristics of
the SG 50S listed under Pertormance Requirementsin the
Specifications section of this manual. If the instrument
{ails to meet the requirements given in this Performance
(Check, the Adjustments procedure should be performed.
Go the Performance Check with the instrument operating
at an ambient temperature of O°C to 50°C. For con
venienea, some steps in this procedure check the perfor=
mance of this instrument at only one vatuein ihe specified
performance range. Any value, with appropriate limits,
withia the specified range may be substituted
Test Equipment Required
‘Test equipment used in the Performance Check is
isted in Table 4-1 at the begineing of this section.
Preparation
1, Engure thet all power switenes are off and that the
power module ang all test equipment are adapted for the
ine voltage available.
2. Install the SG 505 in the power module and connect
ne power module and test equipment to the line voltage
3. Turn on the power module and test equipment.
Allow at least 20 minutes warm-up time for the SG $05 (60
minutes after storage in a high humicity environment)
PROCEDURE
‘Check Frequency Accuracy
a. Set the 8G $08 controls as follows:
FREQ VERNIER centerea
OUTPUT LEVEL (@8m 0
(OUTPUT LEVEL (8m)
cal fully ow
ON-OFF ON ia)
GNOED-FLTG FLTG jouty
INTERMOD TEST SIG
Pushbutton (Opt) OFF (out)
'. Conneet the SG 805 SYNC OUT through a coaxial
cable to the counter input.
‘¢. Set the counter resolution end the SG 808 controls
as listed in Table 4-2.
Table 42
FREQUENCY ACCURACY CHECK
8G 508 Counter Reading
Counter | _ Frequency Hz Limits
Resolution | Dial Pushbutton (kH2)
T 0.0097 to 0.0103
9.0194 t0 0.0206
x10 0.0485 to 0.0518
00879 to 0.0721
| 9.0970 to 0.1030,
19.097 to 0.103
0.194 to 0.208
x10 0.485 100.515
0.679 100.721
0.970 to 1.090
aaTate 1.030
1.940 to 2.060,
| aasoto 5.150
6.7900 7.210
9.700 to 19.300
a70te 10.30
19.40t0 20.60
x 10k 48.50 to 51.50
67.90t0 72.10
97.00 to 103.00
z
tee
tHe
10 He
4. CHECK—that the counter reads within the limits
listed ia Table 42,
2. Leave the connections ang control settings and
proceed to the next step.
2. Check Frequency Vernier Range
a, Change the $6 505 controls as follows:
FREQUENCY Hz Dial
FREQUENCY Hz
Pushbutton xk
43
Calibration Procedure—SG 505
Performance Check
», Set the counter resolution to 1 Hz.
c, Adjust the FREQUENCY He dial for a counter
reading of 1000 He
d, Rotate the FREQ VERNIER contro! fully cow.
2. CHECK-—that the counter reading 1s <0,990 kHz.
Rotate the FREQ VERNIER control fully ow.
g. CHECK-—that the counter reads 31.010 kHz.
fh. Remove all connections to the $G 505,
3. Check Output Level Accuracy
a. Set the SG $05 controls as follows:
FREQUENCY Hz Dial
EQUENCY Hz
Pushbutton xtk
FREQ VERNIER centered
QUTPUT LEVEL (48m) 0
OUTPUT LEVEL (dm)
CAL fully ow
ON-OFF ON Gin}
GNDED-FLTG FLTG (out)
INTERMOD TEST SiG
Pushbutton (Opt.) OFF (out)
2, Connect the SG 505 OUTPUT through a coaxial
‘cable to the calibration fixture {067-0838-00) input
€. Connect the calibration fixture Output through an
18 inch coaxial cable to the rms voltmeter input.
1, Set the calibration fixture Mode to Flat (out) and
nen to 0 dB (out)
2, CHECK—that the rms voltmeter reads between
0.787 and 0.793 V rms.
f. Remove all connections to the SG 505.
4, Check Output Level Step Accuracy
Step 6 is an altarnative method for checking output
level step accuracy. Either stop 4 or step 5 may be
performed,
44
1. Set the SG 505 controls as follows
FREQUENCY Hz Dial 1
FREQUENCY Hz
Pushbutton xk
FREQ VERNIER centered
OUTPUT LEVEL {28m} +10
‘OUTPUT LEVEL {48m}
CAL uy ow
ON-OFF ON Gin)
GNDED-FLTG: FLTG (out}
INTERMOD TEST SIG
Pushbutton (Opt) OFF (out)
b. Connect the SG 505 OUTPUT through a coaxial
‘cable to the calibration fixture Input
c. Connect the calibration fixture Output through an
18 inch coaxial cable to the citferentiai amplifier + input
4. Connect the differential amplifier output through a
coaxial cable to the wide band rms voltmeter input, Setthe
cifterential amplifier inputs 10 de coupled and not ground
fd, Set the high frequency 3 d8 control to 1 MHz.and tne
Tow frequency 3.48 control to 0.1 Hz
fe. Set the calibration fixture Mode to Flat (out) and
Aten to 0 8 (cut).
£. Set the aitferantial amplifier gain to the first vatue
shown in Table 4-3,
9. Set the SG 50 OUTPUT LEVEL (48m) control to
the first value listed in the table.
h. Adjust the differential amplifier variable gain for the
first rms voltmeter reading shown in the table,
i. Sethe SG 505 OUTPUT LEVEL (8m) control tothe
second value listed in the table.
j. CHECK—that the ems voltmeter reads within the
limits listed in Table 4-3
k, Repeat step 4 parts f through j for each of the
remaining lines in the table
Calibration Procedure—SG $05
Performance Check
Table 4-3
OUTPUT LEVEL STEP ACCURACY CHECK
|
x10 -10 dam | 1.800 V | -20 dBm 0,562 to 0.576 V
100 =40.dBm | 0.700 v | -80 dm | 0.218 10 0.224 v
x10 | -80d8m | 1.800 v | 60 cam 0.87
|. Ramove all connections to the SG 506.
5, Check Output Level Step Accuracy (alternative
method)
4, Set the SG 505 controls as follows:
FREQUENCY Hz Dish 1
FREQUENCY Hz
Pushbutton atk
FREQ VERNIER centered
OUTPUT LEVEL (8m) +10
OUTPUT LEVEL (dm)
CAL tally ew
ON-OFF ON (in)
GNDED-FLTG FLTG (out)
INTERMOD TEST SIG
Pushbutton (opt) oF
(out)
b. Connect the SG 505 OUTPUT through a coaxial
cable to the calibration fixture Input
©. Connect the calibration fixture Output through an
18 inch coaxial cable to the differential amplifier + input.
Set the differential amplifier inputs to de coupled ana not
‘rounded, Set the nigh frequency 3.48 control to 1 MHz
and the low frequency 3 d8 control to 0.1 Hz
1. Connect the differential amplifier Output through a
coaxial cableta tne ascilloscope differential comparator
input.
©. Set the calibration fixture Mode to Flat (out) and set
the Atten to 60 4B (in)
{. Sat the vertical amplifier valts/civ to SO mV/div. Set
the cifferential comparator input to gnd and adjust the
vertical position cantral to place the trace on the center
orizontat graticule ine, Make certain the de comparison
voltage is connected to the — input of the differential
‘comparator via front panel selection and the + input is de
coupled
1g. Set the differential amplifier gain control anc
pushbutton as listed in the first line of Table 4-4
h. Set the differential comparator voltage to the first
‘value shown in tne table.
i. Adjust the differential comparator variable gain to
position ihe wavufurm peaks on the oscilloscope display
to the center horizontal graticule line,
|. Change the 8G 505 OUTPUT LEVEL (d8m} contro!
to the value shown in the table.
k. Adjust the differential comparator voltage to oosi-
tion the waveform peaks onthe center horizontal graticule
line,
|. CHECK—that the differential comparator voltage is
within the limits shown in the tabie,
im, Repeat step § paris g through I lor the remaining
tines of the table,
45
Calibration Procedure~SG 505
Pertormance Check
Table 4
4
OUTPUT LEVEL STEP ACCURACY CHECK
Ditlerena
itera Ditrentia item eases | Comparator
Amplifier Amplifier | Comparator. | OUTPUT LEVEL Voltage
Sain Node _|___volage (am) Conol__| Limite
700 7 100 oa v 28m Gaara roa
‘09 #100 toy | =10.e8m dave to 0328 ¥
Ve zim | aay | 208m 1000 1988
1k +109 ov “20 ¢8m 03%6 1003264
429 Nom aizc0 v ~10 com 100 to 1084
409 Noa 101 v “20 ¢6m dare too 326 y
te NORM aiaco v “20 66m 1000 1924
1. Remove all connections to the SG 505.
& Check Output Level Variable Range
2. Set the 8G 505 controls as follows:
FREQUENCY Mz Dial
FREQUENCY Hz
1
Pushbutton xk
FREQ VERNIER centered
OUTPUT LEVEL (dBm) 0
OUTPUT LEVEL (dBm)
CAL fully ow
ON-OFF ON (in)
GNDED-FLTS GOED (in)
INTERMOD TEST SIG
Pushbutton (Opt.) OFF (out)
. Connect the SG 508 OUTPUT through a coaxial
cable t0 the calibration fixture Input.
Connect the calibration fixture Output through an
18 inch coaxial cable to the rms voltmeter input.
1d, Set the calibration fixture Mode to Flat (out) and
AAtton to 0 dB (out). :
2. Turn the SG 505 OUTPUT LEVEL (48m) CAL,
contro} slightly cew (just out of detent),
1. CHECK—thattherms voltmeter reads 31.000 Vrms.
g. Turn the SG S05 OUTPUT LEVEL (dBm) CAL
control fully ecw.
46
h. CHECK—that the rms voltmeter reads <0.245 Vv
|. Leave the connections and controt settings and
proceed to the next step.
7. Check Level Flatness
Step 8 is an alternative method for checking level
flatness, Either step 7 or step 8 may be performed.
a. Change the SG 506 controls as follows:
(OUTPUT LEVEL (dBm)
aL. fully ew
. Connect the calibration fixture Output through an
1Binch coaxial cable to the wide band+ms voltmeter ingut.
¢, Adjust the OUTPUT LEVEL (8m) CAL control tora
voltmeter reading of 0.75 V. Do nat change this control
position for the rest of step 7.
©, Set the SG 505 FREQUENCY Hz dial and FRE.
QUENCY Hz pushbutton as listed in Tabie 4-5
e. CHECK—that the rms voltmeter reading is within
the limits listed in Table 4-5,
1, Repeat step 7 parts c 1
lines of the table.
ugh e for the remaining
Tal
Calibration Procedura—SG 505
Perlormance Check
ble 4-5
LEVEL FLATNESS CHECK
8G 505 8G 505
FREQUENCY Hz | FREQUENCY Hz Ams Voltmeter
Dial Pushbutton Reading Limits z
7 «10 : (0.766 to 0.784 Vrms
2 x 10K
5 | x 10K 0.787 to 0.783 V ems
10 l x 10K
g. Remove all connections to the $G 505,
& Check Level Flatness (alternative method)
a. Set the SG 505 controls as follows:
FREQUENCY Hz Dial
FREQUENCY Hz
1
Pushbutton xk
FREQ VERNIER centered
OUTPUT LEVEL (28m) +10
OUTPUT LEVEL (gm)
om fully ew
ON-OFF (ON tin}
GNDED-FLTG FLTG (out)
INTERMOD TEST SIG
Pushbutton {Ost OFF (out)
b. Connect the SG 505 OUTPUT through @ coaxial
cable (6 the calibration fixture Input
cc. Connect the calibration fixture Output through an
18 inch coaxial cable to the oscilloscope differential
comparator + input
4, Set the calibration fixture Made to Flat (out) and set
the Atten to ~80 dB (in)
@. Set the input coupling to ground and adjust vertical
position to place tne trace on the center horizontal
graticule line. Make certain the de comparison voltage is,
Connected to tne ~ input of necifferential comparator via
front panel selection ang the + input is ce coupled
f. Adjust the differential comparator voltage to
1.727 V. Adjust the SG 505 OUTPUT LEVEL (dBm) CAL.
‘entrol to position the waveform peaks on the center
horizontal graticule ine.
9. Change the SG S05 FREQUENCY Hz dial end
pushbutton as listed in Table 4-6.
h. Adjust the differential comparator voltage to repesi-
tion the wavetorm geaks on tne center horizontal graticule
line,
i, CHECK—that the comparator voltage readout is
within the limits lites in Table 48 for each frequency
setting
Table 4-6
LEVEL FLATNESS CHECK
SG.S0S FREQUENCY Hz__| Comparator
Pushbuiton | _Vottage Limits
10
z 410 1.707 to 1747
z 10K
10 10K 1.687 to 1.767
ji. Remove all connections to the SG 506.
9. Check Distortion
Nore
A complex and lengthy procedure is required to
venly the SG 508 ultra-low distortion, Unless there
is reason to suspect the SG 505 may nat meat its
Gistortion specification because Of recent repair or
accidental abuse, i1)s suggested that this procedure
bbe omitted. Distortion can de easily and quickly
checked fo the residual limits of almost any commer-
cially available distortion or specteum analyzer
Performance Check
a Set the SG 505 controls as follows:
FREQUENCY Hz Dial =
FREQUENCY Hz
Pushbutton x10
FREO VERNIER centered
OUTPUT LEVEL (68m) +10
OUTPUT LEVEL (8m)
CAL just out of detent
ON-OFF ON {in}
GNDED-FLTS FLTG (out)
INTERMOD TEST SIG
Pushbutton (Opt) OF F (out)
b. Connect the SG 505 OUTPUT through a coaxial
cable to the calibration fixture Input. Connect the calibra-
tion fixture Output thraugh an tBinch coaxial cabletothe
differantial amplifier + Input. Connect the differential
amplifier output through @ coaxial cable to L3 input.
Connect @ 509 termination or short to the differential
amplifier ~ input. Set ihe differential amplifier gain to 100.
‘Set both input coupling to de. Setthe high frequency 3 8
control to 1 MHz and the low frequency 3 d8 control to
ot He
c. Set the calibration fixture controls as follows:
NOTCH FREQUENCY 10 Hz
Move Flat (out)
ATTEN ~80 68 (in)
4, Set the 7LS controls as follows:
FREQUENCY 50 Hz/div
RESOLUTION ioHe
TMEV 10 sec/div
Los 10 aB/aiv
SOURCE MODE FREE RUN, NORMAL
Set the L3 controls to 1 MQ, dBv.
@, Set the 7LS.A & B to off and manual sweep. Adjust
the 7L5 manual sweep dial to position the dot horizontally,
In line with the 10 H2 graticule mark (see Fig. 4-1). Adjust
the 7LS Reference level control to position the dot
Vertically on the top gratieula tine, This ine is the ~80 dB
reference level
1. Set the calibration fixture Mode to Notch (in)
position and the Atten to 0 dB (out). Adjust the SG 505,
FREQ VEANIER cial and the calibration fixture Ad) For
Null controls to position the dot vertically to the most
stable paint below the ~80 dB level on the display. (See
Fig, 4-1) Set the 7L5 A & 8 to then position and normal
sweep mode,
10e/toe soz
Fig, 1. 10 Hz null adjustment
9. Note the 2nd, 3rd, 4th, and Sth harmonics on the
displayed waveform (see Fig, 4-2). If the harmonic
“amplituces on either side of the 0 Hz are slightly different,
average the two readings for each harmonic.
Fig ¢
2. 10 Hz harmonic distortion display.
NOTE
Due to the purely passive nature of the 087-0998-00
Calibration Fixture, the losses at the various far-
monies must be fakon into account 10 correct the
harmonic values noted an the spectrum analyzer
display, The following ioss correction) tactors must
be added to the displayed values fo ootain corrected
values
Table 4-7
HARMONIC CORRECTION FACTORS
CN ae
| Notch Frequency Setting
JO Hz to
2okHz | SokH2 | 100 kHz
a5 10 105
60 85 7
45 5 88
Las 4 45
fh. Compute the total harmonic distortion (thd) using
the harmonic valuas nated and eitner of the two following
metneds.
Formula Method for Computing th
‘Substitute the narmonic values (in 48}, noted in step 9
part g, in the following formula:
thd=20 X log A
pea Sg
eg ga MO
The numbers added to the harmonic values In the
formula are correction factors or the calibration fixture at
10 Hz Notch Frequency.
1. For example, using the harmonic distortion levelsin
Fig, 42 and the corrections factors in the previous
formula
2nd harmonic = ~110 48 + 9.5
3rd harmonic = —107 dB +6
4th harmonic = ~115 48 + 4.5
Sth harmonic = ~121 dB +35
dividing by 10 and raising 10 to this power gives:
100.5 + 10 = ~10.08 107! = 89.12 X 10
stor = 105-101 10" = 79.49 x 10%
110.5 + 10 = ~11,05 10" = B91 X 10%
117.5 + 10 = ~11.05 10"? = 1.77 X 10
Te2xio
taking the square root results ini
fie2cie 34x 107
raking the log:
logis 1.24 10° = 487
multiplying by 20:
4,87 X20 = -97.46 dB thd
REV A OCT 1980
Calibration Procedure—SG 505
Performance Check
Table Method for Computing tha:
‘Add the calibration fixture correction factors to the
harmonic distortion levels noted in step 9 part g. For
example, using the harmonic distortion levels in Fig. 4-2
and the calibration fixture correction factors for 10 Hz
Noten Frequency,
2nd harmonic = ~110 48 +95 = ~1005
3¢g harmonic = ~107 dB +6 = =10t
th harmonic = 115 dB + 4.5 =
Sth harmonic = ~121 dB + 3.5
Compute the arithmetic difference between the two
numerically lower dB values—in this case, —100.5 and
“101. Locate this diference value (0.5) in Table +6. Ifthe
soLv7II980
‘ASHD NI GaLOIdad HO
2661 wy Age
eae 961 190 nau
s01e47959—peys
mo Bunoons@igne1 ee “Bk
‘Oustu ‘OLSIA
Lorin ‘oorin 49949
rear}
zero “aowis 128U9
Tene
Dzuty “OuLis "9 OPIS
vaisi “best x84.
Oe “eto
inpaserd stuouisnioy,
voleL ‘DoLvis Ho0ud Lieto “aotvis $051,
Jou ur ¢ dais, wiokeg
224 oot
tngino
‘tr
THF
0 mH ADNaNDALS HS
41001
©} 2H AONanOgES 19S
gomuaini %
S482 330-No "way
ZH LO} SS 9S,
@ @® uo1vtoso
o
sos 9s
Ayo 30N3H3434 LNaNOUINOD
“IMWHO MOT Sik BOLT ISO
Table 8-3
COMPONENT REFERENCE CHART
P/O AIO ASSY Output
Gireut Schematic Board Pf) cwcut Schematic. Board
Number Location Location MJ NumberLocalion Location
"SEE PARTS LIST FOR SERIAL
NUMBER RANGES
xi@x] aC]
To 20 30 40 50 50
xiK] 8
[12011019 90 90 70
clee ee eo
s meee 0 0 0 0 0 oO
si410
chee ee 8 8
ee e@ 0 © © © oO
io 20 30
ON-OFF] & [ ecole
GNDED °° 0 0
ritc |- Co} 6 0 6
NOTES:
VIEWED FROM BACK
OF BOARD
wean 5861 Av Aa
‘yddns smod—veys
oy Sujooysayqnony 9 “Bis
pou samod wt nh res Tour for
ssta sous pub “o9ituD. r HWS,
OLLLO “W LOLA WEN “W22hL PEELYD YORK ZiibUO.“OLLLO | ¥>8D
Eiusug eet ozerd
22ua pue ofmpou Jomod
24 208I10n Bult OOD
ompou
somod uy soyseuen see
seuss pue suonsouUe>
soeuaiur seer xo,
“az ude vous 10)
Sinpow samed
“tei seed sou2s 3249
‘ainpow'romod ur ose
i ssed so08 0K),
vin
tei
‘axyisod ds0w
faddne ast
Pio1in w200|
LObIn pUe aLLLO ¥DeHD
fivrent
<> Alddns uamod
$05 98
AUVHO 3ONSUIISY INsHOSWOD
HadnS W3MROd~ LUO MOTE SL
Table 8-4
COMPONENT REFERENCE CHART
PIO RIO ASSY Power supply Gp
Circuit Schematic Board [J Ciroull Schemelle ~~ Boara
Number Location Location J Number Location Location
i018
vaio
&
POWER SUPPLY
sos os
TAdHWAA WIGAN. LNANOdHOD
@ardains wanod
Reais.
Revues
vigrin
“UeLw)ptoquondo awis-e°813
ey T
8
ZoLie 10 oouep
wos uaannr
fom
gun
out
ove
Zou
“sawn ope00y —_uoREa0y
aneweuss ino. piwog neways
D verso on assy suv
LYVHO JONSYSIIY LNSNOdWOO
$-8 21021
dl¥S NOILVD01 SLuVvd
sos 98
1uyHO 3ONRUaI3u LN3NOdNOD
(ASSv tL) NOLLWS01SLuWe
Imo OPTION
$05 98
“> NoLLdo oH oss avy As
ovis [pte i834]
ses 95
Ohi cosnaanncmntannisage:
003 “AUD NI G3191430 YO
zur GNITLNO Siva dO SSONVE
WRaWAN Iwiuas ONY Sana
arTuva dod 1817 Suva 338
woore.
4 Ga nse sp £Lec: (SEE Pt110 REPL)
(oerion‘0% ont)
352-0163-05 2 HDR, TERA ConW:5 MIRE, cREEN 0009 262-0163
REV SEP 1986 9-5
sos OS
8G 505
A3NIavo 2 "O12
[ADD MAY 1885
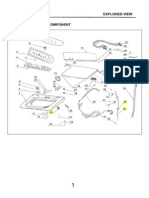
Replaceable Mechanical
Parts ~ $6 508,
Fig. &
Index Tektronx —_Serial/Assembly No. Mtr.
Now Part No, EMtectwe"Dscont _oty 12345 _Name_& Description ce_Mtr Part No.
24 105-0932-00 aoazze0 2 LATCH, PeNeL:sI0E noes 195-0852-00
“2 Zae-3968-00 B0ea2e0 2 FASTENER, LATOMEACETAL, St. GRA po0a 21¢-3568-00
<3 3:7-3038-00 spsaze0 2 swe clec:si0e foca 337-2038-00
“&— 3e6-1051-07 soaaze0 3 ewoe LATCH: IVORY 6 0.625 x 0.25 x 1.09 ‘00c8 365-¥857-05
“5 0§-0865-00 s0eaze0 4 ane, LATCH ause: ‘008 195-0g65-00
“6 4os-oeee-00 spazze0 1 Lert RETAINING: sorery ‘ocs 105-0668-00
7 preates-oo apze0 1) SPRING HUEXT:0.125 0D x 0.585 | XLOOP soca 214-3763-00
3 353-1855-00 soaaze0 1 FRONT BNC 85 ‘ocs 333-1855-00
STANDARO ONLY}
399-1950-00 5062790 1 FRONT ONL aSSY 008 333-s860-00
(OPTt0N o7 ONL)
-8 337-g010-00 ansaze0 4 SHIELD.caT gnoce 397-0010~
Sto 24e-3406-00 apazze0 1) SPRING, FLAT: 1.98 LX 0.725 M,C0 BE ‘soos 219-3<06-29
sit eg-0725-24 speazeo 1 FR Sect. Puus-invoP 08 425-0725~
(arTacnins ats)
2 arr-oror-9o apeezeo 2 SCRON,WACHINES4-£0 x 0.25,FUxH,100 DEG, STL WOH3E ORDER OY DescR
(Bo ATTACK 60675)
13 426-0725-25 soezze0 4 FR SECT PUNG-IN:s0TTOM ce 425-0724-25,
(arTacsins ats)
2ri-o10-00 e0ez2<0 4 SCRON MACHINE: €0 x 0.25,FUH 100 EG, STL 10495 oBoER By D856
244-0025-00 5062240 1 SCRON‘MACHINE:4-a0 x 9.975,FUK,100 O86 T0495 ORDER BY DESCR
(0 arracwiNg 90675)
306-4965-00 a08z240 1 SUPPORT FRBME: SER, a noes 385-#866-09,
(artacking pa2Ts)
213-0793-00 8082280 2 SERON,TPO,TF:8-32 4 0.4975, TRPTITE, FIA 3see 239-006-405089
‘sawoae accessoe1es
070-2823-00 4 wana TECH: INSTR 80009, 070-2023-09
REV SEP 1986 9-7
8G 505
ACCESSORIES:
Fig &
Index Tekisonve Serial/Mode! No mtr
No PartNo. Eff ——Dscont_ aly 12345 Name & Description Cove Mitr Past Number
70-262%-00 1 MANUAL, TECH: INSTR, S505 OSCLLLATOR sn009 970-2623-00
saluoss390Vv
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- LG LFX31945 Refrigerator Service Manual MFL62188076 - Signature2 Brand DID PDFDocument95 pagesLG LFX31945 Refrigerator Service Manual MFL62188076 - Signature2 Brand DID PDFplasmapete71% (7)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- GE Fridge DiagnosticsDocument6 pagesGE Fridge DiagnosticsplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Automatic Washer: Study Course (Belt Drive Models)Document24 pagesAutomatic Washer: Study Course (Belt Drive Models)plasmapeteNo ratings yet
- 1042 EI24ID81SS0A Solaro Dishwasher SM V3.0Document73 pages1042 EI24ID81SS0A Solaro Dishwasher SM V3.0plasmapeteNo ratings yet
- Ge Laundry Diagnostic ModesDocument128 pagesGe Laundry Diagnostic ModesplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- KitchenAid Range KESC3008WH11 - Service ManualDocument6 pagesKitchenAid Range KESC3008WH11 - Service ManualplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- Automatic Washer: Study Course (Direct Drive Models)Document16 pagesAutomatic Washer: Study Course (Direct Drive Models)plasmapeteNo ratings yet
- 2016 Electrolux LuxCare DryerDocument57 pages2016 Electrolux LuxCare DryerplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- 1043 Refrigerator EW28BS87SS0 04252017 V2.0Document96 pages1043 Refrigerator EW28BS87SS0 04252017 V2.0plasmapeteNo ratings yet
- Automatic Washer: Study CourseDocument32 pagesAutomatic Washer: Study CourseplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- #2 PDFDocument20 pages#2 PDFplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- MSA VMW PP PresentationDocument65 pagesMSA VMW PP PresentationplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- GE 2012 Washer TrainingDocument106 pagesGE 2012 Washer TrainingplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- Haier Rwt350aw-Ex (081227)Document3 pagesHaier Rwt350aw-Ex (081227)plasmapeteNo ratings yet
- 31 14544 2Document2 pages31 14544 2plasmapeteNo ratings yet
- v22 v24 v23 - DtoDocument70 pagesv22 v24 v23 - DtoplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- WR55X10552 Motherboard Replacement PDFDocument2 pagesWR55X10552 Motherboard Replacement PDFplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- FAV9800AWW Service Manual 16022808Document98 pagesFAV9800AWW Service Manual 16022808plasmapeteNo ratings yet
- Amana Refrigerator S130 - 3R0Document95 pagesAmana Refrigerator S130 - 3R0plasmapeteNo ratings yet
- GEMonogramSXSTechManual31 9091 Defrost HeaterDocument1 pageGEMonogramSXSTechManual31 9091 Defrost HeaterplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- Supco Refrigeration CatalogDocument78 pagesSupco Refrigeration CatalogplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- 809 DW1002 Getting An E01 Error Code On The ControlDocument2 pages809 DW1002 Getting An E01 Error Code On The ControlplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- WM3070HRADocument57 pagesWM3070HRAplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- Tech Sheet - W10162408Document10 pagesTech Sheet - W10162408plasmapete100% (1)
- Masterpiece OvensDocument33 pagesMasterpiece OvensplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- 809 DW1002 Getting An E01 Error Code On The ControlDocument2 pages809 DW1002 Getting An E01 Error Code On The ControlplasmapeteNo ratings yet
- HLP21E Service ManualDocument31 pagesHLP21E Service ManualplasmapeteNo ratings yet