Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Orifice and Nozzle
Uploaded by
MasterTopup0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesIntroduction to Orifice and Nozzle
Original Title
Introduction to Orifice and Nozzle
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIntroduction to Orifice and Nozzle
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesIntroduction To Orifice and Nozzle
Uploaded by
MasterTopupIntroduction to Orifice and Nozzle
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
INTRODUCTION TO ORIFICE AND NOZZLE
ORIFICE
An orifice is a small opening provided on the side or bottom of a tank, through which a fluid
is flowing. The opening can be of any shape or cross-section, like rectangular, triangular or
circular. The orifices may discharge fluid into the atmosphere or from one tank to another.
Orifices are classified based on the shape or the cross-sectional area as:
Rectangular orifice
Circular orifice
Triangular orifice and
Square orifice
Orifices are classified based on the size of the orifice and the head of fluid above the orifice
as:
Small orifice and
Large orifice
Depending on the shape of the upstream edge of the orifices, they are classified as:
Sharp-edged orifice and
Bell-mouthed orifice
They are also classified based on the nature of the discharge as:
Partially submerged or drowned orifice
Fully submerged or drowned orifice
Free discharging orifices
NOZZLE
A nozzle is a device designed to control the direction or characteristics of a fluid flow
(especially to increase velocity) as it exits (or enters) an enclosed chamber or pipe.
A nozzle is often a pipe or tube of varying cross sectional area, and it can be used to direct or
modify the flow of a fluid (liquid or gas). Nozzles are frequently used to control the rate of
flow, speed, direction, mass, shape, and/or the pressure of the stream that emerges from them.
In nozzle velocity of fluid increases on the expense of its pressure energy.
BERNOULLI EQUATION ON ORIFICE AND NOZZLE
Bernoulli equation is an approximate relation between pressure, velocity, and elevation, and
is valid in regions of steady, incompressible flow where net frictional forces are negligible.
For steady and incompressible flow, the Bernoulli equation is:
(1)
(2)
THE EFFICIENCY OF ORIFICE AND NOZZLE
You might also like
- Wafer Moving Range UCL X-Ray (100 )Document27 pagesWafer Moving Range UCL X-Ray (100 )MasterTopupNo ratings yet
- Ech 3701 Reaction Kinetics Engineering Project 1Document2 pagesEch 3701 Reaction Kinetics Engineering Project 1MasterTopupNo ratings yet
- Visit ReportDocument2 pagesVisit ReportMasterTopup100% (1)
- Latest Edited KineticsDocument14 pagesLatest Edited KineticsMasterTopupNo ratings yet
- OriginalDocument5 pagesOriginalMasterTopupNo ratings yet
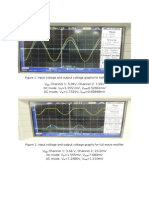
- Results: V Channel 1: 5.04V, Channel 2: 1.92V V 3.3551mV, V 0.52661mV AC Mode: V 1.7529V, V 0.69848mVDocument3 pagesResults: V Channel 1: 5.04V, Channel 2: 1.92V V 3.3551mV, V 0.52661mV AC Mode: V 1.7529V, V 0.69848mVMasterTopupNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)