Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) ISRO Syllabus
(WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) ISRO Syllabus
Uploaded by
VikasAroraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) ISRO Syllabus
(WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) ISRO Syllabus
Uploaded by
VikasAroraCopyright:
Available Formats
Electronics and Telecommunication
ISRO Syllabus for Electronics And Communication
NETWORK: Network graphs:
matrices associated with graphs; incidence, fundamental cut set and fundamental
circuit matrices. Solution methodsl; nodal and mesh analysis. Network theorems;
superposition, Thevenin and Nortan's, maximum power transfer, wye-delta
transformation, steady state sinusoidal analysis using phasors, fourier series,
linear constant coefficient differential and difference equations; time domain
analysis of simple RLC circuits. laplace and Z transforms: frequency domain
analysis of RLC circuits, convolution,2-port network parameters, driving point and
transfer functions, state equation for networks.
ANALOG CIRCUITS:
characteristics and equivalent circuits(large and small singnal) of
diodes,BJT,JFETs and MOSFET simple diode circuits: clipping, clamping, rectifier,
biasing and bias stability of transistior and FET amplifiers. Amplifiers: single and
multi-stage, differential, operational, feedback and power. Analysis of amplifers;
frequency response of amplifiers. Simple op-amp circuits. Filters. Sinusoidal
oscillators; criterion for oscillation; single-transistor and op-amp configurations.
Function generators and wave-shaping circuits, Power supplies.
DIGITAL CIRCUITS:
Boolean algebra; minimization of boolean functions; logic gates; digital IC
families( DTL,TTL,ECL,MOS,CMOS). Combinational circuits: airthmetic circuits,
code converters, multiplexers and decoders. Sequential circuits: latches and flipflops, counters and shift-registers. Comparators, timers, multivibrators. Sample
and hold circuits, ADCs and DACs. Semiconductor memories. Microprocessor
(8085): architecture, programming, memory and I/O interfacing.
CONTROL SYSTEMS:
Basic control system components; block diagrammatic descripption,reduction of
block diagrams,properties of systems: linearity,timeinvariance,stability,causality.Open loop and closed loop (feedback)
systems.Special properties of linear time- invariance(LTI) systems-transfer
function, impulse responce,poles,zeros,their significance, and stability analysis of
these systems. Signal flow graphs and their use in determining transfer functions
of systems; transient and steaty state analysis of LTI system and frequency
responce. Tools and techniques for LTI control system analysis: Root, loci,
Routh_Hurwitz criterion, Bode and Nyquist plots; Control system compensators:
elements of lead and lag compensations, elements ofPropotional-integral.
-Derivative(PID) control. State variable representation and solution of state
equation for LTI systems.
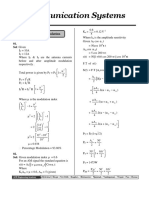
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS:
Fourier analysis of signals - amplitude, phase and power spectrum, autocorrelation and cross-correlation and their Fourier transforms. Signal transmission
through linear time-invariant(LTI) systems,impulse responce and frequency
responce,group delay phase delay. Analog modulation systems-amplitude and
angle modulation and demodulation systems, spectral analysis of these
operations, superheterodyne receivers, elements of hardwares realizations of
analog communications systems. Basic sampling theorems. Pulse code
modulation(PCM), differential pulse code modulation(DPCM), delta
modulation(DM). Digital modulation schemes: amplitude, phase and frequency
shift keying schemes(ASK,PSK,FSK). Multiplexing - time division and frequency
division. Additive Gaussian noise; characterization using correlation, probability
density function(PDF),power spectral density(PSD). Signal- to-noise rasio(SNR)
calculations for amplitude modulation(AM) and frequency modulation(FM) for low
noise conditions.
ELECTROMAGNETICS:
Elements of vector calculus: gradient, dicergence and curl; Gauss and strokes
theorems, maxwells equation: differential and integral forms. Wave equation.
Poynting vector. Plane wavwes: propagation through various media; reflection
and refraction; phase and group velocity; skin depth Transmission lines:
Characteristic impedence; impedence transformation; smith chart; impedence
matching pulse excitation. Wave guides: modes in rectangular waveguides;
boundary conditions; cutt-off frequencies; dipersion relations. Antennas; Dipole
antennas; antenna arrays; radiation pattern; reciprocity theorem; antenna gain.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- RED Short Film Production PlanDocument26 pagesRED Short Film Production Planblankstage100% (2)
- Jon Gomm-Passionflower PDFDocument8 pagesJon Gomm-Passionflower PDFKestern Hanah de SousaNo ratings yet
- Pulitzer Bookamrk DramaDocument2 pagesPulitzer Bookamrk DramamohammadNo ratings yet
- Thompson2012 PDFDocument9 pagesThompson2012 PDFGayathri K MNo ratings yet
- Herman Hertzberger - Space and The Architect Lessons in Architecture 2Document294 pagesHerman Hertzberger - Space and The Architect Lessons in Architecture 2blackmy89% (9)
- Beautiful Friendship ReharmDocument1 pageBeautiful Friendship ReharmJussi JänttiNo ratings yet
- Aleluya CeltaDocument2 pagesAleluya Celtarlh2022No ratings yet
- 8-Doc-Skin Response Meter Based On Body ResistanceDocument18 pages8-Doc-Skin Response Meter Based On Body Resistancenishant02111989No ratings yet
- Luminaria LED IPDocument46 pagesLuminaria LED IPAldo Marcelo Soliz AngolaNo ratings yet
- Late Elementary To Early Intermediate Works by 12 Important Composers of Standard Teaching LiteratureDocument6 pagesLate Elementary To Early Intermediate Works by 12 Important Composers of Standard Teaching LiteratureJames KeeNo ratings yet
- Rajshahi VGRJ Aerodrome ChartDocument11 pagesRajshahi VGRJ Aerodrome Charts ramanNo ratings yet
- Lss Commissioning RitesDocument2 pagesLss Commissioning Ritesmiggy13No ratings yet
- Engr Abid AliDocument3 pagesEngr Abid AliAbid AliNo ratings yet
- Pierre Rode Twenty Four CapricesDocument64 pagesPierre Rode Twenty Four CapricesAndrés García-Camino100% (7)
- Cod CP 0420Document138 pagesCod CP 0420Alberto AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Pantalla Repetidora LG M2262DL ManualDocument27 pagesPantalla Repetidora LG M2262DL ManualJair Jesús Cazares RojasNo ratings yet
- Indian Arrival DayDocument7 pagesIndian Arrival DayRenee RamdialNo ratings yet
- Queen Mab WorksheetDocument1 pageQueen Mab Worksheetapi-204991049No ratings yet
- InglésDocument6 pagesInglésVioleta MartinezNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Cargadora 972GDocument28 pagesCatalogo Cargadora 972GRodrigo CatotaNo ratings yet
- Rare Vilayat Khan InterviewDocument3 pagesRare Vilayat Khan Interviewapi-3852143No ratings yet
- Synth MakerDocument3 pagesSynth MakerDj-XienefMixNo ratings yet
- Microwave CourseDocument43 pagesMicrowave CourseSohaib Omer SalihNo ratings yet
- Using Correct EnglishDocument2 pagesUsing Correct EnglishCamelia PleșaNo ratings yet
- Crane SafetyDocument166 pagesCrane Safetymordidomi100% (2)
- EmailsDocument16 pagesEmailsеленаNo ratings yet
- Final II Q.paper '09-Reading and LiteratureDocument7 pagesFinal II Q.paper '09-Reading and LiteratureRoshan P NairNo ratings yet
- 2218 You Are MineDocument3 pages2218 You Are MineSid CherryNo ratings yet
- Mẫu đề 2Document7 pagesMẫu đề 2Tran Phuong AnhNo ratings yet
- 05 - Communication All Chapters PDFDocument52 pages05 - Communication All Chapters PDFthumatimadhusudhanNo ratings yet