Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Networks
Uploaded by
23wingsCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Networks
Uploaded by
23wingsCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Networks Prof.
Hema A Murthy
Stop and Wait Protocol
• Frame number to be included
• What is the minimum of bits required?
• ambiguity between m and m+1
– 1 bit sequence number
• sender: knows which frame to send next
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Computer Networks Prof. Hema A Murthy
Stop and Wait Protocol
• receiver: knows which frame to expect next
• counters: incremented modulo 2
• Sending process:
• if event = DLL Send then
– increment next FrameNo modulo 2
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Computer Networks Prof. Hema A Murthy
Stop and Wait Protocol
• Receiver Process:
• if event = DLLRecv then
• if recv.Seqnum = expected Seqnum then
• DLL State = receiving
• getFrameFrom PhysLayer(r, buffer)
• Sent To NWL(buffer)
• increment NextFrame Expected modulo 2
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Computer Networks Prof. Hema A Murthy
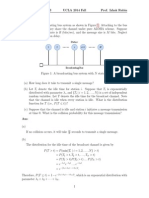
Stop and Wait: Timing diagram
Time Out
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Computer Networks Prof. Hema A Murthy
ThroughPut
• Error Free Case: Throughput is :
Tf
U=
Tt
T f - Time take to transmit a frame
Tt - Total time engaged in the transmission of a frame
Tt = T f + Tprop + Tack + Tproc + Tprop
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Computer Networks Prof. Hema A Murthy
Example
• Error free case: T f = 10 × 8 × 1024 /(106 )
– Frame size = 10 KB
= 0.08192
– RTT = 100ms =
0.1s T f + 0.1 = 0.18912
– Bandwidth = 1 0.08192
Mbps U= = 0.43
0.18912
Throughput = 430 kbps
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Computer Networks Prof. Hema A Murthy
Errors in transmission
• Let N r = E [number of retransmissions]
Tf
U=
N rTt
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Computer Networks Prof. Hema A Murthy
Stop and Wait: Analysis
Tprop -- is propagation delay
Tack -- time take for acknowledgement
Tproc -- time taken for processing at the receiver
If Tack , Tproc are negligible then
1
U= , a = T f / Tp
1 + 2a
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Computer Networks Prof. Hema A Murthy
Expected Number of
Retransmissions
∞
N r = ∑ iPr [i transmissions]
i =1
∞
= ∑ iP i −1 (1 − P)
i =1
1
=
1− P
(1 − P)
U=
1 + 2a
where P is the probability of a frame being in error
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
Computer Networks Prof. Hema A Murthy
Error Analysis
Let p be the probability that a bit is in error
Let F be the number of bits in a frame
P = 1 − (1 − p ) F
Indian Institute of Technology Madras
You might also like
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Noise in Nanoscale Semiconductor DevicesFrom EverandNoise in Nanoscale Semiconductor DevicesTibor GrasserNo ratings yet
- FDDI Analysis: Computer Networks Prof. Hema A MurthyDocument5 pagesFDDI Analysis: Computer Networks Prof. Hema A Murthy23wingsNo ratings yet
- The Ethernet Frame Format: 64 Bit 48 Bit 48 Bit 16 Bit Data 32 BitDocument18 pagesThe Ethernet Frame Format: 64 Bit 48 Bit 48 Bit 16 Bit Data 32 Bit23wingsNo ratings yet
- Access To The Shared Medium: - Different Topologies - Different Multiplexing SchemesDocument23 pagesAccess To The Shared Medium: - Different Topologies - Different Multiplexing Schemes23wingsNo ratings yet
- Lecture17 Aloha EthernetDocument15 pagesLecture17 Aloha Ethernet23wingsNo ratings yet
- Fibre Distributed Data Interface: - Runs On Fibre and Not Copper - Dual RingDocument14 pagesFibre Distributed Data Interface: - Runs On Fibre and Not Copper - Dual Ring23wingsNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument14 pagesComputer Networks23wingsNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Prof. Hema A MurthyDocument17 pagesComputer Networks Prof. Hema A Murthy23wingsNo ratings yet
- Error Detection: - Add Redundant BitsDocument14 pagesError Detection: - Add Redundant Bits23wingsNo ratings yet
- Lec8 MPIalgorithmDesignDocument12 pagesLec8 MPIalgorithmDesignAnirudh SethNo ratings yet
- Wireless Lans: - Infrared, RadioDocument12 pagesWireless Lans: - Infrared, Radiosaroj.xtrim8440No ratings yet
- Error Control / Reliable Transmission: - Acknowledgements (Acks) - TimeoutsDocument23 pagesError Control / Reliable Transmission: - Acknowledgements (Acks) - Timeouts23wingsNo ratings yet
- LEC6 parallelAlg-BroadcastingDocument15 pagesLEC6 parallelAlg-BroadcastingSAINo ratings yet
- Performance Metrics: - Bandwidth (Throughput) - Latency (Delay) - BandwidthDocument17 pagesPerformance Metrics: - Bandwidth (Throughput) - Latency (Delay) - Bandwidth23wingsNo ratings yet
- Data Communication And: NetworkingDocument69 pagesData Communication And: NetworkingKiều Quốc AnhNo ratings yet
- CS F303 (Computer Networks) : Vishal GuptaDocument28 pagesCS F303 (Computer Networks) : Vishal Guptayaganti sivakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Access Control Update in NetworkingDocument39 pagesAccess Control Update in NetworkingThe MatrixNo ratings yet
- Hwk3 4 Su10 SolDocument11 pagesHwk3 4 Su10 SolKun LiNo ratings yet
- Queuing AnalysisDocument64 pagesQueuing AnalysisgaziahmadNo ratings yet
- Connection À L'entrepriseDocument41 pagesConnection À L'entrepriseLarbi RahmaniNo ratings yet
- Medium Access Sublayer: - Topology of The Network - ProtocolsDocument14 pagesMedium Access Sublayer: - Topology of The Network - Protocols23wingsNo ratings yet
- IEEE 802.5 Token Ring: - A Special Sequence of Bits - Circulates Around The RingDocument21 pagesIEEE 802.5 Token Ring: - A Special Sequence of Bits - Circulates Around The Ring23wingsNo ratings yet
- G S D(S) N S D S N S D S: EC5: Control SystemsDocument7 pagesG S D(S) N S D S N S D S: EC5: Control SystemsMANOJ KUMAR DASNo ratings yet
- Ee132b Hw3 SolDocument7 pagesEe132b Hw3 SolDylan Ler100% (1)
- Intro To Communication: - AdvantagesDocument13 pagesIntro To Communication: - AdvantagesXin ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Sheet - 1 Solution SummaryDocument7 pagesSheet - 1 Solution SummarySara JEBRINo ratings yet
- Hardware Building Blocks: - NodesDocument7 pagesHardware Building Blocks: - Nodes23wingsNo ratings yet
- Accuracy of Sine-Wave Frequency Estimation by An Iterative Interpolated DFT AlgorithmDocument6 pagesAccuracy of Sine-Wave Frequency Estimation by An Iterative Interpolated DFT AlgorithmKassaye GizawNo ratings yet
- 0 Encoding 1 0 1 0 1 1 1: Indian Institute of Information Technology Design and Manufacturing, KancheepuramDocument6 pages0 Encoding 1 0 1 0 1 1 1: Indian Institute of Information Technology Design and Manufacturing, KancheepuramDark SlayerNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 TE-321 Digital Signal Processing: Sr. No Course Learning Outcomes Plos Blooms TaxonomyDocument1 pageAssignment 1 TE-321 Digital Signal Processing: Sr. No Course Learning Outcomes Plos Blooms Taxonomyruss90No ratings yet
- b1 - Intro Noise - Comm TheoremDocument42 pagesb1 - Intro Noise - Comm Theoremhafiz azmanNo ratings yet
- ECE 391 Supplemental Notes - #1: Lumped vs. Distributed CircuitsDocument16 pagesECE 391 Supplemental Notes - #1: Lumped vs. Distributed CircuitsAnh Viet NguyenNo ratings yet
- Virtual Networks and TunnelsDocument22 pagesVirtual Networks and Tunnels23wingsNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series and Fourier Transform of Signals AIMDocument3 pagesFourier Series and Fourier Transform of Signals AIMgkkishorekumarNo ratings yet
- 1707 01697 PDFDocument5 pages1707 01697 PDFDivine Grace BurmalNo ratings yet
- Ref 19Document11 pagesRef 19Sandeep SunkariNo ratings yet
- CMPE 150 - Winter 2009: January 13, 2009 yDocument73 pagesCMPE 150 - Winter 2009: January 13, 2009 ysai420No ratings yet
- Security Enhancement of AODV Routing Protocol in Mobile Ad Hoc NetworkDocument7 pagesSecurity Enhancement of AODV Routing Protocol in Mobile Ad Hoc NetworkAbdul RazzakNo ratings yet
- Friis Transmission Equation: Chrystian Viteri 452 Cristian Monar 246286 Mauricio Tobar 638 Dayana Ordoez 659Document2 pagesFriis Transmission Equation: Chrystian Viteri 452 Cristian Monar 246286 Mauricio Tobar 638 Dayana Ordoez 659Chrystian Viteri HernándezNo ratings yet
- 2 2 Queuing TheoryDocument18 pages2 2 Queuing TheoryGilbert RozarioNo ratings yet
- Hw1 10 SolutionsDocument3 pagesHw1 10 SolutionsYi ZhangNo ratings yet
- L16 Little'StheoremDocument11 pagesL16 Little'StheoremRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual # 08 (LCS) (2018-CPE-07)Document8 pagesLab Manual # 08 (LCS) (2018-CPE-07)Momel FatimaNo ratings yet
- Queueing Theory-2Document21 pagesQueueing Theory-2divyaagarwal9251No ratings yet
- Local Area Netowrks 1Document80 pagesLocal Area Netowrks 1parham59No ratings yet
- Complexity Analysis of DE Based CE-UD MIMO System: Zaid Bin Tariq Muhammad Adnan KhanDocument5 pagesComplexity Analysis of DE Based CE-UD MIMO System: Zaid Bin Tariq Muhammad Adnan KhanM. Adnan KhanNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument10 pages1 PDFHesham MahmoudNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument10 pages1 PDFHesham MahmoudNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument10 pages1 PDFHesham MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Quickest Spectrum Detection Using Hidden Markov Model For Cognitive RadioDocument7 pagesQuickest Spectrum Detection Using Hidden Markov Model For Cognitive RadioDino kongkhamNo ratings yet
- Queueing TheoryDocument61 pagesQueueing Theory李冠霆No ratings yet
- The Basic Principles of OFDMDocument30 pagesThe Basic Principles of OFDMsureshya22No ratings yet
- Analyzing Poisson Traffic: Lab-Experiment # 04 by Engr. Naveed A. UmraniDocument22 pagesAnalyzing Poisson Traffic: Lab-Experiment # 04 by Engr. Naveed A. UmraniMehboob KhokharNo ratings yet
- Robustness of DS-CDMA Multiuser Detectors: Pål Orten and Tony OttossonDocument5 pagesRobustness of DS-CDMA Multiuser Detectors: Pål Orten and Tony OttossonEmraan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Network Management System: Simple SolutionDocument23 pagesNetwork Management System: Simple Solution23wingsNo ratings yet
- IP Packet Format: This HostDocument19 pagesIP Packet Format: This Host23wingsNo ratings yet
- Smith Thakurta13 Nearly Optimal Online Algorithms Privater LearningDocument9 pagesSmith Thakurta13 Nearly Optimal Online Algorithms Privater Learningsamsiphi_13No ratings yet
- Fifth Problem Assignment: EE603 - DSP and Its ApplicationsDocument2 pagesFifth Problem Assignment: EE603 - DSP and Its Applicationschandan choudharyNo ratings yet
- The Key Elements of A Communication ModelDocument12 pagesThe Key Elements of A Communication ModelMD. SHAHIDUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- 28 Getting Started in Ladakhi A PhrasebookDocument143 pages28 Getting Started in Ladakhi A PhrasebookHoai Thanh Vu100% (8)
- Physical and Data Link Layer: Kameswari Chebrolu Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT KanpurDocument19 pagesPhysical and Data Link Layer: Kameswari Chebrolu Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur23wingsNo ratings yet
- Lec01 Overview ChebroluDocument31 pagesLec01 Overview Chebrolu23wingsNo ratings yet
- Physical and Data Link Layer: Kameswari Chebrolu Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT KanpurDocument11 pagesPhysical and Data Link Layer: Kameswari Chebrolu Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur23wingsNo ratings yet
- BHU - Overall Ranking-2011Document3 pagesBHU - Overall Ranking-2011Yogesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Report of Development of Gujarat Under Narendra Modi Till 2007Document49 pagesReport of Development of Gujarat Under Narendra Modi Till 2007ravighiyarNo ratings yet
- CS1991Document13 pagesCS1991api-3726503No ratings yet
- Egovernance FoundationsDocument56 pagesEgovernance Foundations23wingsNo ratings yet
- Lec01 Overview BhaskarDocument31 pagesLec01 Overview Bhaskargleen mathewNo ratings yet
- CS425/EE673 Summary Lecture: Bhaskaran Raman Kameswari Chebrolu Indian Institute of Technology, KanpurDocument20 pagesCS425/EE673 Summary Lecture: Bhaskaran Raman Kameswari Chebrolu Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur23wingsNo ratings yet
- Transport Protocols: Kameswari Chebrolu Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT KanpurDocument27 pagesTransport Protocols: Kameswari Chebrolu Dept. of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur23wings100% (2)
- Lecture 11Document14 pagesLecture 1123wingsNo ratings yet
- Security Overview-Cryptography and Network SecurityDocument17 pagesSecurity Overview-Cryptography and Network SecurityHaveit12No ratings yet
- CS425: Computer Networks: Bhaskaran Raman (Braman) AT (Cse - Iitk.ac - In)Document11 pagesCS425: Computer Networks: Bhaskaran Raman (Braman) AT (Cse - Iitk.ac - In)23wingsNo ratings yet
- CableDocument27 pagesCableSandhya PandeyNo ratings yet
- Utp and Fiber CablingDocument17 pagesUtp and Fiber Cabling23wingsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document12 pagesLecture 823wingsNo ratings yet
- Configuring Cisco Switch and RouterDocument23 pagesConfiguring Cisco Switch and Router23wingsNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 DCNDocument18 pagesLecture2 DCNkartheek32777No ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document23 pagesLecture 1Vikas DhimanNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Network ImplementationDocument19 pagesEnterprise Network Implementation23wingsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16&17Document30 pagesLecture 16&17kasavenkat7434No ratings yet
- 802.11 Wireless LAN: Network Connectivity To The Legacy Wired LANDocument12 pages802.11 Wireless LAN: Network Connectivity To The Legacy Wired LANvizooooNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document11 pagesLecture 723wingsNo ratings yet
- Physical Media: - Cables: - Same Room / Same Building - Cat - 3 - Cat - 5 - Bandwidths 10-100Mbps, Distance 100mDocument23 pagesPhysical Media: - Cables: - Same Room / Same Building - Cat - 3 - Cat - 5 - Bandwidths 10-100Mbps, Distance 100m23wingsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document15 pagesLecture 523wingsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15Document18 pagesLecture 1523wingsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document13 pagesLecture 923wingsNo ratings yet
- Link State Routing: Computer Networks Prof. Hema A MurthyDocument15 pagesLink State Routing: Computer Networks Prof. Hema A Murthy23wingsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document11 pagesLecture 1023wingsNo ratings yet
- Email 1Document4 pagesEmail 1Ali AmarNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Macroeconomics Sec 222Document163 pagesIntermediate Macroeconomics Sec 222Katunga MwiyaNo ratings yet
- Mess Total TransectionsDocument92 pagesMess Total TransectionsFaisal ParachaNo ratings yet
- Ele Unit5 Revision PDFDocument2 pagesEle Unit5 Revision PDFNatalia ZapataNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Setting Company in CGDocument6 pagesPower Plant Setting Company in CGdcevipinNo ratings yet
- Escalation How Much Is Enough?Document9 pagesEscalation How Much Is Enough?ep8934100% (2)
- Civil TutorialDocument638 pagesCivil TutorialEmmanuel Mends FynnNo ratings yet
- Zalando SE Q3 2023 Financials PDFDocument7 pagesZalando SE Q3 2023 Financials PDFHjraNo ratings yet
- Lirik KoreaDocument6 pagesLirik KoreaSabrina Winyard ChrisNo ratings yet
- Magic Maze: Props IncludedDocument4 pagesMagic Maze: Props IncludedarneuhüdNo ratings yet
- Growrich PinoyDocument59 pagesGrowrich PinoyMarites FerolinoNo ratings yet
- ASVAB Core ReviewDocument208 pagesASVAB Core Reviewstanley100% (1)
- Ho Chi Minh City Water Environment Improvement Project: Concrete Pour Record (Internal)Document4 pagesHo Chi Minh City Water Environment Improvement Project: Concrete Pour Record (Internal)Archie Joseph LlanaNo ratings yet
- Robin Hood Case StudyDocument1 pageRobin Hood Case StudyNikunjGuptaNo ratings yet
- M.D. (Acu) SyllabusDocument5 pagesM.D. (Acu) SyllabusS Ve SuriyaNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Touch-Up Paint and Repair of Unitized Curtain WallDocument6 pagesMethod Statement For Touch-Up Paint and Repair of Unitized Curtain WallNESTOR YUMULNo ratings yet
- Green ConcreteDocument19 pagesGreen ConcreteAnubhav KalNo ratings yet
- Ball Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesBall Lesson Planapi-350245383No ratings yet
- Ibuprofen JP XVIIDocument2 pagesIbuprofen JP XVIIcamilo.carrilloNo ratings yet
- PPSTDocument24 pagesPPSTCrisnelynNo ratings yet
- Site Induction PresentationDocument17 pagesSite Induction PresentationalisyalalaNo ratings yet
- Legalese and Legal EnglishDocument16 pagesLegalese and Legal English667yhNo ratings yet
- Of Delhi in Criminal Appeal No. - of 2018)Document18 pagesOf Delhi in Criminal Appeal No. - of 2018)AnukritiNo ratings yet
- Professional Practice - X Sem - 2017-18 As On 16032018Document89 pagesProfessional Practice - X Sem - 2017-18 As On 16032018harshinireddy mandadiNo ratings yet
- History of Sultan KudaratDocument9 pagesHistory of Sultan Kudaratjimmy_andangNo ratings yet
- Proposal For Pitch An IdeaDocument2 pagesProposal For Pitch An Ideaaaron mathewsNo ratings yet
- Safeguarding Humanitarian Spce Chellenges UNHCRDocument367 pagesSafeguarding Humanitarian Spce Chellenges UNHCRalvaromelladoNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment and Narrative Report OctDocument4 pagesAccomplishment and Narrative Report OctGillian Bollozos-CabuguasNo ratings yet
- Tugas Lk7 Dan 10 Garuda PancasilaDocument5 pagesTugas Lk7 Dan 10 Garuda PancasilaarifuddinNo ratings yet
- PUP College of Law - FAQsDocument15 pagesPUP College of Law - FAQsAlvin ClaridadesNo ratings yet