Professional Documents
Culture Documents
COBIT 5 Foundation
COBIT 5 Foundation
Uploaded by
Hugo Medina SosaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
COBIT 5 Foundation
COBIT 5 Foundation
Uploaded by
Hugo Medina SosaCopyright:
Available Formats
COBIT 5 Foundation
Overview:
This course provides an overview the main concepts of IT Governance according to COBIT 5, ISACA s latest
governance framework, and how they can be applied.
Who Should Attend:
Business Management, IT /IS Auditors, Internal Auditors, Information Security and IT Practitioners; Consultants, IT/IS
Management looking to gain an insight into the Enterprise Governance of IT and looking to be certified as a COBIT
Implementer or Assessor.
Duration:
Classroom Learning - 3 Day(s)
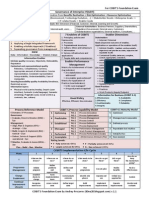
Lesson 1: The key features of COBIT 5
The Reasons for the Development of COBIT 5
The History of COBIT
The Drivers for developing a Framework
The Benefits of using COBIT 5
The COBIT 5 Format & product Architecture
COBIT 5 and Other Frameworks
Lesson 2: The COBIT 5 principles
Enabler Focus
Control Objectives to Management Practices
From COBIT4.1 Management Guidelines to COBIT5: Enabling Processes Guidelines
Lesson 3: The COBIT 5 enablers
Enabler 1 Principles, Policies and frameworks
Enabler 2 Processes
Enabler 3 Organisational Structures
Enabler 4 Culture, Ethics, and Behaviour
Enabler 5 Information
Enabler 6 Services, Infrastructure and Applications
Enabler 7 People, Skills and Competencies
Walk Through on using Goals cascade to scope Processes
Lesson 4: Introduction to COBIT 5 implementation
The Life cycle Approach
Inter related components of the life cycle
Understanding the enterprise internal and external factors
Key success factors for implementation
The seven phases of the Life Cycle model explained
The seven Change Enablement characteristics used in the life cycle.
Change Enablement relationships to the Continual Improvement Life Cycle
Making the Business case
The differences between COBIT 4.1 and COBIT 5
Lesson 5: Process capability assessment model
What is a process assessment
What is the COBIT Assessment Programme
The differences between a capability and maturity assessment
Differences to the COBIT 4.1 CMM
Overview of the COBIT Capability Model & Assessments
The Process Reference Model (PRM)
The Process Assessment Model (PAM)
The Measurement Framework
Introduction to the Assessor Training Steps
Lesson 6: Exam
preparation for the exam
taking the exam
COBIT 5 Qualifications
COBIT 5 is ideal for assurance, security, risk, privacy and compliance professionals or business leaders and stakeholders
who are involved in or affected by governance and management of information and information systems.
For additional COBIT resources or to learn more about how ISACAs new evolutionary framework can help your enterprise
establish a renewed trust in and value from your information systems, visit the COBIT 5 website.
APMG-International will be responsible for the accreditation of training providers and the development of the qualification
scheme. There will be three separate qualifications:
Foundation
Implementation level
Assessment level.
Benefits for Individuals
Understand levels of IT-related risk and make informed decisions to reduce information
security incidents. Deliver this understanding and risk awareness to improve prevention, detection
and recovery within an organization.
Provide tools for organizations to maintain high quality information to support business
decisions.
Help an organization to meet with regulatory and statutory or government requirements.
Understand COBIT approach to governance and its relationship with other IT best practices.
Benefits for Organizations
Achieve strategic goals and realise business benefits through the effective and innovative
use of IT.
Support compliance with relevant laws, regulations, contractual agreements and policies and
gain competitive edge over other organizations.
Reduce complexity and increase cost-effectiveness due to improved and easier integration
of information security standards, good practices and/or sector-specific guidelines resulting in
operational excellence through reliable, efficient application of technology.
Improved integration of information security in the enterprise, resulting in increased user
satisfaction with information security arrangements and outcomes.
Foundation Level
Obtaining the Foundation qualification will show that you have sufficient knowledge and understanding of
the COBIT 5 guidance to be able to:
Understand the governance and management of enterprise IT
Create awareness with your business executives and senior IT management
Assess the current state of enterprise IT in your department or organization
Scope which aspects of COBIT 5 would be appropriate to implement.
Exam Format
Multiple Choice format
50 questions per paper
25 mark or more required to pass (out of 50 available) - 50%
40 minute duration
Closed book.
Implementation Level
Get a practical understanding of how to apply COBIT 5 to specific business problems, pain points, trigger
events and risk scenarios within the organization. Learn how to effectively implement and apply COBIT 5
into your enterprise or how you can integrate components into client initiatives. Attendees will walk away
with an appreciation of how to effectively use COBIT 5 for different organizational and or client scenarios.
Following completion of the COBIT 5 Implementation course and examination, you will understand:
How to analyze enterprise drivers
Implementation challenges, root causes and success factors
How to determine and assess current process capability
How to scope and plan improvements
Potential implementation pitfalls
The latest good practices.
Exam Format
Objective testing
4 questions per paper with 20 marks available per question
40 marks or more required to pass (out of 80 available) - 50%
2 hours duration
Open book (COBIT 5 Implementation book only).
Assessor Level
The Assessor course provides methods to help guide implementation activities and is supported by
several case studies. You will learn how to perform a process assessment and how to analyze the results
to provide a clear determination of process capability. You will also learn how these results can be used
for process improvement, measuring the achievement of current or projected business goals,
benchmarking, consistent reporting and organizational compliance ultimately driving value to the
business.
Following completion of the COBIT 5 Assessor course and examination, you will understand:
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
o
How to perform a process capability assessment using the Assessor Guide: using COBIT 5.
How to apply the Process Assessment Model (the PAM) in performing a process capability
assessment. Specifically:
To use the Process Reference Model, in particular to be able to use the 37 processes
outlined in the PRM.
To apply and analyse the measurement model in assessing process capability levels.
To apply and analyse the capability dimension using generic criteria outlined in the
PAM.
How to identify and assess the roles and responsibilities in the process capability
assessment process.
How to perform and assess the 7 steps outlined in the Assessor Guide. Specifically:
Initiate a process assessment
Scope an assessment, using the tools provided and the PAM for the selection of
the appropriate processes
Plan & Brief the teams
Collect & Validate the data
Do a process attribute rating
Report the findings of the assessment.
How to use the self-assessment guide.
Exam Format
Objective testing
8 questions per paper with 10 marks available per question
40 marks or more required to pass (out of 80 available) - 50%
2 hours duration
Open book (COBIT 5 Assessor Guide: Using COBIT 5 and COBIT Process Assessment
Model (PAM): Using COBIT 5 books only).
Please Note: The availability of the Implementation and Assessor courses will be announced soon.
The COBIT framework allows enterprises to achieve their governance and
management objectives, i.e., to create optimal value from information and
technology by maintaining a balance amongst realizing benefits, managing risk
and balancing resources. Further benefits include but are not limited to:
Maintain high-quality information to support business decisions
Achieve strategic goals and realize business benefits through the effective and
innovative use of IT
Achieve operational excellence through reliable, efficient application of
technology
Maintain IT-related risk at an acceptable level
Optimize the cost of IT services and technology
Support compliance with relevant laws, regulations, contractual agreements
and policies
COBIT 5 provides an end-to-end business view of the governance of enterprise
IT that reflects the central role of information and technology in creating value
for enterprises.
five areas of focus:
1. Strategic alignment
This covers the alignment of the enterprises and ITs perspective, position,
plans, and patterns.
2. Value delivery
From a customer perspective, value is expressed in terms of the desired business
outcomes, their preferences, and their perceptions in regards to the product or
service.
3. Resource management
It is important to include the following elements as resources: funding,
applications/software, infrastructure/hardware, information/data, and of
course people. In order to properly manage their resources, enterprises must
develop and maintain the following capabilities: management, enterprise,
processes, knowledge, and people.
4. Risk management
A risk may be defined as the uncertainty of an outcome whether positive or
negative. The management of the risk includes the identification of the tangible
and intangible items to be protected, the various (real or potential) threats
facing those items and the level of vulnerability of the items in regards to a
specific threat. The enterprise must then decide an appropriate means of
mitigating the risk; this may range from doing nothing to attempting to fully
protect the item from the threat.
5. Performance measures
Before establishing any measure an enterprise needs to identify the reason for
the measure. There are four basic reasons for measuring: they are to direct,
to validate, to justify, and to intervene. The enterprise needs to identify many other criteria for
the measures. These criteria include, but are not limited to,
compliance, performance, quality, and value. Furthermore, the measures can
be quantitative (objective) or qualitative (subjective). All the measures must
also adhere to the SMART principle where
S = Specific
M = Measurable
A = Achievable
R = Realistic
T = Timely or time bounded
It is a set of guidelines and supporting toolset for
governance of enterprise IT that is accepted worldwide. Auditors and enterprises use
it as a mechanism to integrate technology in implementing controls and meet specific
business objectives. COBIT is well suited to enterprises focused on risk management and
mitigation.
The framework integrates all knowledge previously dispersed over different
ISACA frameworks13 such as COBIT, Val IT, Risk IT, and the Business Model for
Information Security (BMIS) and the IT Assurance Framework (ITAF).
You might also like
- COBIT 2019 Bridge Sample PaperDocument8 pagesCOBIT 2019 Bridge Sample PaperGodfrey MbizoNo ratings yet
- COBIT 2019 - RACI by Role - April 2020Document295 pagesCOBIT 2019 - RACI by Role - April 2020gaston6711100% (1)
- EDM01 Ensure Governance Framework Setting and Maintenance Audit Assurance Program - Icq - Eng - 0214Document28 pagesEDM01 Ensure Governance Framework Setting and Maintenance Audit Assurance Program - Icq - Eng - 0214fatsolaNo ratings yet
- COBIT 5 Foundation Workshop CoursewareDocument166 pagesCOBIT 5 Foundation Workshop CoursewarePedro Pamplona100% (6)
- Cobit 2019 Design ImplementationDocument1 pageCobit 2019 Design ImplementationParvez2z0% (1)
- Exercises COBIT 2019 Foundation CourseDocument5 pagesExercises COBIT 2019 Foundation CourseKhoirulHudaNo ratings yet
- CompTIA Network+Document3 pagesCompTIA Network+homsom100% (1)
- DSS01-Manage-Operations Icq Eng 1214Document28 pagesDSS01-Manage-Operations Icq Eng 1214LorenzoNo ratings yet
- 5036 Assignment 2 Pham Le Ngoc ThaoDocument20 pages5036 Assignment 2 Pham Le Ngoc ThaoBùi Thu HàNo ratings yet
- Cobit 5 ChecklistDocument21 pagesCobit 5 Checklist8octavociclo100% (1)
- Governance of Enterprise IT based on COBIT 5: A Management GuideFrom EverandGovernance of Enterprise IT based on COBIT 5: A Management GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- COBIT - 188 QuestionsDocument64 pagesCOBIT - 188 QuestionsGuillaume-David Teboko100% (2)
- Isaca: Cobit Assessment Programme (PAM) Tool Kit: Using COBIT 5Document2 pagesIsaca: Cobit Assessment Programme (PAM) Tool Kit: Using COBIT 5lgaleanoc0% (1)
- COBIT 5 CheatsheetDocument2 pagesCOBIT 5 Cheatsheetducuh100% (3)
- Assurance COBIT2019Document51 pagesAssurance COBIT2019Kumar Puvanes Tharumalingam100% (1)
- Student Guide: COBIT® 2019 Design & ImplementationDocument10 pagesStudent Guide: COBIT® 2019 Design & Implementationsamir sahliNo ratings yet
- Cobit GuideDocument65 pagesCobit Guidehoanthanhhai100% (3)
- Vendor Audit QuestionsDocument5 pagesVendor Audit QuestionsvantonilinNo ratings yet
- COBIT 2019 - ISO 27001 (2013 - 14 - 15) CrossoverDocument66 pagesCOBIT 2019 - ISO 27001 (2013 - 14 - 15) CrossoverYanto100% (1)
- COBIT® 2019 Foundation: Student GuideDocument14 pagesCOBIT® 2019 Foundation: Student Guidesriy4nto100% (1)
- Cobit 2019 and Risk Management PDFDocument34 pagesCobit 2019 and Risk Management PDFMuhammad makhrojal100% (5)
- Togaf 9.1 Level 1Document2 pagesTogaf 9.1 Level 1homsomNo ratings yet
- Robbins mgmt11 ppt01Document29 pagesRobbins mgmt11 ppt01Ahmed hassan100% (2)
- 01 BIM Project Execution Planning Guide V2.1 (One-Sided)Document134 pages01 BIM Project Execution Planning Guide V2.1 (One-Sided)Mois DanielNo ratings yet
- COBIT 2019 Major Differences With COBIT 5Document12 pagesCOBIT 2019 Major Differences With COBIT 5Parvez2zNo ratings yet
- For COBIT 5 Foundation Exam v1.1 PDFDocument1 pageFor COBIT 5 Foundation Exam v1.1 PDFpaxa100% (15)
- COBIT 2019 Foundation Exam GuideDocument10 pagesCOBIT 2019 Foundation Exam GuideMarcos Varela100% (2)
- COBIT-2019-Design-Guide Res Eng 1218Document150 pagesCOBIT-2019-Design-Guide Res Eng 1218Funnyjohn007No ratings yet
- Cobit Exam Test 2Document9 pagesCobit Exam Test 2TiagoJoseMoreira100% (1)
- Cgeit NotesDocument2 pagesCgeit NotesKaye Akin25% (4)
- Certificate Program Exam Guide v1 PDFDocument14 pagesCertificate Program Exam Guide v1 PDFHemangNo ratings yet
- Cobit 2019 Mapping To IT GOALDocument1 pageCobit 2019 Mapping To IT GOALZee Zioa100% (1)
- COBIT 2019 Exam Guide - FINAL - Jan102020Document11 pagesCOBIT 2019 Exam Guide - FINAL - Jan102020GEORGE FARD100% (1)
- cbtb19 - Bridge Course PDFDocument3 pagescbtb19 - Bridge Course PDFThilakPathirageNo ratings yet
- COBIT 2019 Foundation Sample ExamsDocument4 pagesCOBIT 2019 Foundation Sample ExamsnoahNo ratings yet
- Cgeit Exam FrameworksDocument34 pagesCgeit Exam FrameworksAyman Al-sayyed100% (2)
- COBIT 5 Implementation IntroductionDocument6 pagesCOBIT 5 Implementation IntroductionJavier Torres Solis25% (4)
- Cobit 2019 FoundationDocument94 pagesCobit 2019 Foundationprogis100% (4)
- Cloud Computing An Internal Audit PerspectiveDocument43 pagesCloud Computing An Internal Audit PerspectiveHambarr Jahbreey RickyNo ratings yet
- COBIT-2019-Design-Guide Res Eng 1218 PDFDocument150 pagesCOBIT-2019-Design-Guide Res Eng 1218 PDFJesus Barrera IshiharaNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument16 pagesExamCarlos F. Núñez100% (1)
- KRI Basics For It GovernanceDocument10 pagesKRI Basics For It GovernanceAnonymous hVs9sgryeNo ratings yet
- IT Governance at INGDocument19 pagesIT Governance at INGChandan KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Cgeit Risk ManagementDocument28 pagesCgeit Risk ManagementAyman Al-sayyedNo ratings yet
- COBIT 2019 DESIGN-IMPLEMENTATION COURSE INHOUSEv1 PDFDocument4 pagesCOBIT 2019 DESIGN-IMPLEMENTATION COURSE INHOUSEv1 PDFEarl RaisNo ratings yet
- Cobit Case Study - OracleDocument11 pagesCobit Case Study - OracleAdil AbdelganiNo ratings yet
- CgeitExamPrep Intro 032310Document19 pagesCgeitExamPrep Intro 032310Ajay TyagiNo ratings yet
- COBIT 5 Foundation Exam Revision On A PageDocument1 pageCOBIT 5 Foundation Exam Revision On A PageSergiö Montoya100% (1)
- COBITDocument179 pagesCOBITBecky Horn100% (1)
- IT Governance Implementation Framework in Small and Medium EnterpriseDocument18 pagesIT Governance Implementation Framework in Small and Medium EnterpriseDwdroo DiwokNo ratings yet
- COBIT 2019 Foundation Exam GuideDocument11 pagesCOBIT 2019 Foundation Exam GuideVinay TiwariNo ratings yet
- Cobit 2019 Design-Implementation Course Syllabus - New Look 2019 EN V1.0Document13 pagesCobit 2019 Design-Implementation Course Syllabus - New Look 2019 EN V1.0Dipayan Chakraborty100% (1)
- Risk It Framework NotesDocument2 pagesRisk It Framework NotesJuliet Peñaranda100% (1)
- The Components of The IT Audit Report - Joa - Eng - 0120 PDFDocument4 pagesThe Components of The IT Audit Report - Joa - Eng - 0120 PDFImmanuel GiuleaNo ratings yet
- (System Name) : Security Categorization: LowDocument14 pages(System Name) : Security Categorization: LowhomsomNo ratings yet
- (System Name) : Security Categorization: HighDocument16 pages(System Name) : Security Categorization: HighhomsomNo ratings yet
- (System Name) : Security Categorization: ModerateDocument16 pages(System Name) : Security Categorization: ModeratehomsomNo ratings yet
- Application Submission: Acceleration ProgramDocument4 pagesApplication Submission: Acceleration ProgramhomsomNo ratings yet
- Acceleration Program - FasterCapitalDocument10 pagesAcceleration Program - FasterCapitalhomsomNo ratings yet
- Professionalism & Ethics Module Spec - v2Document9 pagesProfessionalism & Ethics Module Spec - v2homsomNo ratings yet
- C Ase: Certified Application Security EngineerDocument14 pagesC Ase: Certified Application Security EngineerhomsomNo ratings yet
- Phonetic AlphabetDocument1 pagePhonetic AlphabethomsomNo ratings yet
- Computer Studies: Complete The Following Questions For Your Exam Revision. 1. What Is An Actuator?Document3 pagesComputer Studies: Complete The Following Questions For Your Exam Revision. 1. What Is An Actuator?homsomNo ratings yet
- TDI Backend ToutorialDocument39 pagesTDI Backend ToutorialhomsomNo ratings yet
- Surya TrainingManual LowDocument52 pagesSurya TrainingManual LowhomsomNo ratings yet
- Ellen Macarthur ActivitiesDocument3 pagesEllen Macarthur ActivitieshomsomNo ratings yet
- Totara 20individual 20learning 20plans KineoDocument2 pagesTotara 20individual 20learning 20plans KineohomsomNo ratings yet
- Hdi Dst Desktop Support Technician: ددع مايالا Course Number يساسلا رضاحملاDocument1 pageHdi Dst Desktop Support Technician: ددع مايالا Course Number يساسلا رضاحملاhomsomNo ratings yet
- Business Continuity Training, Certification, Consulting, Asessment and A...Document15 pagesBusiness Continuity Training, Certification, Consulting, Asessment and A...homsomNo ratings yet
- Oxford Training Org Anization CenterDocument1 pageOxford Training Org Anization CenterhomsomNo ratings yet
- Agenda For CBCI Workshop (Aligned To ISO22301) - March 2014Document5 pagesAgenda For CBCI Workshop (Aligned To ISO22301) - March 2014homsomNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Prezi Presentations 101Document7 pagesLesson Plan - Prezi Presentations 101mahfuzahismailNo ratings yet
- BTEC WorkSkills GuideDocument13 pagesBTEC WorkSkills GuidehomsomNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Office Excel 2010 Level 2Document3 pagesMicrosoft Office Excel 2010 Level 2homsomNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Module 8 SlideshowDocument14 pagesGrade 11 Module 8 SlideshowJac SeyNo ratings yet
- What Is An Executive and Legislative Agenda (ELA) ?Document8 pagesWhat Is An Executive and Legislative Agenda (ELA) ?Kara ClarkNo ratings yet
- Styles of Management in Pharmaceutical Industry Lecture # 4Document33 pagesStyles of Management in Pharmaceutical Industry Lecture # 4Umair MazharNo ratings yet
- Sydney Pexton Business Article Mcom 320Document7 pagesSydney Pexton Business Article Mcom 320api-710422057No ratings yet
- MBO Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesMBO Lecture NotesDr reena SethiNo ratings yet
- Anticipation RewardsDocument252 pagesAnticipation RewardsHao NguyenNo ratings yet
- An Overview of OT by SulemanDocument4 pagesAn Overview of OT by SulemanOscar PinillosNo ratings yet
- Project Initiation & Pre-StudyDocument36 pagesProject Initiation & Pre-StudyTuấn Nam NguyễnNo ratings yet
- BSMH 5023 Strategic Human Resource Management: Individual Assignment Forum 3 & 4Document7 pagesBSMH 5023 Strategic Human Resource Management: Individual Assignment Forum 3 & 4Mogana GunasigrenNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Interpretative DanceDocument14 pagesRubric For Interpretative DanceChristian EaNo ratings yet
- Balanced Scorecard and Hoshin KanriDocument6 pagesBalanced Scorecard and Hoshin KanriAntonio CervantesNo ratings yet
- Retail Revenue ManagementDocument17 pagesRetail Revenue ManagementfkkfoxNo ratings yet
- IN6 Hold 2 Out 7: 10-Minute Toughness Summary WorksheetDocument6 pagesIN6 Hold 2 Out 7: 10-Minute Toughness Summary WorksheetmrpablosanchezNo ratings yet
- Group2 Week2 Arc181 Abusmaa1Document7 pagesGroup2 Week2 Arc181 Abusmaa1Amorsolo TolozaNo ratings yet
- 2004 - CaproniDocument12 pages2004 - CaproniJamie BorgNo ratings yet
- CFEE Financial Literacy and Essential Skills - Final Report July 2012Document72 pagesCFEE Financial Literacy and Essential Skills - Final Report July 2012Jaime Tiburcio CortésNo ratings yet
- Fhs NotesDocument16 pagesFhs NotessurajpopatNo ratings yet
- Student Motivation Case StudyDocument10 pagesStudent Motivation Case Studyapi-239375707No ratings yet
- What Is An A3Document128 pagesWhat Is An A3ebuk123100% (1)
- Program Assessment Tool Kit:: A Guide To Conducting Interviews and Surveys A Guide To Conducting Interviews and SurveysDocument74 pagesProgram Assessment Tool Kit:: A Guide To Conducting Interviews and Surveys A Guide To Conducting Interviews and Surveyswinter55No ratings yet
- URP 203 Lecture Note 1Document5 pagesURP 203 Lecture Note 1alaofiyinfoluwa48No ratings yet
- Principles of CoachingDocument33 pagesPrinciples of CoachingAaqib Musadiq MirNo ratings yet
- TR - Mechatronics ServicingDocument53 pagesTR - Mechatronics Servicing062691No ratings yet
- Aligning HR & Business StrategiesDocument25 pagesAligning HR & Business StrategiesAnwar RabiaNo ratings yet
- LeadershipDocument156 pagesLeadershipjames lai96% (26)
- Michael MirandaDocument3 pagesMichael MirandawearemafaNo ratings yet
- Job InterviewDocument2 pagesJob InterviewcamNo ratings yet