Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STPM - Genetic Engineering
Uploaded by
jennieOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
STPM - Genetic Engineering
Uploaded by
jennieCopyright:
Available Formats
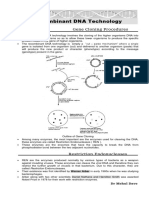
Genetic engineering/recombinant DNA technology
This is DNA in which genes from two different sources, often different species are combined in vitro
into the same molecule.
Genes from one organism are introduced into the genome of an unrelated organism.
Reminder:
Gene: the basic unit of inheritance; a length of DNA on a chromosome.
Genome: the complement of genes of an organism (or of a cell).
Genotype: the genetic constitution of an organism; genes acting together with environmental factors produce the
organisms appearance (phenotype).
The genetic engineers tool kit of enzymes
Genetic engineering makes use of purified enzymes that enable DNA and RNA to be manipulated in precisely
known ways.
Enzyme
Natural sources
Application in recombinant DNA technology
Restriction enzymes
Cytoplasm of bacteria combats Cuts/cleaves DNA molecules into shorter
(restriction
viral infection by breaking up
segments/fragments, at specific nucleotide
endonucleases)
viral DNA
sequences
DNA ligase
With nucleic acid in nuclei of
Joins together DNA molecules during
cells of all organisms
replication of DNA
Polymerase
With nucleic acid in nuclei of
Synthesises nucleic acid strands from
cells of all organisms
nucleotides, guided by a template strand of
nucleic acid
Reverse transcriptase
Found in particular types of RNA Synthesises a DNA strand complementary to
viruses called retroviruses
an existing RNA strand
You might also like
- Genetic Engineering: Fundamental of and Its Applications in MedicineDocument48 pagesGenetic Engineering: Fundamental of and Its Applications in MedicineTamilarasi SasivarnamNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology)Document4 pagesGenetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA Technology)Geo NalobNo ratings yet
- rDNA PDFDocument11 pagesrDNA PDFbroken reedNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology: Presented by M QasimDocument15 pagesBiotechnology: Presented by M QasimFaiza RashidNo ratings yet
- Rajkumar Biology Unit - 9 by RajatDocument12 pagesRajkumar Biology Unit - 9 by RajatprasannandaNo ratings yet
- Welcome: BY Divya. B I Year Bio Chemistry Sacw ColegeDocument31 pagesWelcome: BY Divya. B I Year Bio Chemistry Sacw ColegeVino KannanNo ratings yet
- Genetic Technology: What You'll LearnDocument29 pagesGenetic Technology: What You'll LearnYadiNo ratings yet
- BENG 100 Frontiers of Biomedical Engineering Professor Mark SaltzmanDocument10 pagesBENG 100 Frontiers of Biomedical Engineering Professor Mark Saltzmantaryll_01No ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and Processes NotesDocument9 pagesBiotechnology Principles and Processes NotessameemNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Techniques in BiotechDocument250 pages1.1 Techniques in BiotechJoyce ChingNo ratings yet
- Principles of BiotechnologyDocument8 pagesPrinciples of BiotechnologyENGETS IT7No ratings yet
- Biotechnology Comp Unit in One Shot Mindmaps by Rakshita SinghDocument7 pagesBiotechnology Comp Unit in One Shot Mindmaps by Rakshita Singhkchahar886No ratings yet
- Biotechnology - Principles and Processes - Notes - June 2023Document15 pagesBiotechnology - Principles and Processes - Notes - June 2023Tahsinul islamNo ratings yet
- BIOTECH MOD.1Q3Document24 pagesBIOTECH MOD.1Q3Aaron Janapin MirandaNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DnaDocument3 pagesRecombinant DnaleicatapangNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY XII Study Material 2022-23 Chapter Wise PrepDocument29 pagesBIOLOGY XII Study Material 2022-23 Chapter Wise PrepashwinkumarcoimatoreNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument1 pageGenetic Engineeringmayzel14No ratings yet
- Micro BiotechDocument28 pagesMicro Biotechreynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Bio Project 2019Document7 pagesBio Project 2019Ericom On RiqcousNo ratings yet
- 6.molecular Method Cloning, Therapy, RecombinantDocument18 pages6.molecular Method Cloning, Therapy, Recombinantaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- RT-week10-Lecture10-April 6 2023Document24 pagesRT-week10-Lecture10-April 6 2023amirkhan091018No ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles & ProcessesDocument3 pagesBiotechnology Principles & ProcessesKambaska Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- How To Sequence The Human Genome-Mark KielDocument8 pagesHow To Sequence The Human Genome-Mark KielDANIELLE THERESE IRINGANNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument31 pagesBiotechnologyJijendarNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument2 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologyAllynn JunioNo ratings yet
- CAPE 1 Biology - Genetic EngineeringDocument80 pagesCAPE 1 Biology - Genetic EngineeringTamicka BonnickNo ratings yet
- Notes - BiologyDocument41 pagesNotes - BiologyJamie Rose FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Recombinant Dna TechnologyDocument15 pagesRecombinant Dna TechnologyManish kumarNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering: o o o o o o o o o o o o o oDocument24 pagesGenetic Engineering: o o o o o o o o o o o o o oMasthankhan PatanNo ratings yet
- R DNA TechnologyDocument17 pagesR DNA TechnologyDRMEHUL DAVENo ratings yet
- Dr. Peter John M.Phil, PHD Assistant ProfessorDocument25 pagesDr. Peter John M.Phil, PHD Assistant ProfessorMehak ToorNo ratings yet
- GCMBDocument5 pagesGCMBHarshita SinhaNo ratings yet
- Gene Technologies Allow The Study and Alteration of Gene Function Allowing A Better Understanding of Organism Function and The Design of New Industrial and Medical ProcessesDocument43 pagesGene Technologies Allow The Study and Alteration of Gene Function Allowing A Better Understanding of Organism Function and The Design of New Industrial and Medical ProcessesMaisarah HalimNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DnaDocument35 pagesRecombinant DnaCamella Beatrice Lujan ValleNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument27 pagesGenetic EngineeringSeema QureshiNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering:: Q: How Can Genetically Engineered Mosquito Larvae Be Identified?Document6 pagesGenetic Engineering:: Q: How Can Genetically Engineered Mosquito Larvae Be Identified?Debarshi SahooNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Genetic Material - Since DNA Exists Within The Cell Membrane Along With OtherDocument3 pagesIsolation of Genetic Material - Since DNA Exists Within The Cell Membrane Along With OtherMarkuz SenonNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNADocument2 pagesRecombinant DNAKarylle MaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Genetics and BiotechnologyDocument43 pagesChapter 13 Genetics and BiotechnologyMUHAMMAD SAALIM100% (2)
- 19 - Genetic TechnologyDocument6 pages19 - Genetic TechnologyAhana KatyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 12Document13 pagesChapter # 12Shahzaib AhmedNo ratings yet
- BiotechDocument5 pagesBiotechkaiaNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument5 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologyMonika KanojiaNo ratings yet
- ELS - Q2 - Week 4aDocument11 pagesELS - Q2 - Week 4aShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Notes-1Document6 pagesBiotechnology Notes-1Exporting WarriorNo ratings yet
- Cloning Procedu-WPS OfficeDocument19 pagesCloning Procedu-WPS Officedeepak gupta100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Biotechnology Principle and ProcessDocument50 pagesChapter 11 Biotechnology Principle and ProcessMkisneymar Meymar100% (1)
- Gene Splicing FinDocument18 pagesGene Splicing FinNoellah Jeannica MacamNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles and ProcessesDocument23 pagesBiotechnology Principles and ProcessesRoshan KumarNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA Technology - Definition, Steps, ApplicationsDocument7 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology - Definition, Steps, ApplicationsVikas PatreyNo ratings yet
- Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument3 pagesRecombinant DNA TechnologyJennifer Davis CondimanNo ratings yet
- 11.1: Principles of BiotechnologyDocument10 pages11.1: Principles of BiotechnologyMauz KhanNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Principles & Processes PDFDocument3 pagesBiotechnology Principles & Processes PDFMEGHA KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Gene Technology & ApplicationsDocument6 pagesChapter 20 Gene Technology & ApplicationsIrish Jem BantolinoNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology: Biology For TechnologyDocument58 pagesBiotechnology: Biology For TechnologyLeonardoFloresNo ratings yet
- Bio TechnologyDocument51 pagesBio Technologylalithadithya85No ratings yet
- Recombinant DNADocument19 pagesRecombinant DNAAbhash0% (1)
- Biotechnology - Its Tools and TechniquesDocument31 pagesBiotechnology - Its Tools and TechniquesRalph Rezin MooreNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument1 pageReproductionjennieNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument1 pageRespirationjennieNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument1 pageRespirationjennieNo ratings yet
- Structure of Cells and OrganellesDocument2 pagesStructure of Cells and OrganellesjennieNo ratings yet
- Pieris Homo Lathyrus Sapiens OdoratusDocument1 pagePieris Homo Lathyrus Sapiens OdoratusjennieNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals: The Cardiac CycleDocument2 pagesTransport in Animals: The Cardiac CyclejennieNo ratings yet
- Variation and Theory of EvolutionDocument1 pageVariation and Theory of EvolutionjennieNo ratings yet
- Control in Cells-STPMDocument2 pagesControl in Cells-STPMjennieNo ratings yet
- Hormone STPMDocument1 pageHormone STPMjennieNo ratings yet
- Development Animal ImplantationDocument1 pageDevelopment Animal ImplantationjennieNo ratings yet
- Immunity STPMDocument2 pagesImmunity STPMjennie0% (1)
- Gaseous Exchange-STPMDocument2 pagesGaseous Exchange-STPMjennieNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry of A Cell-StpmDocument3 pagesBasic Chemistry of A Cell-StpmjennieNo ratings yet
- STPM GrowthDocument1 pageSTPM GrowthjennieNo ratings yet