Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5.1.4.4 Packet Tracer - Identify MAC and IP Addresses Instructions IG
Uploaded by
John MuvatiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5.1.4.4 Packet Tracer - Identify MAC and IP Addresses Instructions IG
Uploaded by
John MuvatiCopyright:
Available Formats
Packet Tracer - Identify MAC and IP Addresses (Instructor
Version)
Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
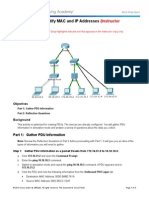
Topology
Objectives
Part 1: Gather PDU Information
Part 2: Reflection Questions
Background
This activity is optimized for viewing PDUs. The devices are already configured. You will gather PDU
information in simulation mode and answer a series of questions about the data you collect.
Part 1: Gather PDU Information
Note: Review the Reflection Questions in Part 2 before proceeding with Part 1. It will give you an idea of the
types of information you will need to gather.
Step 1: Gather PDU information as a packet travels from 172.16.31.2 to 10.10.10.3.
a. Click 172.16.31.2 and open the Command Prompt.
b. Enter the ping 10.10.10.3 command.
c.
Switch to simulation mode and repeat the ping 10.10.10.3 command. A PDU appears next to
172.16.31.2.
d. Click the PDU and note the following information from the Outbound PDU Layer tab:
Destination MAC Address: 00D0:BA8E:741A
Source MAC Address: 000C:85CC:1DA7
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 1 of 3
Packet Tracer - Identify MAC and IP Addresses
Source IP Address: 172.16.31.2
Destination IP Address: 10.10.10.3
At Device: Computer
e. Click Capture / Forward to move the PDU to the next device. Gather the same information from Step 1d.
Repeat this process until the PDU reaches its destination. Record the PDU information you gathered into
a spreadsheet using a format like the table shown below:
Example Spreadsheet Format
Test
At Device
Dest. MAC
Src MAC
Src IPv4
Dest IPv4
Ping from
172.16.31.2
to
10.10.10.3
172.16.31.2
00D0:BA8E:741
A
000C:85CC:1DA
7
172.16.31.
2
10.10.10.
3
Hub
--
--
--
--
Switch1
00D0:BA8E:741
A
000C:85CC:1DA
7
--
--
Router
0060:4706:572B
00D0:588C:240
1
172.16.31.
2
10.10.10.
3
Switch0
0060:4706:572B
00D0:588C:240
1
--
--
Access
Point
--
--
--
--
10.10.10.3
0060:4706:572B
00D0:588C:240
1
172.16.31.
2
10.10.10.
3
Step 2: Gather additional PDU information from other pings.
Repeat the process in Step 1 and gather the information for the following tests:
Ping 10.10.10.2 from 10.10.10.3.
Ping 172.16.31.2 from 172.16.31.3.
Ping 172.16.31.4 from 172.16.31.5.
Ping 172.16.31.4 from 10.10.10.2.
Ping 172.16.31.3 from 10.10.10.2.
Part 2: Reflection Questions
Answer the following questions regarding the captured data:
1. Were there different types of wires used to connect devices? Yes, copper and fiber
2. Did the wires change the handling of the PDU in any way? No
3. Did the Hub lose any of the information given to it? No
4. What does the Hub do with MAC addresses and IP addresses? Nothing
5. Did the wireless Access Point do anything with the information given to it? Yes. It repackaged it as wireless
802.11
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 2 of 3
Packet Tracer - Identify MAC and IP Addresses
6. Was any MAC or IP address lost during the wireless transfer? No
7. What was the highest OSI layer that the Hub and Access Point used? Layer 1
8. Did the Hub or Access Point ever replicate a PDU that was rejected with a red X? Yes
9. When examining the PDU Details tab, which MAC address appeared first, the source or the destination?
Destination
10. Why would the MAC addresses appear in this order? A switch can begin forwarding a frame to a known MAC
address more quickly if the destination is listed first
11. Was there a pattern to the MAC addressing in the simulation? No
12. Did the switches ever replicate a PDU that was rejected with a red X? No
13. Every time that the PDU was sent between the 10 network and the 172 network, there was a point where the
MAC addresses suddenly changed. Where did that occur? It occurred at the Router
14. Which device uses MAC addresses starting with 00D0? The Router
15. To what devices did the other MAC addresses belong? To the sender and receiver
16. Did the sending and receiving IPv4 addresses switch in any of the PDUs? No
17. If you follow the reply to a ping, sometimes called a pong, do the sending and receiving IPv4 addresses
switch? Yes
18. What is the pattern to the IPv4 addressing in this simulation? Each port of a router requires a set of nonoverlapping addresses
19. Why do different IP networks need to be assigned to different ports of a router? The function of a router is to
inter-connect different IP networks.
20. If this simulation was configured with IPv6 instead of IPv4, what would be different? The IPv4 addresses
would be replaced with IPv6 addresses, but everything else would be the same.
Suggested Scoring Rubric
There are 20 questions worth 5 points each for a possible score of 100.
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 5.1.4.4 Packet Tracer - Identify MAC and IP Addresses Instructions IGDocument3 pages5.1.4.4 Packet Tracer - Identify MAC and IP Addresses Instructions IGJohn MuvatiNo ratings yet
- Intro To GSMDocument22 pagesIntro To GSMThiaguNo ratings yet
- Ss7 TutorialDocument23 pagesSs7 Tutorialarifbudianto100% (3)
- CDMA Basic Call ProcessingDocument41 pagesCDMA Basic Call Processingapi-384463092% (12)
- CDMA ArchitectureDocument11 pagesCDMA ArchitectureIdrees MohammedNo ratings yet
- CDMA ArchitectureDocument11 pagesCDMA ArchitectureIdrees MohammedNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Ims 6Document83 pagesTutorial Ims 6nabeelmansur100% (2)
- CDMA ArchitectureDocument11 pagesCDMA ArchitectureIdrees MohammedNo ratings yet