Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sliding Failure
Sliding Failure
Uploaded by
Ahlid YeahhOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sliding Failure
Sliding Failure
Uploaded by
Ahlid YeahhCopyright:
Available Formats
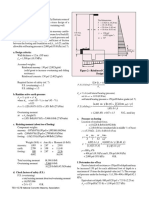
1.
What is retaining structure
A retaining wall is a structure that holds or retains soil behind it. There are many
types of materials that can be used to create retaining walls like concrete
blocks, poured concrete, treated timbers, rocks or boulders. Some are easy to
use, others have a shorter life span, but all can retain soil.
2.State the types of retaining structures that commonly used in Malaysia
Sheetpile wall
Gabion meshes
Soil nailing
Geotextile
Pre-cast crib walls
Explain some common failure modes of retaining structure
Sliding failure
Sliding failure is nothing but sliding of wall away from backfill when there us
shearing failure at the base of wall.
Overturning failure
Overturning failure is rotation of wall about is toe due to exceeding of
moment caused due to overturning force to resisting forces.
Bearing capacity failure
The pressure extend by resultant vertical force at toe of wall must not exceed
the allowable bearing capacity of the soil.
4. Explain the construction consideration for retaining structure
Materials. When choosing materials, select the type that is best suited for the required
result. Many long-lasting materials are available for landscape use including flagstone rock,
recycled concrete paving treated timbers, vertical poles, precast concrete modular units, poured
concrete, and brick veneer.
Foundations. A wall is only as good as its foundation and all retaining walls should be built on
structurally sound, compacted foundation sub-base material. Leveled and compacted earth or
gravel fill are acceptable. The foundation material should extend at least one foot beyond the
front and back of the base width of the wall. When building dry-laid stone walls, place the
largest, most stable stones on the bottom of the wall, and be aware that the base width may
need to be as wide as the wall is high.
Type of wall. The type of wall you choose should be determined by need. Decide if you
need a poured-in-place concrete "structural" wall or a much less expensive "dry-laid wall"
consisting of stacked, open-joint material.
5.State the laboratory testing that involved before construct the retaining structures.
Mechanical analysis
Unconfined compression
Shrinkage factors
Permeability
Plastic limit (PL) and Liquid limit (LL)
6.Discuss the solution on how to prevent retaining structure from failure.
Drainage. The lack of proper drainage is the most common reason for
retaining wall failure. When water is absorbed into the soil behind a retaining
wall and it has no place to go, the pressure behind the wall is increased. If
the water continues to build up, it will eventually push the wall out, causing it
to bulge or collapse. Installing drain pipes and using a clean, granular rock
for both the backfill and the base of the wall will allow water to drain out.
The pressure will be released and wall failure will be prevented.
Compaction. Poor compaction will eventually cause a retaining wall to shift,
producing large gaps within the wall. The soil needs to be compacted once
at the point of excavation, again after the gravel base has been added, and
each time backfill is added. (Backfill should be added after each course of
the wall has been installed). The most effective way to do this is to use a
piece of machinery called (you guessed it!) a compactor.
7. Find one example of case study that related to retaining structure. The topic involved
in the case study may be related to the type if retaining structure that used, construction
method, failure mode and solution on how to prevent the failure. Explain all the topic
involved in the case study. Attached the case study at the end of this assignment.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- BOQ Lotus Hotel Final 080709Document26 pagesBOQ Lotus Hotel Final 080709Jane NixonNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- BS EN 1997 - Geotechnical Design Examples PDFDocument14 pagesBS EN 1997 - Geotechnical Design Examples PDFBolanle OlaawoNo ratings yet
- RISA Foundation Verification ProblemsDocument62 pagesRISA Foundation Verification ProblemsCésar Cristóbal Pino Guzmán100% (1)
- Permanent Steel Sheet Piling (LRFD)Document2 pagesPermanent Steel Sheet Piling (LRFD)shujaNo ratings yet
- Cantilever Masonry Wall Example PDFDocument14 pagesCantilever Masonry Wall Example PDFJosé Alberto Garcia CordovaNo ratings yet
- KantileverDocument6 pagesKantileverDerry WijayadiNo ratings yet
- Singapore - GCCM Talk SlidesDocument115 pagesSingapore - GCCM Talk SlidesChimhuee ChuaNo ratings yet
- Can Bamboo Be A Suitable Replacement For Steel in The Use of Gabions?Document3 pagesCan Bamboo Be A Suitable Replacement For Steel in The Use of Gabions?Engineers Without Borders UKNo ratings yet
- Research Paper of Shanping ProjectDocument8 pagesResearch Paper of Shanping ProjectSophaneth USPHEA100% (1)
- Example 11 Cast in Place Concrete Cantilever Retaining Wall - 20200101Document15 pagesExample 11 Cast in Place Concrete Cantilever Retaining Wall - 20200101Angela GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Retaining Walls With Relief ShelvesDocument13 pagesRetaining Walls With Relief ShelvesMike VictorNo ratings yet
- Mse Retaining Wall Design Considerations by Marcus Galvan, P.E. Txdot Bridge Division Geotechnical BranchDocument57 pagesMse Retaining Wall Design Considerations by Marcus Galvan, P.E. Txdot Bridge Division Geotechnical Branchkhairul4008No ratings yet
- Slab Track On Different SubgradesDocument9 pagesSlab Track On Different SubgradesfranalhamaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 23 Anchored Sheet Pile WallDocument21 pagesTutorial 23 Anchored Sheet Pile WallBambang Eko WidyantoNo ratings yet
- Design of Retaining Wall For 1.5M HeightDocument1 pageDesign of Retaining Wall For 1.5M HeightManupriya KapleshNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundations (Parts A and B) : NIOEC-SP-10-12Document11 pagesPile Foundations (Parts A and B) : NIOEC-SP-10-12Ak OraNo ratings yet
- Earth Pressures Retaining Walls Rock Faces Numerical SolutionDocument7 pagesEarth Pressures Retaining Walls Rock Faces Numerical SolutionAnonymous hRWwL7pZnCNo ratings yet
- HydraulicsDocument10 pagesHydraulicsAnonymous QinVShNo ratings yet
- S-Curve and Bar ChartDocument1 pageS-Curve and Bar ChartJet Arca0% (1)
- CE2305 FOUNDATION ENGINEERING Anna University Question Bank Question Paper 2 Marks and 16 MarksDocument11 pagesCE2305 FOUNDATION ENGINEERING Anna University Question Bank Question Paper 2 Marks and 16 MarksPrabhumk07No ratings yet
- RT Wall Drawing FinalDocument604 pagesRT Wall Drawing FinalYazer ArafathNo ratings yet
- MSE Design - Example 1Document22 pagesMSE Design - Example 1Yassin Abd El Aal100% (1)
- SG Load Types and CombinationsDocument5 pagesSG Load Types and CombinationsRsjBugtongNo ratings yet
- Go, Charles Warren M. (Problem Set 4)Document21 pagesGo, Charles Warren M. (Problem Set 4)Charles Warren GoNo ratings yet
- Reinforced EarthDocument28 pagesReinforced EarthKumar RavishankerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Soil Retaining StructuresDocument101 pagesChapter 4 Soil Retaining StructuresAlemayehu MitekuNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering PDFDocument60 pagesFoundation Engineering PDFNabin YadavNo ratings yet
- Applied Sciences: Stability of Reinforced Retaining Wall Under Seismic LoadsDocument13 pagesApplied Sciences: Stability of Reinforced Retaining Wall Under Seismic LoadsHazbullah ShajiNo ratings yet
- BT3 Finals ReviewerDocument31 pagesBT3 Finals ReviewerJano AgbigayNo ratings yet
- Standard Specifications For TunnelingDocument6 pagesStandard Specifications For Tunnelingsalah400% (2)