Professional Documents
Culture Documents
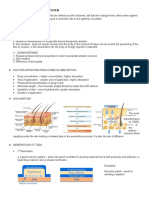
Analgesics: Are A Class of Drugs Used To Relieve Pain. The Pain Relief
Uploaded by
Esther Faith Gabriel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views12 pagesThe document discusses several classes of drugs used to treat different medical conditions. Analgesics are used to relieve pain by blocking pain signals or interfering with pain interpretation. Antiseptics kill or inhibit microorganisms on the body's external surfaces. Antiasthmatic drugs treat or prevent asthma attacks. ACE inhibitors are used to treat hypertension and heart failure.
Original Description:
Analgesics
Original Title
Analgesics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses several classes of drugs used to treat different medical conditions. Analgesics are used to relieve pain by blocking pain signals or interfering with pain interpretation. Antiseptics kill or inhibit microorganisms on the body's external surfaces. Antiasthmatic drugs treat or prevent asthma attacks. ACE inhibitors are used to treat hypertension and heart failure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views12 pagesAnalgesics: Are A Class of Drugs Used To Relieve Pain. The Pain Relief
Uploaded by
Esther Faith GabrielThe document discusses several classes of drugs used to treat different medical conditions. Analgesics are used to relieve pain by blocking pain signals or interfering with pain interpretation. Antiseptics kill or inhibit microorganisms on the body's external surfaces. Antiasthmatic drugs treat or prevent asthma attacks. ACE inhibitors are used to treat hypertension and heart failure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Analgesics are a class of drugs used to relieve pain.
The pain relief
induced by analgesics occurs either by blocking pain signals going to the
brain or by interfering with the brain's interpretation of the signals, without
producing anesthesia or loss of consciousness.
Antiseptic, agent that kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms on
the external surfaces of the body. Antiseptics should generally be
distinguished from drugs such as antibiotics that destroy microorganisms
internally, and from disinfectants, which destroy microorganisms found on
nonliving objects.
Antiasthmatic drugs are medicines that treat or prevent asthma
attacks.
ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, are
a group of pharmaceuticals that are used primarily in treatment of
hypertension and congestive heart failure, in some cases as the drugs of first
choice.
Chloramphenicol-used chiefly in the treatment of infections caused
by certain bacteria, by rickettsiae, and by certain viruses.
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of drugs that
lower cholesterol levels in people.
Hematenics- a drug or other agent that increases blood hemoglobin
Biguanide- a drug that lowers blood sugar. Used for the treatment of
non-insulin-dependent diabetes.
Corticosteroid- Use for reduction of inflammation and allergic
reactions, prevention of graft rejection.
Antibiotics- Drug that kills or inactivates bacteria, but has no effect
against viruses.
Aminopenicillins are a group of antibiotics.[1] They belong to the penicillin
family and comprise the members ampicillin, amoxicillin, and bacampicillin.[2]
Macrolides are a group of drugs (typically antibiotics) whose activity stems
from the presence of a macrolide ring, a large macrocyclic lactone ring to
which one or more deoxy sugars, usually cladinose and desosamine, may be
attached.
Thyroid Hormone Replacement
Antihistamine
Antithrombotic
You might also like
- Drug Categories 2Document4 pagesDrug Categories 2Michaela Jem Marie BitonNo ratings yet
- General Drug Categories - FDADocument5 pagesGeneral Drug Categories - FDAkazyhabib.dgdaNo ratings yet
- Types of Medicines 3Document14 pagesTypes of Medicines 3John Lloyd OcampoNo ratings yet
- Drug CategoriesDocument4 pagesDrug CategoriesAizeiah Reigne LabradorNo ratings yet
- Topik 13. Medicine CategoriesDocument4 pagesTopik 13. Medicine CategoriesioakasNo ratings yet
- Drug ClassesDocument4 pagesDrug ClassesMeriem KerboubNo ratings yet
- Medicine Categories RDNDocument6 pagesMedicine Categories RDNmila alghinaNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical DrugsDocument92 pagesPharmaceutical DrugsFranco RazonNo ratings yet
- Intro To PharmacyDocument13 pagesIntro To PharmacyYudah IsraelNo ratings yet
- General Drug CategoriesDocument7 pagesGeneral Drug CategoriesShaila FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Module Pharma TXDocument2 pagesModule Pharma TXmackie_041992No ratings yet
- Drugs Which Are Used For The Treatment of Cardiovascular DiseasesDocument3 pagesDrugs Which Are Used For The Treatment of Cardiovascular DiseasesЛюбов ВітькоNo ratings yet
- What Are The Therapeutic Classes of DrugsDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Therapeutic Classes of DrugsFrank GomesNo ratings yet
- Pharmaco TherapeuticsDocument19 pagesPharmaco TherapeuticsJareena BegumNo ratings yet
- NCM 61 Pharmacology - Digital Scrapbook-: By: Hannah Angelu S. Cabading Bsn2DDocument35 pagesNCM 61 Pharmacology - Digital Scrapbook-: By: Hannah Angelu S. Cabading Bsn2DHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- What Are Analgesics?Document10 pagesWhat Are Analgesics?Betsy Brown ByersmithNo ratings yet
- Pers Pharm F1 Category of DrugsDocument2 pagesPers Pharm F1 Category of Drugsjanineamorin1017No ratings yet
- Topics PDFDocument3 pagesTopics PDFRyuk AnNo ratings yet
- Clayton & Willihnganz: Basic Pharmacology For Nurses, 17th EditionDocument4 pagesClayton & Willihnganz: Basic Pharmacology For Nurses, 17th EditionabsianoNo ratings yet
- 8 - Anti Allergic DrugsDocument8 pages8 - Anti Allergic DrugsMoataz TrabehNo ratings yet
- Perspective PharmacyDocument3 pagesPerspective PharmacyeiramNo ratings yet
- Wa0123.Document2 pagesWa0123.Darling LcNo ratings yet
- Drugs On RespiratoryDocument17 pagesDrugs On RespiratoryIrwan M. IskoberNo ratings yet
- General Drug CategoriesDocument3 pagesGeneral Drug CategoriesUswatun HasanahNo ratings yet
- Administration of DrugsDocument4 pagesAdministration of DrugsHoàng Kiều OanhNo ratings yet
- Classification of Drugs and Their Physiological Effects: Jeo Yvan I Ejorcadas Grade 9 - Emerald 5Document5 pagesClassification of Drugs and Their Physiological Effects: Jeo Yvan I Ejorcadas Grade 9 - Emerald 5ejorcadasjeoyvanibacarraNo ratings yet
- Cmpi MidtermDocument185 pagesCmpi MidtermAubrey MadelaineNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Powerpoint Group 1Document38 pagesPharmacology Powerpoint Group 1Daniel LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Fanny B.inggrisDocument5 pagesFanny B.inggrisFanny FarlyashaNo ratings yet
- Assignments Pharmacodynamics 2 - Iffah Arizan (2219092) PDFDocument2 pagesAssignments Pharmacodynamics 2 - Iffah Arizan (2219092) PDFNur Iffah Hanna ArizanNo ratings yet
- Drug Names and Classes: Appendix ADocument25 pagesDrug Names and Classes: Appendix AJermaine DomingoNo ratings yet
- QuesrtionsDocument4 pagesQuesrtionsrolandpaulagbayani1014No ratings yet
- Drug ClassificationsDocument4 pagesDrug ClassificationsRouwi DesiatcoNo ratings yet
- Anti Epileptics and Medicinal PlantsDocument3 pagesAnti Epileptics and Medicinal PlantsAnnisaNo ratings yet
- Additive Therapy: Important Terms Related To General and Systemic Veterinary PharmacologyDocument9 pagesAdditive Therapy: Important Terms Related To General and Systemic Veterinary PharmacologySanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Chem ProjectDocument33 pagesChem Projectricardojosephj6No ratings yet
- Classification of Medicine NotesDocument24 pagesClassification of Medicine NotesMikaela KayeNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification - EuchariaDocument4 pagesDrug Classification - Euchariakwoke chizobaNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic DrugsDocument38 pagesPsychotropic DrugsEdgar Manood100% (1)
- Pharmacology 2Document13 pagesPharmacology 2Maria Nichole JavarNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology IntroDocument7 pagesPharmacology IntroJaeNo ratings yet
- ch-16 NcertDocument9 pagesch-16 NcertTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics: Penicillin AmoxycillinDocument18 pagesAntibiotics: Penicillin AmoxycillinRowell HernandezNo ratings yet
- HST 690038Document10 pagesHST 690038gpkjs314No ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Drug ClassificationsDocument4 pagesPharmaceutical Drug Classificationshiteshchavada100% (2)
- 1 AnalgesicsDocument10 pages1 Analgesicsalhesham141No ratings yet
- M M M M: MR - Vijayakumar MR - Vijayakumar M.SC., M.SC., M.Phil. M.Phil., PGDCA.., PGDCA.Document23 pagesM M M M: MR - Vijayakumar MR - Vijayakumar M.SC., M.SC., M.Phil. M.Phil., PGDCA.., PGDCA.murugs92No ratings yet
- AntacidsDocument5 pagesAntacidsRowela Mae LibradillaNo ratings yet
- Anti HistaminesDocument15 pagesAnti HistaminesMuhammad ZakriaNo ratings yet
- NR 446 Week 6 ATI Weekly Tips Mental HealthDocument16 pagesNR 446 Week 6 ATI Weekly Tips Mental HealthChristine LansdownNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Everyday LifeDocument6 pagesChemistry in Everyday LifeNeha UdeshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Group 5Document44 pagesChapter 20 - Group 5Thanh TrúcNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Antibiotics and Medicine?: Drugs Cardiac Arrhythmias Myocardial Infarction HypertensionDocument1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between Antibiotics and Medicine?: Drugs Cardiac Arrhythmias Myocardial Infarction HypertensionVimal KumarNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Science C7Document94 pagesYear 8 Science C7Ventus TanNo ratings yet
- Notre Dame of Dadiangas University Marist Avenue, General Santos CityDocument18 pagesNotre Dame of Dadiangas University Marist Avenue, General Santos CityKathleen GasparinNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - TREATMENT OF MENTAL DISEASESDocument52 pagesTopic 2 - TREATMENT OF MENTAL DISEASESprashant singhNo ratings yet
- Jasmine M. Medina BSN Ii - 2: A. Drug DefinitionDocument4 pagesJasmine M. Medina BSN Ii - 2: A. Drug DefinitionJasNo ratings yet
- EverydayDocument2 pagesEverydayNaveen ChavaliNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemOctavia. GNo ratings yet
- Migraines: Migraine Treatment and Prevention Options: The most important information you need to improve your healthFrom EverandMigraines: Migraine Treatment and Prevention Options: The most important information you need to improve your healthNo ratings yet
- COLUMN CHROMATOGRAPHY OutlineDocument4 pagesCOLUMN CHROMATOGRAPHY OutlineEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- Latent Heat of VaporizationDocument11 pagesLatent Heat of VaporizationEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- Topic: Structural Functional IsmDocument2 pagesTopic: Structural Functional IsmEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- RTI ZidovudineDocument5 pagesRTI ZidovudineEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- Blessed Assurance Chords ADocument2 pagesBlessed Assurance Chords AEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- Column Chromatography OutlineDocument4 pagesColumn Chromatography OutlineEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- Build It Better ChordsDocument2 pagesBuild It Better ChordsEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- Shepherd: TEMPO - 75bpm (6/8) Key - A Verse 1 A E F#MDocument1 pageShepherd: TEMPO - 75bpm (6/8) Key - A Verse 1 A E F#MEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Interpretation of Standard Score or Development IndexDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Interpretation of Standard Score or Development IndexEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular AgentsDocument22 pagesCardiovascular AgentsEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- Early Literacy Behavior Oral LanguageDocument3 pagesEarly Literacy Behavior Oral LanguageEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- Thesis Proposal Defense 2016Document2 pagesThesis Proposal Defense 2016Esther Faith Gabriel0% (1)
- Transdermal Drug Delivery System - ManufDocument13 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery System - ManufEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- Main Branches of ChemistryDocument4 pagesMain Branches of ChemistryEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- Herbal Soap MakingDocument2 pagesHerbal Soap MakingEsther Faith Gabriel100% (3)
- CMO 03 S 2006-PharmacyDocument65 pagesCMO 03 S 2006-PharmacyAnnabelle Paredes Acedera100% (1)
- Biopharmaceutical Ingredients and ExcipientsDocument3 pagesBiopharmaceutical Ingredients and ExcipientsEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument2 pagesReflectionEsther Faith Gabriel0% (2)
- Experiment No. 6 Enzymes Group Data and ResultsDocument2 pagesExperiment No. 6 Enzymes Group Data and ResultsEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet