Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CIEM, Trung tâm Thông tin - Tư liệu
Uploaded by
PhiPhiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CIEM, Trung tâm Thông tin - Tư liệu
Uploaded by
PhiPhiCopyright:
Available Formats
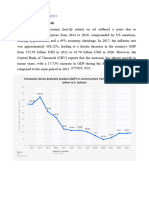
really urgent need in the coming period as Vietnam is to maintain the growth rate
to escape the vicious cycle trap of low-income countries, and the prerequisite is to
reduce disparity and poverty. However, in terms of capacity, the possibility for
Vietnams sustainable development is a big question, given the perspective of
rapid economic growth basing on reducing the income gap between individuals
and regions across the country.
The contradic picture of the rich and the poor in Vietnam shows another
perspective of economic growth process, and that the income gap in Vietnam is
widening. This fact is consistent with the assessment of the World Bank that the
rich and poor gap in Vietnam is moving away from relatively equal in 2002 to
rather difference because the income gap keeps growing among current resident
groups. This remark is no surprise as according to the Ministry of Labour - Invalids
and Social Affairs, the gap between income levels of different labor groups is
widening, especially in large cities.
Compared to other countries having the same development level (in income
per capita) around the world, Vietnams income disparity remains at a moderate
level, approximately 0.45 in 2010. However, it is noteworthy that the difference
tends to increase and may reach alarming levels in the future if there is no attempt
to stop now. This fact is manifested in many different compared dimensions, such
as: the gap between the 20% of richest population and 20% of poorest population.
In summary, in Vietnam, the Gini index Index is around 0.4. According to the
international organizations, distribution of income in Vietnam is still at a safe
level. Socially, though people's lives have been improved, poverty has reduced,
Gini index in Vietnam is high, and keeps increasing over the years (the index in
2004 was 0.423,and in 2006 the number reached 0.425).
High Gini index shows the disparity of income as well as the rich and poor
gap among different resident groups. According to the World Bank, before 1990,
countries with low income experienced Gini coefficient from 0.389 (Bangladesh)
to 0.550 Kenya, the average income Gini coefficient was from 0.378 (South Korea)
to 0.605 (Brazil), the number in industrial market-oriented economy is from 0.285
(Japan) to 0.404 (Australia), of socialism countries (before 1990) was from 0.284
to 0.317. Thereby, income gap in Vietnam is relatively high compared to the
world, and is noteworthy that this gap has been growing in recent years as
described in the working-paper.
CIEM, Trung tm Thng tin T liu
You might also like
- Giảm Khoảng Cách Chênh Lệch Thu Nhập To Reduce Income Gap In VietnamDocument54 pagesGiảm Khoảng Cách Chênh Lệch Thu Nhập To Reduce Income Gap In VietnamThuy BuiNo ratings yet
- Hoàng Thị Huyền 5093106410 Đặng Thị Yến 5093106371Document7 pagesHoàng Thị Huyền 5093106410 Đặng Thị Yến 5093106371Linh NgaaNo ratings yet
- The State of Inequality - Un Zambia Signature Issue Paper 1 - June 2013Document28 pagesThe State of Inequality - Un Zambia Signature Issue Paper 1 - June 2013Ndime UsoNo ratings yet
- Final Script in VietnamDocument8 pagesFinal Script in Vietnamkianna doctoraNo ratings yet
- Review of SDG 10, BrazilDocument6 pagesReview of SDG 10, BrazilSomaNo ratings yet
- 2021 FAS Trends and DevelopmentsDocument11 pages2021 FAS Trends and DevelopmentsVrushank Aithal KNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Development EconomicsDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Development EconomicsKhant Zaw ThantNo ratings yet
- Economics DevelopmentDocument20 pagesEconomics DevelopmentFTU.CS2 Nguyễn Hà Phương DungNo ratings yet
- CSA 01 Progress in The Struggle For More Meaningful Development - BrazilDocument1 pageCSA 01 Progress in The Struggle For More Meaningful Development - BrazilRodelle DacumosNo ratings yet
- The Recitals March 24 PDF 65245bb587Document104 pagesThe Recitals March 24 PDF 65245bb587JATIN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Income DistributionDocument2 pagesIncome DistributionGallyn Ditya ManggalaNo ratings yet
- Comparitive Economic Development: The 2020 GNI Per Capita Thresholds AreDocument8 pagesComparitive Economic Development: The 2020 GNI Per Capita Thresholds AreAmber KhanNo ratings yet
- ECO303 Research Paper 1Document24 pagesECO303 Research Paper 1Mahi SinthiaNo ratings yet
- The Business Environment in Japan: Group Apex 5Document10 pagesThe Business Environment in Japan: Group Apex 5nhi.vimicoNo ratings yet
- Methodology: Povcalnet DatabaseDocument3 pagesMethodology: Povcalnet DatabaseJagrut PatilNo ratings yet
- Pestle (E&t)Document4 pagesPestle (E&t)Ngoc Huỳnh HyNo ratings yet
- Taxation Paper PDFDocument8 pagesTaxation Paper PDFJacobNo ratings yet
- EBU 1033 Russell Floyd Albert (81069) IADocument7 pagesEBU 1033 Russell Floyd Albert (81069) IARussell FloydNo ratings yet
- Rising Income Inequality in BangladeshDocument6 pagesRising Income Inequality in BangladeshShakif AhmedNo ratings yet
- ED XLIX 4 250114 A Hare-Brained ProposalDocument2 pagesED XLIX 4 250114 A Hare-Brained ProposalShay WaxenNo ratings yet
- Growth Without Development (Brazil)Document3 pagesGrowth Without Development (Brazil)Danica Christele AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Income Inequality in IndiaDocument12 pagesIncome Inequality in IndiaRøhãñ PãrdëshîNo ratings yet
- Summary of Indonesia'S Poverty Analysis: Adb Papers On IndonesiaDocument6 pagesSummary of Indonesia'S Poverty Analysis: Adb Papers On Indonesiafitri yantiNo ratings yet
- Softskill ReportDocument12 pagesSoftskill ReportBhargav VijayNo ratings yet
- GDP at Current Prices - US$: Source: World BankDocument5 pagesGDP at Current Prices - US$: Source: World BankAlankrit ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Subject Subject Code Semester/Year SectionDocument8 pagesSubject Subject Code Semester/Year SectionTamanna 2020No ratings yet
- Paper Djialeu PDFDocument3 pagesPaper Djialeu PDFMoundhir MhamadiNo ratings yet
- Publication 1Document18 pagesPublication 1Tinotenda DubeNo ratings yet
- Chaitanya Pareek Economics AssignmentDocument10 pagesChaitanya Pareek Economics AssignmentChetanye ManjhuNo ratings yet
- Challenges Galore Despite Laudable Economic ProgressDocument3 pagesChallenges Galore Despite Laudable Economic ProgressMd. Didar HusainNo ratings yet
- Gini CoefficientDocument3 pagesGini CoefficientDBRANLU StudentsNo ratings yet
- StatDocument12 pagesStatazazelNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Poverty Measurement From Multidimensional Perspective FinalDocument24 pagesEvaluation of Poverty Measurement From Multidimensional Perspective FinalParthiban S. GopalNo ratings yet
- Online Annex 1.1. How Will The COVID-19 Pandemic Affect Poverty and Inequality?Document34 pagesOnline Annex 1.1. How Will The COVID-19 Pandemic Affect Poverty and Inequality?Vdasilva83No ratings yet
- Brazil Paper AnalysisDocument60 pagesBrazil Paper AnalysisJella SantillanaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledMay JuniorroarNo ratings yet
- 08-How Does Income Inequality Affects Economic Growth at Different Income LevelsDocument22 pages08-How Does Income Inequality Affects Economic Growth at Different Income LevelsKristine Romero ManzonNo ratings yet
- CWORLD2Document1 pageCWORLD2taehyung trashNo ratings yet
- Economical AnalysisDocument7 pagesEconomical AnalysisManas GargNo ratings yet
- M1 Essay On Distinctions Between Economic Growth and DevelopmentDocument2 pagesM1 Essay On Distinctions Between Economic Growth and Developmentkris salacNo ratings yet
- R215 Living Standards Poverty and Inequality in The UK 2022Document78 pagesR215 Living Standards Poverty and Inequality in The UK 2022Vickfor LucaniNo ratings yet
- Economic Development ProjectDocument9 pagesEconomic Development ProjectمحمودعليNo ratings yet
- Income Inequality, Poverty and GrowthDocument18 pagesIncome Inequality, Poverty and Growthpinkranger-4No ratings yet
- Poverty inDocument4 pagesPoverty inAli TahirNo ratings yet
- Consumption and Other Indirect TaxesDocument1 pageConsumption and Other Indirect TaxesMR. PU7INNo ratings yet
- ECW3301 Case Studies in International Trade: BrazilDocument30 pagesECW3301 Case Studies in International Trade: BrazilDenagamage de SilvaNo ratings yet
- Global Social Report 2020.Document4 pagesGlobal Social Report 2020.Willder MojicaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Taxation On Poverty in PakistanDocument19 pagesImpact of Taxation On Poverty in PakistanIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- Report SubmissionDocument9 pagesReport Submissionnikhilkumarmp40No ratings yet
- Poverty and DevelopmentDocument12 pagesPoverty and Developmentarun yadav100% (1)
- Assignment-2 Bangladesh EconomicsDocument4 pagesAssignment-2 Bangladesh Economicsashraf07sNo ratings yet
- GD TopicsDocument166 pagesGD TopicsNaina JhaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Effect of Tax Revenue On Poverty Rates in Indonesia in 2019 - 2020Document11 pagesAnalysis of The Effect of Tax Revenue On Poverty Rates in Indonesia in 2019 - 2020QARRA SALMA SETIAWANNo ratings yet
- 15 Poverty EradicationDocument3 pages15 Poverty EradicationAmanNo ratings yet
- Contrasts in The Global South 1Document11 pagesContrasts in The Global South 1Rizwan AliNo ratings yet
- Income Inequality and The Condition of Chronic PovertyDocument39 pagesIncome Inequality and The Condition of Chronic PovertyChristen JohnsonNo ratings yet
- 2.3. The Relationship Between Government Spending and Poverty Alleviation in Emerging Markets Empirical Evidence From VietnamDocument29 pages2.3. The Relationship Between Government Spending and Poverty Alleviation in Emerging Markets Empirical Evidence From Vietnamngọc thảo nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Income Security For Older Persons in Viet NamDocument4 pagesIncome Security For Older Persons in Viet NamErine ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- LAC Poverty and Labor Brief, February 2014: Social Gains in the Balance - A Fiscal Policy Challenge for Latin America and the CaribbeanFrom EverandLAC Poverty and Labor Brief, February 2014: Social Gains in the Balance - A Fiscal Policy Challenge for Latin America and the CaribbeanNo ratings yet
- CB Acid BazeDocument25 pagesCB Acid BazePhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Huong Dan Giai de Thi Minh Hoa THPT Quoc Gia 2020 Mon Toan Cua Bo Giao Duc Va Dao Tao Lan 2Document29 pagesHuong Dan Giai de Thi Minh Hoa THPT Quoc Gia 2020 Mon Toan Cua Bo Giao Duc Va Dao Tao Lan 2PhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Sinh Tong Hop Rna - 2013Document41 pagesSinh Tong Hop Rna - 2013PhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Nguyen Ly May Bui Trong Hieu Tong Hop de Thi (Cuuduongthancong - Com)Document23 pagesNguyen Ly May Bui Trong Hieu Tong Hop de Thi (Cuuduongthancong - Com)PhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Ky Thuat Sua Chua Xe Dap DienDocument141 pagesKy Thuat Sua Chua Xe Dap DienPhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Bo de On Thi THPT Quoc Gia 2017 Mon Sinh HocDocument329 pagesBo de On Thi THPT Quoc Gia 2017 Mon Sinh HocPhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Giao Trinh An Toan Lao Dong Trong Xay DungDocument152 pagesGiao Trinh An Toan Lao Dong Trong Xay DungPhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Nguyen Van A: Fanpage: 30 Phút Tiếng Anh Mỗi Ngày Website: Langmaster.Edu.VnDocument1 pageNguyen Van A: Fanpage: 30 Phút Tiếng Anh Mỗi Ngày Website: Langmaster.Edu.VnPhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Lễ Tân Khách SạnDocument2 pagesLễ Tân Khách SạnPhiPhiNo ratings yet
- 100 Bài Luận Hay Cho Kỳ Thi ĐHDocument106 pages100 Bài Luận Hay Cho Kỳ Thi ĐHPhiPhiNo ratings yet
- Nguyen Van A: Fanpage: 30 Phút Tiếng Anh Mỗi Ngày Website: Langmaster.Edu.VnDocument1 pageNguyen Van A: Fanpage: 30 Phút Tiếng Anh Mỗi Ngày Website: Langmaster.Edu.VnPhiPhiNo ratings yet