Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MaxDemandBook Lom6 PDF
Uploaded by
Mohamed MagdyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MaxDemandBook Lom6 PDF
Uploaded by
Mohamed MagdyCopyright:
Available Formats
MAXIMUM DEMAND CONTROL SYSTEMS
Maximum Demand Control
There are three terms that appear on the majority of electric company bills:
Active energy consumption (kWh)
Reactive energy consumption (kvarh)
Maximum Demand
Traditionally, utility companies have concentrated their energy saving efforts
on two items:
Reduction of Kilowatt Hour consumption
Improving the electrical systems Power Factor
There is a third item to consider when reducing the amount of the electric
company bill, proper kW Demand management which allows:
The reduction of the contracted power
Adjusting to the new kW limit
Avoiding kW Demand limit penalties
WHAT IS MAXIMUM DEMAND?
Maximum Demand is the power consumed over a
predetermined period of time, which is usually between 8
30 minutes.
The most common period of time, in the majority of
countries, is 15 minutes.
This power is calculated and billed by a kW demand meter,
which records the highest kW value in one 15 minute
period, over a months time.
CALCULATING MAXIMUM DEMAND
There are several different ways to calculate Maximum Demand:
Fixed Demand (Block Demand)
The utility company sends a signal to synchronize the start of the Maximum Demand period.
Rolling demand
In a 15 minute window, the last kW value in the current window is used as the first kW value in the next 15 minute window.
The kW value is updated every second.
Time Synchronization window
This type of demand is a Fixed Demand. The utility company sends a signal at the start of the day to synchronize the start
of the first period. The meter, using its own internal clock, synchronizes each period thereafter until, at the end of the day,
the utility company send a signal to reset the meters clock to match the utilitys clock.
Thermal demand
This demand is calculated by a bimetallic, analog kW demand meter or an electronic
version of a bimetallic kW demand meter.
MAXIMUM DEMAND CONTROL SYSTEMS
HOW DOES THIS EFFECT YOU BILL?
This example shows how excess power consumption effects the electric company bill:
Contracted power: 136 kW
kW Demand meter reading: 253 kW
Maximum demand calculated without
surcharge*:
136 kW x 1.05 = 142.80 kW
Excess power consumed *:
253 kW - 142.80 kW = 110.2 kW
kW penalty *:
110.2 kW x 2 = 220.4 kW
Total kW to be billed:
220.4 kW + 253 kW = 473.4 kW
Proper management of kW
powerconsumption would not have
allowed 136 kW to be exceeded and
205.1 would have been charged
instead of 713.28 .
71.25 % LESS!
* In other countries, the formulas used in calculating kW penalties are different and may even be more rigid.
HOW TO CONTROL MAXIMUM DEMAND?
The purpose of controlling the demand is, not to
exceed the contracted maximum demand limit.
One way to do this is to shed non-critical loads.
Possible loads to be disconnected:
Lights
Compressors
Air conditioners
Pumps
Fans and extractors
Packaging machinery
Shredders
Others...
Without maximum
demand control
With maximum
demand control
Generally, all those machines which do not affect the main production process or which are not essential.
In addition to controlling kW demand, the following equipment is suitable for processes which have large variations in kW
demand and low loading factors, such as companies in the smelting, mining, automobile, textile, paper industries, etc.
MAXIMUM DEMAND CONTROL SYSTEMS
Equipment to Control Maximum Demand
Measurlogic offers all the necessary equipment for optimum
energy / demand management.
The following equipment measures instantaneous power and
automatically calculates and determines if and when the
kW demand will exceed the limit set forth by the utility company.
This is done by reliably disconnecting and reconnecting
non-critical loads using relays which are built into the equipment.
The CVM - R8 CPP and the CA - 4 can also be programmed
with different Tariffs (Time of Use periods) to shed loads within
different contracted limits.
METHOD
METH
D OF OPERATION
OPER ION
There are two methods used to avoid excess Maximum Demand:
Preventive
The Preventive method is suitable for those companies who do not want to allow the automatic connection or disconnection
of loads.
This system operates using visual or audible alarms indicating that the kW demand limt is going to be exceeded and that
an operator should manually disconnect certain loads.
Predictive
The predictive method is most often used.
The unit predicts what is going to happen, based on the load at the end of the current period and optimises the loads
in order to have as many loads connected without exceeding the maximum demand limit, which is preset in the unit.
This method of control is used when calculating demand using the fixed or synchronised demand methods.
Type
DH96 CPP
Number of loads controlled
Company impulse input
Software used
DH96 CPP-RS
128
Rolling or fixed demand
Preventive or predictive
Predictive
Preventive or predictive
RS-232 or RS-485
5
(2)
CPP-BT / CPP-CT
Fixed demand
Page
(1)
(2)
Easy Comm
Communications
17
Any
System operation
Method of operation
CVM-R8 CPP
With CVM-R10 extension module
(1)
--
Power C
--
RS-232
MAXIMUM DEMAND CONTROL SYSTEMS
DH96 CPP
Control up to four loads or groups of loads using contactors
Minimal response time to disconnect / connect loads
Connects to the utility meters isolated pulse output. Can also
connect to any of our measuring devices when a utility pulse is not
available.
Calculates Maximum Demand using either the Rolling, Fixed
(Block) Synchronization or Thermal demand methods.
Prioritizes the loads to be disconnected when reaching the
maximum demand limit.
Comes with software, when ordered with communications, to trend
from 1 60 minute records of both consumption and relay change of
states (opening and closing of relays).
Substantial recording and control capabilities housed in a standalone unit priced for a short-term return on investment.
Select between Preventive or Predictive demand control in the
same unit.
Type
Code
DH96 CPP
M54031
SOFTWARE
SO
ARE
MAXIMUM DEMAND CONTROL SYSTEMS
Features
tures
Power supply circuit
Consumption
Frequency
115 / 230 V (-15 % / +20 %)
Input circuit
Resolution
0,5% 1 dig
10 bits
Overvoltage (permanent / for 10 s)
1,2 Un / 2 Un
Current overload
(permanent / for 10 s)
1,2 In / 5 In
Measurement margin
2 ...120%
N. of conversions per cycle
Display
32
7 x 14 mm segments, red
Digits
Display refresh
Decimal point
Range excess indicator
Between input, measurement
and optional output card
Test voltatge
3 kV , 50 HZ , 1 min
Impulse test
4 kV (1,2 / 50 s)
4 VA (without card) 7 VA (with card)
45 ... 65 Hz
Accuracy on reading
Innsulation
< 1s
Programmable
"----"
Output relays
Insulating voltage
Thermal current (Ith)
Maximum operating power
Mechanical life
Electrical life
Digital inputs
5A
750 VA
2 x 107 operations
30 000 operations at 5 A and 250 V
2 inputs, potential free contacts
(20 mA-24 V d.c.)
Environmental conditions
Storage temperature
- 40 C / +70 C
Operating temperature
-10 C / +65 C
Assembly features
Casing material
ABS V0, anthracite grey
Protection grade
Casing and terminals: IP
20 / Front: IP 54
Weight
Standards
ACCESSORIES 5 A
Converters
(see M.5 catalogue)
1 single contact
750 V contact-contact 2
000 V contact-coil
550 g
IEC 1010, IEC 348, IEC 664,
VDE 0110, VDE 0435
MAXIMUM DEMAND CONTROL SYSTEMS
CVM-R8 CPP
Control up to seventeen loads or groups of loads using
contactors
Minimal response time to disconnect / connect loads
Connects to the utility meters isolated pulse output. Can also
connect to any of our measuring devices when a utility pulse is not
available.
Calculates Maximum Demand using Fixed (Block) demand
method.
Prioritizes the loads to be disconnected when reaching the
maximum demand limit.
Utilizes load connection offsets to prevent tripping of circuits due
to motor start up curves.
Alarm indication in the event of synchronization signal loss.
Predictive demand control.
There are three additional inputs used to select tariffs and to
control the loads associated with those tariffs.
Type
Code
CVM-R8 CPP
M60311
Fixed demand
The CVM - R8 CPP is connected to the synchronization pulse generated from the utility companys demand.
When the CVM-R8 CPP receives the pulse it ends one demand period and starts the next demand period.
Measurement by impulse
Measurement of consumed energy (kWh), during each demand period, is calculated by counting KYZ pulses from the utilty meter.
If a utility pulse is not available then connect the CVM-R8 CPP to any of our measuring devices that elicit a pulse.
Features
tures
Power supply circuit
Voltage
Frequency
consumption
Display
Single-phase 220 V a.c.
(+10 % / -15 %)
50 ... 60 Hz
7 VA
Number of relays
8
270 V a.c. / 125 V d.c.
Thermal current (Ith)
3A
A. C. 11 Ie / Ue
2 A / 250 V a.c.
D. C. 11 Ie / Ue
2 A / 30 V d.c.
Maximum operating power
Mechanical life
Electrical life
Digital inputs
Analogue inputs
Environmental conditions
Operating temperature
-10 C / +65 C
Assembly features
Output relay features
Insulating voltage (Ui)
Alphanumeric display with 1 x 8 characters (50 x 15 mm)
750 VA a.c. - 90 W d.c.
Casing type
Modular self-extinguishing plastic
Connection
Metal terminals with posidriv
Screws
Front of the box
Protection
Mounting DIN 46277
(EN 50022) rail coupling
(Screw mounting option)
Lexan front
Built in relay: IP 41: IP 41
Terminals: IP 20
2 x 10 operations
2 x 105 operations (at full loading)
6 6 inputs, potential free
contacts (20 mA - 24 V d.c.)
Dimensions
Safety
Standards
140 x 70 x 110 mm (8 modules)
Category II (EN 61010)
IEC 255, IEC 348, UNE 21 136,
IEC 664, VDE 0110, UL 94
2 entradas de 0 ... 2 V d.c.
MAXIMUM DEMAND CONTROL SYSTEMS
CA-4
A-4 / MR-3
Minimal response time to disconnect / connect loads
Connects to the utility meters isolated pulse output. Can also
connect to any of our measuring devices when a utility
pulse is not available.
Calculates Maximum Demand using either the Rolling, Fixed
(Block) demand methods.
Using the PS12 DC auxiliary power supply allows for the
connection of mid voltage loads to the unit.
Unit can be tested by a simulated program in order to prevent
unwanted operations.
Prioritizes the loads to be disconnected when reaching the
maximum demand limit.
Substantial control capabilities housed in stand-alone unit(s)
priced for a short-term return on investment.
Type
code
CA-4 4 (load controller + software)
M60411
MR-3 3 (expansion 3 lines)
M60412
CPP-B: Basic power control kit (3 loads)
1 CA-4 Controller
1 PS-12 DC Supplier
1 Power control software already
installed casing (280 x 280 x 150)
M60421
LOAD CONTROL
Control up to one hundred twenty eight (128) loads or groups of loads using
contactors
Prioritizes the loads to be disconnected when reaching the maximum demand limit.
Option to create groups of loads having the same priority of connection and
disconnection: FIFO or LIFO.
Status identification of each controlled load, defined as: Active, Inactive, Forced
active and Forced inactive. For example: By programming the load to Forced
inactive the load can be repaired without the fear of having the load energized
during the repair.
MODULAR SYSTEM
vModular design which can be added to in order to handle the number of loads to be controlled.
Modules can be installed near each load in order to simplify wiring and improve response time.
It has a modular system which allows the load connection/disconnection to be near to the loads
themselves, to simplify cabling, to reduce cabling distances and to improve response time
MAXIMUM DEMAND CONTROL SYSTEMS
SOFTWARE
SO
ARE
Software is able to display the state of each relay as well as record and date stamp
each relays change of state.
Ability to program the software with a two year contracted power calendar. Programming to include hours in the day,
type of day (weekday, weekend, holiday), etc.
Software has load calendars, which can be programmed for each controlled load. Calendars can be programmed not
only to automatically start and stop each load, but control the kW demand as well. It does this by knowing, in advance,
the priority of each load, which loads are operating, what the kW demand limit is so it can determine which loads can be
connected and which loads can be disconnected.
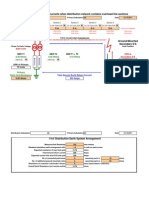
First, the user defines the basic parameters for the
power control, such as: type of window, integration
period, etc.
The type of calendar under contract, to be carried out,
is assigned along with the TOU periods of each day to
which the tariffs will be applied by the utility company.
The software supports up to 8 tariffs in 8 different TOU
periods in each day.
Assigning basic parameters
Assigning calendar
Assigning tariff
Second, the groups of loads are defi ned, as well as the
order of disconnection of each load, within the group
(FIFO or LIFO) and the order of disconnection of the
group as related to the other groups defined in the
software.
These groups are created according to the installation
(for example: groups of compressors or lights, etc.).
Then, each group is assigned to the corresponding
loads from any MR3 or the CA4. Loads in each group
are limitless.
The disconnection order for the power consumed, by
each load, including the total power per group, is shown
at all times with information showing if it is a FIFO or
LIFO sequence.
Creation of
loads groups
MAXIMUM DEMAND CONTROL SYSTEMS
SOFTWARE
SO
ARE
Once the groups have been created, it is necessary
to program each loads controlling relay. It is also
possible to create a specifi c calendar for each load.
NOTE: For personell safety, it is possible to force any
load (machine) to remain disconnected (locked out) for a
certain period of time without the option to reconnect it.
A calendar schedule, of up to two years, can be
programmed due to the large memory capacity of the
CA-4.
List of loads
Calendar schedule
New load
When all parameters have been defined, a simulation
may be created to check the proper operation of the
system and make any final corrections.
After opening the software, Power Control displays the
status of each load, in real time. The user can then
choose to manually change the staus of each load or let
the software oversee the system.
The loads status remains clearly defined because the
display lights indicate the current status:
- Green light: Load active
- Red light: Load disconnected
- Yellow light: Load inactive
Monitoring in real time
10
MAXIMUM DEMAND CONTROL SYSTEMS
Features
tures CA 4
Power supply circuit
24 V d.c. ( 25 %)
Environmental conditions
Consumption
500 mA
Operating temperature
Output relays
4 relays
Assembly features
Insulating voltage
1 000 V contact-contact
4 000 V contact-coil
Thermal current (Ith)
Mechanical life
Electrical life
Digital inputs
Front of the box
3A
Maximum operating power
Mounting
Safety
1 500 VA
3 x 107 operations
Standards
350 operations / hour (at full loading)
-10 C / +65 C
DIN 46277
(EN 50022) rail coupling
Lexan front
Category I (EN 61010)
EN 50082-1, EN 50082-2, EN 610003-2, EN 61000-3-3, EN 61010-1
4 inputs free of potential
(10 mA - 24 V d.c.)
Features
tures MR3
Power supply circuit
24 V d.c.
Consumption
65 mA
Output relays
3 relays of 10 A / 250 V a.c.
Digital inputs
3 polarised inputs
Communications
RS-485
Environmental conditions
Operating temperature
-10 C / +65 C
ACCESSORIES 5 A
Converters
(see M.5 catalogue)
Direct power source PS-12-V DC.
M60413
Dimensions / Connections
DH96 CPP
Fixing flange
CVM-R8 CPP
11
MAXIMUM DEMAND CONTROL SYSTEMS
CA-4
MR-3
12
You might also like
- Electrical Data SheetDocument5 pagesElectrical Data Sheetrajpre1213100% (1)
- 11.example Calculation - TransformerDocument16 pages11.example Calculation - Transformerrajpre1213No ratings yet
- MV Protection RelayDocument200 pagesMV Protection Relayrajpre1213100% (4)
- Surge PDFDocument3 pagesSurge PDFrajpre1213No ratings yet
- Eaton Fire Pump ControllerDocument12 pagesEaton Fire Pump Controllerrajpre1213100% (1)
- System Analysis With The MVA Method For Symmetrical Three-Phase FaultsDocument6 pagesSystem Analysis With The MVA Method For Symmetrical Three-Phase Faultsrajpre1213No ratings yet
- Electrical Network: Selectivity and Protection PlanDocument17 pagesElectrical Network: Selectivity and Protection PlanAnand GopalNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent - Relay Setting 3Document17 pagesOvercurrent - Relay Setting 3Shrikant KajaleNo ratings yet
- Protection Relays TrainingDocument5 pagesProtection Relays Trainingrajpre1213No ratings yet
- Short CircuitDocument40 pagesShort Circuitrajpre1213No ratings yet
- Consultancy ListDocument1 pageConsultancy Listrajpre1213No ratings yet
- ANSI Device NumbersDocument7 pagesANSI Device Numbersrajpre1213100% (1)
- Fire AlarmDocument34 pagesFire Alarmrajpre1213No ratings yet
- Distribution SystemsDocument5 pagesDistribution SystemsKalpa Pathum Welivitigoda100% (2)
- Enclosure Cooling DesignDocument9 pagesEnclosure Cooling Designrajpre1213No ratings yet
- Earth Fault CurrentDocument4 pagesEarth Fault Currentrajpre1213No ratings yet
- HV Cable Sizing Calculation (MOL) - FahahilDocument5 pagesHV Cable Sizing Calculation (MOL) - Fahahilkarikal_valavan100% (3)
- BMS Submittal SampleDocument66 pagesBMS Submittal Sampleaads1984No ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Program Arc Flash CalculatorDocument22 pagesElectrical Safety Program Arc Flash Calculatorshaikhsajid24250% (2)
- Prospect / Retrospect: Setting Motor Protection RelayDocument4 pagesProspect / Retrospect: Setting Motor Protection Relayrajpre1213No ratings yet
- Technical Manual: X3.3 April 2007Document0 pagesTechnical Manual: X3.3 April 2007rajpre1213No ratings yet
- Wbeng 09Document20 pagesWbeng 09rajpre1213No ratings yet
- 7.voltage DropDocument33 pages7.voltage Droprajpre1213No ratings yet
- 4 - Masibus 408Document2 pages4 - Masibus 408rajpre1213No ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- 17EC73-Complete Notes &VTU QPDocument388 pages17EC73-Complete Notes &VTU QPsudarshanNo ratings yet
- Power SystemsDocument54 pagesPower SystemsBindu ChipiriNo ratings yet
- CT PT TusharDocument2 pagesCT PT TusharAnonymous EVFw59No ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8086Document231 pagesMicroprocessor 8086Smarak LenkaNo ratings yet
- C-Band 5.6GHz FMCW RadarDocument20 pagesC-Band 5.6GHz FMCW RadarNameNo ratings yet
- PLC LabDocument4 pagesPLC Laburvish_soniNo ratings yet
- Daily Internal PCBA 08 Mar 2024Document84 pagesDaily Internal PCBA 08 Mar 2024konten idNo ratings yet
- Review of Discrete Fourier Transform: Cwliu@twins - Ee.nctu - Edu.twDocument46 pagesReview of Discrete Fourier Transform: Cwliu@twins - Ee.nctu - Edu.twhakkem bNo ratings yet
- Ceragon 3200T BrochureDocument4 pagesCeragon 3200T BrochureJohn EarleyNo ratings yet
- UCTE Data Exchange Format For Load Flow and Three Phase Short Circuit Studies (Ucte-Def)Document16 pagesUCTE Data Exchange Format For Load Flow and Three Phase Short Circuit Studies (Ucte-Def)DebatherNo ratings yet
- A Microcontroller Implementation of Fractional Order ControllerDocument6 pagesA Microcontroller Implementation of Fractional Order ControllerPraveen MathiasNo ratings yet
- Ek1 VDR 1022 (Eng)Document1 pageEk1 VDR 1022 (Eng)Burhan AhmadNo ratings yet
- ETP4830-A1 Embedded Power User ManualDocument90 pagesETP4830-A1 Embedded Power User ManualBruno SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Ut 621024Document14 pagesUt 621024DarleiDuarteNo ratings yet
- SynchronousDocument53 pagesSynchronousfazzlieNo ratings yet
- Nr-R09-Flexible Ac Transmission SystemsDocument1 pageNr-R09-Flexible Ac Transmission Systemssudhakar kNo ratings yet
- PV1 Owner's Manual and WarrantyDocument71 pagesPV1 Owner's Manual and WarrantyphilaskNo ratings yet
- Afham BMEE Assignment 1Document12 pagesAfham BMEE Assignment 1MhamadafhamNo ratings yet
- Numatics Catalogo de ValvulasDocument52 pagesNumatics Catalogo de Valvulasmendz1100% (1)
- Loudspeaker DesignDocument21 pagesLoudspeaker DesignBlaize110100% (5)
- Service Manual: Audio/Video Control ReceiverDocument71 pagesService Manual: Audio/Video Control ReceiverSaul PerezNo ratings yet
- Sumitomo HF-430 Guìa RápidaDocument31 pagesSumitomo HF-430 Guìa RápidaJohancito Valencia100% (2)
- Spin Doctor User GuideDocument4 pagesSpin Doctor User Guideapi-195490430No ratings yet
- GTP 25 KV VCBDocument8 pagesGTP 25 KV VCBDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- 15 Grundfos Submersible Deep Well - SP 125 - Performance Curve - Kurva PerformanceDocument5 pages15 Grundfos Submersible Deep Well - SP 125 - Performance Curve - Kurva Performanceمعين عزامNo ratings yet
- Alpha Legend en VF (AC12-VEC01) - Manuel D'installation - GB - Du 14 06 05 (7784)Document70 pagesAlpha Legend en VF (AC12-VEC01) - Manuel D'installation - GB - Du 14 06 05 (7784)hieroNo ratings yet
- Inductors and TransformersDocument44 pagesInductors and Transformersmarcelo ustarezNo ratings yet
- DSP Lab 6 (Ztransform)Document8 pagesDSP Lab 6 (Ztransform)abdullah khalid100% (1)
- Variable Frequency Drives - Heat Loss and Required Air CoolingDocument6 pagesVariable Frequency Drives - Heat Loss and Required Air CoolingElectrical DCM AstroNo ratings yet
- Huong Dan REC DPR2700Document16 pagesHuong Dan REC DPR2700Chim ConNo ratings yet