Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Common Core Math Standards 1516
Uploaded by
api-1911250300 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
112 views2 pagesBy the end of Grade 2.OA. 2, know from memory all sums of two one-digit numbers. Work with equal groups of objects to gain foundations for multiplication. Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represents amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones.
Original Description:
Original Title
common core math standards 1516
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBy the end of Grade 2.OA. 2, know from memory all sums of two one-digit numbers. Work with equal groups of objects to gain foundations for multiplication. Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represents amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
112 views2 pagesCommon Core Math Standards 1516
Uploaded by
api-191125030By the end of Grade 2.OA. 2, know from memory all sums of two one-digit numbers. Work with equal groups of objects to gain foundations for multiplication. Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represents amounts of hundreds, tens, and ones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Operations & Algebraic Thinking
Common Core Math Standards
Grade 2
Represent and solve problems involving addition and subtraction.
Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems
involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and
2.OA.1
comparing, with unknowns in all positions (e.g., by using drawings and equations
with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem)
Add & Subtract within 20
Fluently add and subtract within 20 using mental strategies. By the end of Grade
2.OA.2
2, know from memory all sums of two one-digit numbers.
Work with equal groups of objects to gain foundations for multiplication.
Determine whether a group of objects (up to 20) has an odd or even number
2.OA.3 (e.g. by pairing objects or counting them by 2s; write an equation to express an
even number as a sum of two equal addends).
Use addition to find the total number of objects arranged in rectangular arrays
2.OA.4 with up to 5 rows and up to 5 columns: write an equation to express the total sum
of equal addends.
Understand place value.
Understand that the three digits of a three-digit number represents amounts of
hundreds, tens, and ones. (e.g. 706 equals 7 hundreds, 0 tens, and 6 ones).
Number & Operations in Base Ten
2.NBT.1
Understand the following special cases:
100 can be thought of as a bundle of tens-called a hundred.
The numbers 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700, 800, 900, refer to one, toe,
three, four, five, six, seven, eight, or nine hundreds (and 0 tens and 0 ones).
2.NBT.2 Count within 1000; skip count by 5s, 10s, and 100s.
Read and write numbers to 1000 using base-ten numerals, number names, and
2.NBT.3
expanded form.
Compare two three-digit numbers base on meanings of the hundreds, tens, and
2.NBT.4
ones digits, using >, =, < symbols to record the results of the comparison.
Use place value understanding and properties of operations to add and subtract.
Fluently add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value,
2.NBT.5
properties of operations, and/or the relations between addition and subtraction.
Add up to four two-digit numbers using strategies based on place value and
2.NBT.6
properties of operations.
Add and subtract within 1000, using concrete models or drawings and strategies
based on place value, properties of operation, and/or the relationship between
addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method. Understand
2.NBT.7
that in adding or subtraction three-digit numbers, one adds or subtracts hundreds
and hundreds, tens and tens, ones and ones; and sometimes it is necessary to
compose and decompose tens or hundreds.
Mentally add 10 or 100 to a given number 100-900, and mentally subtract 10 or
2.NBT.8
100 from a given number 100-900.
Explain why addition and subtraction strategies work, using place value and the
2.NBT.9
properties of operations.
Geometry
Measurement & Data
Common Core Math Standards
Grade 2
Measure and estimate lengths in standard units.
Measure the length of an object by selecting and using appropriate tools such as
2.MD.1
rulers, yardsticks, meter sticks, and measuring tapes.
Measure the length of an object twice, using length units of different lengths for
2.MD.2 the two measurements; describe how the two measurements relate to the size of
the unit chosen.
2.MD.3 Estimate lengths using units of inches, feet, centimeters, and meters.
Measure to determine how much longer one object is than another, expressing
2.MD.4
the length difference in terms of a standard length unit.
Relate addition and subtraction to length.
Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve word problems involving length
that are given in the same units; (e.g., by using drawings (such as drawing of
2.MD.5
rulers) and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the
problems).
Represent whole numbers as lengths from 0 on a number line diagram with
2.MD.6 equally space points corresponding to the numbers 0, 1, 2 and represent wholenumber sums and differences within 100 on a number line diagram.
Work with time and money.
Tell and write time from analog and digital clock to the nearest five minutes, using
2.MD.7
a.m. and p.m.
Solve word problems involving dollar bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, and pennies,
2.MD.8 using $ and symbols appropriately. Example: If you have 2 dimes and 3 pennies,
how many cents do you have?
Represent and interpret data.
Generate measurement data my measuring lengths of several objects to the
nearest whole unit, or by making repeated measurements of the same object.
2.MD.9
Show the measurements by making a line plot, where the horizontal scale is
marked off in whole-number units.
Draw a picture graph and a bar graph (with single-unit scale) to represent a data
2.MD.10 set with up to four categories. Solve simple put-together, take-apart, and
compare problems using information presented in a bar graph.
Reason with shapes and their attributes.
Recognize and draw shapes having specified attributes, such as a given number
2.G.1
of angles or a given number of equal faces. Identify triangles, quadrilaterals,
pentagons, hexagons, and cubes.
Partition a rectangle into rows and columns of same-size squares and count to
2.G.2
find the total number of them.
Partition circles, and rectangles into two, three, or four equal shares, describe the
shares using the words halves, thirds, half of, a third of, etc. and describe the
2.G.3
whole as two halves, three thirds, and four fourths. Recognize that equal shares of
identical wholes need not have the same shape.
Shelly Sitz/Smiling & Shining in Second Grade
You might also like
- Commoncoremathcheatsheets 2 NDDocument1 pageCommoncoremathcheatsheets 2 NDapi-288064681No ratings yet
- Cuttothecore 2 NdgrademathstandardsDocument8 pagesCuttothecore 2 Ndgrademathstandardsapi-231774176No ratings yet
- CCSSI Math Standards 2Document4 pagesCCSSI Math Standards 2establoid1169No ratings yet
- Second Math StandardsDocument3 pagesSecond Math Standardsapi-233655908No ratings yet
- Math Common Core StandardsDocument5 pagesMath Common Core Standardsapi-167622228No ratings yet
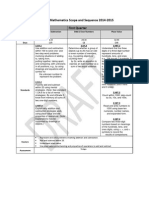
- First Quarter and 2nd Quarter Scope and Sequence MathDocument2 pagesFirst Quarter and 2nd Quarter Scope and Sequence Mathapi-234156613No ratings yet
- CcmathDocument3 pagesCcmathapi-278469988No ratings yet
- Standard Code Second Grade Math StandardsDocument2 pagesStandard Code Second Grade Math Standardsdestiny_eastepNo ratings yet
- Common Core State Standards First Grade MathDocument6 pagesCommon Core State Standards First Grade MathAbby BrinkmanNo ratings yet
- 2 NdgrademathcurriculummapDocument4 pages2 Ndgrademathcurriculummapapi-318489536No ratings yet
- Arizona 2nd Grade Math StandardsDocument8 pagesArizona 2nd Grade Math StandardsJessie OrrettNo ratings yet
- MN Elementary Math StandardsDocument9 pagesMN Elementary Math Standardsapi-322018148No ratings yet
- Math Common CoreDocument1 pageMath Common Coreapi-287040011No ratings yet
- Ccss Mathematics StandardsandaccesspointsDocument61 pagesCcss Mathematics Standardsandaccesspointsapi-131714491No ratings yet
- Commoncoremathcheatsheets 1 STDocument1 pageCommoncoremathcheatsheets 1 STapi-288064681No ratings yet
- 1 Standards HorizontalDocument2 pages1 Standards Horizontalapi-105565933No ratings yet
- Ma 2Document2 pagesMa 2api-335623629No ratings yet
- CCSSMathTasks Grade2Document98 pagesCCSSMathTasks Grade2Rivka ShareNo ratings yet
- k-8 Math Unit Planning TemplateDocument47 pagesk-8 Math Unit Planning Templateapi-252786575No ratings yet
- 2nd Grade Pacing Plan 2013-14Document9 pages2nd Grade Pacing Plan 2013-14api-237255436No ratings yet
- 1st Grade Common Core Math StandardsDocument3 pages1st Grade Common Core Math Standardsalex1413No ratings yet
- G MTH 2 st20 Ccss Ican Stmnts 20120528Document8 pagesG MTH 2 st20 Ccss Ican Stmnts 20120528api-324573119No ratings yet
- 2016NJSLS-M Grade2Document16 pages2016NJSLS-M Grade2Gene HermanNo ratings yet
- Math CCDocument1 pageMath CCapi-290998130No ratings yet
- First Grade Math May 2014Document2 pagesFirst Grade Math May 2014destiny_eastepNo ratings yet
- Common Core Math Standards Editable Checklistrd GradeDocument171 pagesCommon Core Math Standards Editable Checklistrd GradeJessicaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Curriculum - Year 2: Number - Number and Place ValueDocument3 pagesMathematics Curriculum - Year 2: Number - Number and Place ValueMiguel Angel Nadal TurNo ratings yet
- Math Ccss K 12Document98 pagesMath Ccss K 12pgtz7qb7zsNo ratings yet
- First Math StandardsDocument2 pagesFirst Math Standardsapi-233655908No ratings yet
- Academic Standards in Maths PDFDocument47 pagesAcademic Standards in Maths PDFora1userNo ratings yet
- 3 Grade Math Common Core Standards: At-A-Glance Operations & Algebraic ThinkingDocument4 pages3 Grade Math Common Core Standards: At-A-Glance Operations & Algebraic Thinkingapi-298986760No ratings yet
- Placed (Yes/no) Name of Unit(s) Where Placed Power Standard (Yes/no)Document58 pagesPlaced (Yes/no) Name of Unit(s) Where Placed Power Standard (Yes/no)api-288706880No ratings yet
- 9 pl-q2 BenchmarkDocument2 pages9 pl-q2 Benchmarkapi-292890537No ratings yet
- CCSSI Math Standards 1Document4 pagesCCSSI Math Standards 1establoid1169No ratings yet
- 2017 3rd Grade Math Pacing Guide TrimestersDocument3 pages2017 3rd Grade Math Pacing Guide Trimestersapi-378234656No ratings yet
- Math Grade 1 08 11Document4 pagesMath Grade 1 08 11api-246939068No ratings yet
- Analysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 1Document11 pagesAnalysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 1establoid1169No ratings yet
- Grade 2 Mathematics: Learning CompetenciesDocument22 pagesGrade 2 Mathematics: Learning Competenciesshine brightNo ratings yet
- Analysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 2Document15 pagesAnalysis of California Mathematics Standards To Common Core Standards-Grade 2establoid1169No ratings yet
- Arizona 2nd Grade Math StandardsDocument8 pagesArizona 2nd Grade Math StandardsChino GarciaNo ratings yet
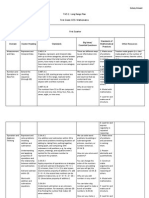
- Long Range Plan KooneDocument6 pagesLong Range Plan Kooneapi-213700287No ratings yet
- 1st Grade Math StandardsDocument7 pages1st Grade Math Standardsapi-470241740No ratings yet
- 4th Grade Math ChecklistDocument3 pages4th Grade Math ChecklistCheryl Dick100% (3)
- 1 ST Math Checklists 2Document6 pages1 ST Math Checklists 2ddfsfsNo ratings yet
- g2 Mathematics Florida StandardsDocument5 pagesg2 Mathematics Florida Standardsapi-290541111No ratings yet
- Iowa CoreDocument6 pagesIowa Coreapi-251303337No ratings yet
- Edm1 Unit 8Document6 pagesEdm1 Unit 8api-268988549No ratings yet
- Grade 1 Unit 8Document6 pagesGrade 1 Unit 8api-233369686No ratings yet
- CCSS Checklist For Math 3rdDocument9 pagesCCSS Checklist For Math 3rdodie01No ratings yet
- 2 ND Math ChecklistsDocument4 pages2 ND Math ChecklistsasdfasdfasNo ratings yet
- Maths Scheme of Work Class 2Document12 pagesMaths Scheme of Work Class 2Anonymous yEPScmhs2qNo ratings yet
- Maths Curriculum Year 6Document3 pagesMaths Curriculum Year 6soe myatmonNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 OverviewDocument5 pagesGrade 3 Overviewapi-233351761No ratings yet
- Concepts Cycle 3 April 2014Document9 pagesConcepts Cycle 3 April 2014api-254416761No ratings yet
- CCSS Math KDocument8 pagesCCSS Math KMegan RasmussenNo ratings yet
- 2014-15 Planning Template 2nd Grade MathDocument10 pages2014-15 Planning Template 2nd Grade Mathapi-249700554No ratings yet
- Stress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9From EverandStress-Free Math: A Visual Guide to Acing Math in Grades 4-9No ratings yet
- Learn Excel Functions: Count, Countif, Sum and SumifFrom EverandLearn Excel Functions: Count, Countif, Sum and SumifRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- SummerwebsitesDocument2 pagesSummerwebsitesapi-191125030No ratings yet
- Kid Friendly Science StandardsDocument1 pageKid Friendly Science Standardsapi-191125030No ratings yet
- Kid Friendly Social Studies Conference Book 1112Document2 pagesKid Friendly Social Studies Conference Book 1112api-191125030No ratings yet
- Kid Friendly Math Standards For Conference Book1112Document7 pagesKid Friendly Math Standards For Conference Book1112api-191125030No ratings yet
- Kid Friendly Languge Standards For Conference Book 1112Document3 pagesKid Friendly Languge Standards For Conference Book 1112api-191125030No ratings yet
- HTTPS://WWW - Scribd.com/read/364450773/la La Land Piano Duet Intermediate Level 1 Piano 4 HandsDocument24 pagesHTTPS://WWW - Scribd.com/read/364450773/la La Land Piano Duet Intermediate Level 1 Piano 4 HandscaringotruNo ratings yet
- TJUSAMO 2013-2014 InequalitiesDocument12 pagesTJUSAMO 2013-2014 InequalitiesChanthana ChongchareonNo ratings yet
- Hwa Chong Institution (High School Section) Subject: Mathematics Level: Sec 2 IP/SBGE 2012 Scheme of WorkDocument27 pagesHwa Chong Institution (High School Section) Subject: Mathematics Level: Sec 2 IP/SBGE 2012 Scheme of WorkLim Kew ChongNo ratings yet
- Exer1 1Document2 pagesExer1 1John Andrae Manglo87% (15)
- Podcast ScriptDocument3 pagesPodcast Scriptapi-475189056No ratings yet
- t13 PDFDocument8 pagest13 PDFMaroshia MajeedNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics Foundation Health Sciences AnalysisDocument5 pagesBiostatistics Foundation Health Sciences AnalysisEri Wijaya HafidNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Mathematical Language and Symbols Week 3 To Week 4Document12 pagesMODULE 2 Mathematical Language and Symbols Week 3 To Week 4Ariane Leslie CambaNo ratings yet
- One - Step - Equations - Easy - WorksheetDocument2 pagesOne - Step - Equations - Easy - WorksheetShanyce MartinNo ratings yet
- Mathematical IntuitionDocument23 pagesMathematical IntuitionAnup SaravanNo ratings yet
- CS229 Problem Set #4 Neural Networks, EM Algorithm, and ConvergenceDocument10 pagesCS229 Problem Set #4 Neural Networks, EM Algorithm, and Convergencenxp HeNo ratings yet
- July F10A: Semester 2 2010Document14 pagesJuly F10A: Semester 2 2010gy880828No ratings yet
- Maths Trigonometry Ratios & Identities Combine PDFDocument14 pagesMaths Trigonometry Ratios & Identities Combine PDFraghavendra jNo ratings yet
- ICE-STEM: 1st International Conference on STEM EducationDocument8 pagesICE-STEM: 1st International Conference on STEM EducationHelen Marisa PasaribuNo ratings yet
- The Dots and Boxes Game RulesDocument8 pagesThe Dots and Boxes Game RulesLeonora Aquino HullanaNo ratings yet
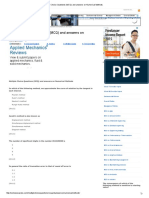
- Multiple Choice Questions MCQ and Answers On Numerical MethodsDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions MCQ and Answers On Numerical MethodsDevashish MoreNo ratings yet
- SQQS1013 Ch5 A122Document48 pagesSQQS1013 Ch5 A122AwnieAzizanNo ratings yet
- Code Wars 2007 - ProgrammingDocument6 pagesCode Wars 2007 - Programmingvishal_tripathiNo ratings yet
- The Law of Cosines: Find Each Measurement Indicated. Round Your Answers To The Nearest TenthDocument4 pagesThe Law of Cosines: Find Each Measurement Indicated. Round Your Answers To The Nearest TenthRaba BethNo ratings yet
- The Rubik's Cube WorkshopDocument26 pagesThe Rubik's Cube Workshopcpt_sparkyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document4 pagesAssignment 4sandeep BhanotNo ratings yet
- Design Via Root LocusDocument53 pagesDesign Via Root LocusAhmed ShareefNo ratings yet
- GropdDocument11 pagesGropdAnonymous BZcvbUNo ratings yet
- Laguerre Equation and Its SolutionDocument12 pagesLaguerre Equation and Its SolutionরাকিবNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - TrigonometryDocument15 pagesModule 2 - TrigonometryJake Canlas100% (1)
- ch3 p01-50Document50 pagesch3 p01-50Jeanne JacksonNo ratings yet
- Algebra Part1Document5 pagesAlgebra Part1Mj AquinoNo ratings yet
- Remarks of T7 AppendixDocument9 pagesRemarks of T7 AppendixWong JiayangNo ratings yet
- Mathematics P2 Nov 2012 Memo EngDocument29 pagesMathematics P2 Nov 2012 Memo EngedwardnephNo ratings yet
- Measure of Central TendancyDocument27 pagesMeasure of Central TendancySadia HakimNo ratings yet