Professional Documents
Culture Documents
QC 2 Uv-Vis HW
QC 2 Uv-Vis HW
Uploaded by
Jessa VallangcaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
QC 2 Uv-Vis HW
QC 2 Uv-Vis HW
Uploaded by
Jessa VallangcaCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
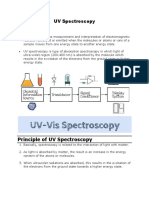
Molecules or parts of molecules that absorb light strongly in the UV-vis region are
called chromophores.
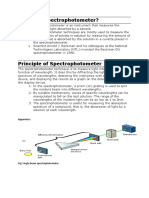
4. Spectrometer - Strictly speaking, a spectrometer is any instrument used to
view and analyze a range (or a spectrum) of a given characteristic for a substance
(for example, a range of mass-to-charge values as in mass spectrometry) , or a
range of wavelengths as in absorption spectrometry like nuclear magnetic radiation
spectroscopy or infrared spectroscopy).
The Vernier Colorimeter is designed to determine the concentration of a solution by analyzing its color intensity.
The color of a solution may be inherent or derived by adding another reagent to it. The Colorimeter measures the
amount of light transmitted through a sample at a user-selectable wavelength.
5. A photomultiplier tube is a vacuum tube consisting of an input window, a photocathode, focusing electrodes, an
electron multiplier and an anode usually sealed into an evacuated glass tube.
Silicon photodiodes are semiconductor devices responsive to high-energy particles and photons.
Photodiodes operate by absorption of photons or charged particles and generate a flow of current in an
external circuit, proportional to the incident power. Photodiodes can be used to detect the presence or
absence of minute quantities of light and can be calibrated for extremely accurate measurements from
intensities below 1 pW/cm2to intensities above100 mW/cm2. Silicon photodiodes are utilized in such
diverse applications as spectroscopy, photography, analytical instrumentation, optical position sensors,
beam alignment, surface characterization, laser range finders, optical communications, and medical
imaging instruments.
You might also like
- Experiment 2 Uv-Visible Determination of An Unknown Concentration of Kmno Solution Theory/BackgroundDocument13 pagesExperiment 2 Uv-Visible Determination of An Unknown Concentration of Kmno Solution Theory/BackgroundMuhammad Azri HaziqNo ratings yet
- Uv Visible SpectrosDocument28 pagesUv Visible Spectrosjoshishravan3003No ratings yet
- UV Spectroscopy - Principle, Instrumentation, Applications - Instrumentation - Microbe NotesDocument5 pagesUV Spectroscopy - Principle, Instrumentation, Applications - Instrumentation - Microbe NotesIJAJ-PHARMA TUTOR100% (2)
- Ultra Violet - Visible SpectrosDocument13 pagesUltra Violet - Visible SpectrosSherin SunnyNo ratings yet
- L3 SpectrophotometerDocument1 pageL3 SpectrophotometerMona JayNo ratings yet
- MidTerm - 18145070 - Dibyajyoti DeyDocument10 pagesMidTerm - 18145070 - Dibyajyoti DeySiddharth VermaNo ratings yet
- Org ChemDocument8 pagesOrg ChemAnam MustafaNo ratings yet
- Principle: Visible and Ultraviolet (Uv) SpectrosDocument10 pagesPrinciple: Visible and Ultraviolet (Uv) SpectrosKalyanNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometer-Principle, Instrumentation, Applications: What Is A Spectrophotometer?Document2 pagesSpectrophotometer-Principle, Instrumentation, Applications: What Is A Spectrophotometer?Talhas Production100% (1)
- AnalyiticalDocument49 pagesAnalyiticalGeleta BekeleNo ratings yet
- UV SpectrosDocument4 pagesUV SpectrosCarlton GrantNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation of Ultra Violet SpectrosDocument43 pagesInstrumentation of Ultra Violet Spectrosimam mahdi tv officialNo ratings yet
- Components of Spectrophotometer-4Document12 pagesComponents of Spectrophotometer-4Muhammad RamzanNo ratings yet
- Uv-Visible Spectroscopy TheoryDocument8 pagesUv-Visible Spectroscopy TheoryHamdan afzalNo ratings yet
- UV SpectrosDocument7 pagesUV Spectrosbszool006No ratings yet
- Assignment Spectrophotometer ModernDocument21 pagesAssignment Spectrophotometer ModernBaim Black RushNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment 1 Name Rishabh Raj Prasad REG-NO 18BEE0069Document7 pagesDigital Assignment 1 Name Rishabh Raj Prasad REG-NO 18BEE0069Kumar RishabhNo ratings yet
- UV VisDocument2 pagesUV Vist4424914No ratings yet
- What Is A Spectrophotometer?Document3 pagesWhat Is A Spectrophotometer?Indra PanchalNo ratings yet
- CH 4 2023Document34 pagesCH 4 2023Kaleb AshikoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Analytical Procedures and InstrumentataionDocument40 pagesChapter 4 Analytical Procedures and InstrumentataionDaniel JirataNo ratings yet
- 2-UV-Vis Molecular SpectrometryDocument27 pages2-UV-Vis Molecular SpectrometryWahyuni EkaNo ratings yet
- UV Visible SpectrosDocument12 pagesUV Visible SpectrosAbdullah Bin TariqNo ratings yet
- SpectrophotometryDocument5 pagesSpectrophotometryKashifntcNo ratings yet
- How Does A Spectrophotometer WorkDocument10 pagesHow Does A Spectrophotometer WorkDuc Nguyen ManhNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometer Mls 3rdDocument14 pagesSpectrophotometer Mls 3rdRuhulla AbbassNo ratings yet
- SpectrophotometryDocument7 pagesSpectrophotometrySantanah Daxene DayloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Analytical Techniques: Prepared By: Michael John R. Aguilar, RMTDocument42 pagesIntroduction To Analytical Techniques: Prepared By: Michael John R. Aguilar, RMTFrankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- SPECTROPHOTOMETERDocument5 pagesSPECTROPHOTOMETERKokab KhanNo ratings yet
- Spectro Photo Me TryDocument8 pagesSpectro Photo Me Trysushil4056No ratings yet
- Report Ni RizaDocument8 pagesReport Ni RizaInga Budadoy NaudadongNo ratings yet
- Spectro Photo Me TryDocument5 pagesSpectro Photo Me Trykapil sharmaNo ratings yet
- F Spectroscopic InstrumentationDocument21 pagesF Spectroscopic Instrumentationmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- SpectrophotometerDocument21 pagesSpectrophotometerbeena gracelyn sarahNo ratings yet
- Tugas B Ingg Ke 2Document6 pagesTugas B Ingg Ke 2Wirda AffiyantiNo ratings yet
- Spetrophotometer 090415095014 Phpapp02Document42 pagesSpetrophotometer 090415095014 Phpapp02anujaNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation: Sources of UV RadiationDocument16 pagesInstrumentation: Sources of UV Radiationexample2000No ratings yet
- InstrumentationDocument4 pagesInstrumentationRainneTayNo ratings yet
- Lab Instrumentation 2Document2 pagesLab Instrumentation 2rlatjorlukNo ratings yet
- What Is UV SpectrosDocument20 pagesWhat Is UV SpectrosSimranNo ratings yet
- Obt751 - Analytical Methods and Instrumentation Lecture - 4Document36 pagesObt751 - Analytical Methods and Instrumentation Lecture - 4Jayashree Sathiyanarayanan100% (4)
- Spectrophotometer: - Class: 1ADocument12 pagesSpectrophotometer: - Class: 1Aniken larasatiNo ratings yet
- Fluorescence SpectrosDocument2 pagesFluorescence SpectrosKing QuesadaNo ratings yet
- Uv Analysis Method Development For Diclofenac and Paracetamol in CombinationDocument28 pagesUv Analysis Method Development For Diclofenac and Paracetamol in Combination0921py100% (5)
- The Principle of A UV SpectrometerDocument4 pagesThe Principle of A UV SpectrometerVignesh AmrNo ratings yet
- Uv VisDocument6 pagesUv VisTannecia BenjaminNo ratings yet
- What Is A Spectrophotometer?: ApparatusDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Spectrophotometer?: ApparatusSambhav ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Part A) Components of Instrument For Optical SpectrosDocument28 pagesChapter 2 (Part A) Components of Instrument For Optical SpectrosaisyahNo ratings yet
- 3 UvDocument15 pages3 UvAnushri VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Ultraviolet Visible SpectrosDocument6 pagesGroup 4 Ultraviolet Visible SpectrosJane Frances JabricaNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet Visible SpectrophotometerDocument11 pagesUltraviolet Visible Spectrophotometerapi-246263792No ratings yet
- S Petro Photo MeterDocument42 pagesS Petro Photo MeterAMASMNo ratings yet
- Photo MeterDocument4 pagesPhoto MeterRKMNo ratings yet
- Uv Spectroscopy 5Document11 pagesUv Spectroscopy 5Emmanuella OffiongNo ratings yet
- Analytic Techniques and Instrumentation Lecture FormatDocument15 pagesAnalytic Techniques and Instrumentation Lecture FormatMandy A. DelfinNo ratings yet
- UV Visible SpectrosDocument7 pagesUV Visible SpectrosIsha RajputNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometry: UV-visible Spectrophotometer: Uses Light Over The Ultraviolet Range (185Document3 pagesSpectrophotometry: UV-visible Spectrophotometer: Uses Light Over The Ultraviolet Range (185azeem999No ratings yet
- CH 4 Anal - Procedures and Instrumentataion2Document33 pagesCH 4 Anal - Procedures and Instrumentataion2tagele hunegnawNo ratings yet
- Shining a Light on Cool Standards: Infrared Spectroscopy Theory Explored.From EverandShining a Light on Cool Standards: Infrared Spectroscopy Theory Explored.No ratings yet