Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Principles 3
Uploaded by
api-2942767490 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
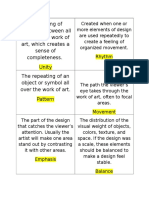
655 views1 pagePattern a regular arrangement of alternated or repeated elements (shapes, lines, colours) or motifs. Balance a feeling of balance results when the elements of design are arranged symmetrically or asymmetrically to create the impression of equality in weight or importance. Rhythm / Movement the use of recurring elements to direct the eye through the image; the way the elements are organized to lead the eye to the focal area.
Original Description:
Original Title
principles3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPattern a regular arrangement of alternated or repeated elements (shapes, lines, colours) or motifs. Balance a feeling of balance results when the elements of design are arranged symmetrically or asymmetrically to create the impression of equality in weight or importance. Rhythm / Movement the use of recurring elements to direct the eye through the image; the way the elements are organized to lead the eye to the focal area.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
655 views1 pagePrinciples 3
Uploaded by
api-294276749Pattern a regular arrangement of alternated or repeated elements (shapes, lines, colours) or motifs. Balance a feeling of balance results when the elements of design are arranged symmetrically or asymmetrically to create the impression of equality in weight or importance. Rhythm / Movement the use of recurring elements to direct the eye through the image; the way the elements are organized to lead the eye to the focal area.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
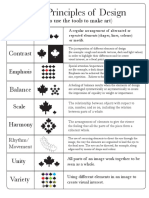
The Principles of Design
(how to use the tools to make art)
Pattern
A regular arrangement of alternated or
repeated elements (shapes, lines, colours)
or motifs.
Contrast
The juxtaposition of different elements of design
(for example: rough and smooth textures, dark and light values)
in order to highlight their differences and/or create
visual interest, or a focal point.
Emphasis
Special attention/importance given to one part of a work of
art (for example, a dark shape in a light composition).
Emphasis can be acheived through placement, contrast, colour,
size, repetition... Relates to focal point.
Balance
A feeling of balance results when the elements of design
are arranged symmetrically or asymmetrically to create
the impression of equality in weight or importance.
Scale
The relationship between objects with respect to
size, number, and so on, including the relation
between parts of a whole.
Harmony
The arrangement of elements to give the viewer
the feeling that all the parts of the piece form a
coherent whole.
Rhythm/
Movement
The use of recurring elements to direct the eye through the
image; the way the elements are organized to lead the eye to
the focal area. The eye can be directed, for example, along
edges and by means of shape and colour.
Unity
Variety
All parts of an image work together to be
seen as a whole.
Using different elements in an image to
create visual interest.
You might also like
- Principles of Design PDFDocument1 pagePrinciples of Design PDFArcelli Surigao Perfectua UsogNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10: Principles of Design: Prepared By: Cathleen AndalDocument10 pagesLesson 10: Principles of Design: Prepared By: Cathleen AndalCathleen AndalNo ratings yet
- PrinciplesofdesignDocument1 pagePrinciplesofdesignapi-246498555No ratings yet
- The Principles of Art or DesignDocument28 pagesThe Principles of Art or DesignChelle Ann BoneteNo ratings yet
- The Elements and Principles of Art DesignDocument17 pagesThe Elements and Principles of Art DesignIVEROLNo ratings yet
- Design and Colour (Review)Document4 pagesDesign and Colour (Review)BrchuduNo ratings yet
- Principles of DesignDocument2 pagesPrinciples of DesignakomeshtsNo ratings yet
- Visual Design PrincplesDocument3 pagesVisual Design PrincplesJann LarNo ratings yet
- 8 ArtsDocument3 pages8 ArtsRhein Antonette LandichoNo ratings yet
- Principles of DesignDocument25 pagesPrinciples of DesignDaisery Jane MalayasNo ratings yet
- Fritch PrinciplesofdesignDocument20 pagesFritch Principlesofdesignapi-308622335No ratings yet
- Delgado, BeaDocument3 pagesDelgado, BeaBëa DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Visual Arts Vocabulary ListDocument6 pagesVisual Arts Vocabulary Listapi-315608861No ratings yet
- Principles of Design: List of Content: Emphasize, Balance, Alignment, Contrast, Repetition and ProportionDocument13 pagesPrinciples of Design: List of Content: Emphasize, Balance, Alignment, Contrast, Repetition and ProportionKanchan ManhasNo ratings yet
- Principles of DesignDocument19 pagesPrinciples of DesignPUNEET MISHRANo ratings yet
- Elements of Visual Art: Chevrolet Franzinne M. Cepe Grade 12-St. Agatha of SicilyDocument3 pagesElements of Visual Art: Chevrolet Franzinne M. Cepe Grade 12-St. Agatha of SicilyFranzinneNo ratings yet
- Elements of ArtDocument3 pagesElements of Artapi-293994498No ratings yet
- VCE Art 2017-2021 VCE Studio Arts 2017-2021 Art Elements and PrinciplesDocument3 pagesVCE Art 2017-2021 VCE Studio Arts 2017-2021 Art Elements and PrinciplesvinamraNo ratings yet
- Appendix B: Elements and Principles of DesignDocument6 pagesAppendix B: Elements and Principles of DesignJennifer StraussNo ratings yet
- 1 - Elements and Principles of ArtDocument4 pages1 - Elements and Principles of ArtMarie BishNo ratings yet
- THURSDAY CLASS - Design Elements & Principles NotesDocument23 pagesTHURSDAY CLASS - Design Elements & Principles Notesapi-281230568No ratings yet
- Elements of ArtDocument2 pagesElements of ArtCrisnalyn AnascoNo ratings yet
- E and P of ArtDocument17 pagesE and P of Artapi-262384001No ratings yet
- Epd Finals ReviewerDocument11 pagesEpd Finals ReviewerandreagabriellecuiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Principles of ArtDocument47 pagesLesson 4 Principles of ArtElla CaraanNo ratings yet
- Principle of ArtsDocument1 pagePrinciple of ArtsAira Nichole TiczonNo ratings yet
- Principles and ElementsDocument2 pagesPrinciples and ElementsAngel Ellene MarcialNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Principles of DesignDocument5 pagesMODULE 2 Principles of DesigndinahadielabrogenaNo ratings yet
- Cpar Lesson 3 Quarter 3 Principles of ArtDocument37 pagesCpar Lesson 3 Quarter 3 Principles of ArtZenon Zogratis100% (1)
- Vocabulary For Visual ArtsDocument9 pagesVocabulary For Visual ArtsEnrique del CerroNo ratings yet
- PrinciplesDocument2 pagesPrinciplesapi-234767369No ratings yet
- Multimedia DesignDocument15 pagesMultimedia DesignZie AhmadNo ratings yet
- The ElementsDocument2 pagesThe ElementsjaxinehyunaleiNo ratings yet
- Line Shape Color Value Texture Space Form Balance Variety Movement Contrast Emphasis Proportion UnityDocument50 pagesLine Shape Color Value Texture Space Form Balance Variety Movement Contrast Emphasis Proportion UnityJaivikas ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Sir Bryan PresentationDocument27 pagesSir Bryan PresentationHaze CloverNo ratings yet
- Principles DesignDocument1 pagePrinciples Designapi-279889431No ratings yet
- Elements Principles of PhotoDocument38 pagesElements Principles of Photofady.milikNo ratings yet
- Principles of Visual DesignDocument21 pagesPrinciples of Visual DesignAngela Cherisse S. RicohermozoNo ratings yet
- The Elements and Principles of DesignDocument2 pagesThe Elements and Principles of DesignShafaq Nazir100% (1)
- Elements of DesignDocument3 pagesElements of Designzettevasquez8No ratings yet
- Teaching Arts in Elementary Grades: Concept ArtDocument40 pagesTeaching Arts in Elementary Grades: Concept Artangel84% (19)
- Elements of Painting Printmaking PhotographyDocument21 pagesElements of Painting Printmaking Photography412137No ratings yet
- Principle of ArtsADocument1 pagePrinciple of ArtsAAira Nichole TiczonNo ratings yet
- Updated Principles of DesignDocument49 pagesUpdated Principles of DesignsonypspaoloNo ratings yet
- Arrange Those Visible Elements To Make Effective Compositions: These Include: Balance, Unity, Variety, Harmony, Movement, Rhythm and EmphasisDocument11 pagesArrange Those Visible Elements To Make Effective Compositions: These Include: Balance, Unity, Variety, Harmony, Movement, Rhythm and EmphasisMark Johnson LeeNo ratings yet
- Principles of DesignDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Designjane barquinNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Eod & Pod TermsDocument20 pages1.2 Eod & Pod TermsSubhojit DasNo ratings yet
- Rva 4Document33 pagesRva 4Jacob Andrew DuronNo ratings yet
- Art TermsDocument6 pagesArt Termsapi-546172080No ratings yet
- Design and ColourDocument35 pagesDesign and ColoursamanthaNo ratings yet
- Principles of DesignDocument17 pagesPrinciples of DesignRomdel SmythNo ratings yet
- Balance:: Symmetrical Balance Wherein Each Side Is The Mirror-Image of The OtherDocument2 pagesBalance:: Symmetrical Balance Wherein Each Side Is The Mirror-Image of The OtherHERNANDO REYESNo ratings yet
- AbdullahDocument9 pagesAbdullahMaaz HassanNo ratings yet
- Elements of ArtDocument36 pagesElements of ArtJUDYLYN MORENONo ratings yet
- Elements of Arts and Principles of DesignDocument10 pagesElements of Arts and Principles of DesignSharlette SaulNo ratings yet
- Las Week 2 Melc 1 Second QuarterDocument4 pagesLas Week 2 Melc 1 Second QuarterDiana MamaticNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Art VocabularyDocument1 pageUnit 1 Art Vocabularyapi-385679506No ratings yet
- Principles of Design:: Rhythm and MovementDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Design:: Rhythm and MovementKimberly IgbalicNo ratings yet
- Applied Design for Printers A Handbook of the Principles of Arrangement, with Brief Comment on the Periods of Design Which Have Most Strongly Influenced Printing Typographic Technical Series for Apprentices #43From EverandApplied Design for Printers A Handbook of the Principles of Arrangement, with Brief Comment on the Periods of Design Which Have Most Strongly Influenced Printing Typographic Technical Series for Apprentices #43No ratings yet
- 144artists Week3 08Document1 page144artists Week3 08api-294276749No ratings yet
- Benefits 2Document4 pagesBenefits 2api-359955054No ratings yet
- Acuarelas TecnicasDocument1 pageAcuarelas TecnicasVanesa GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Elements 3Document1 pageElements 3api-294276749No ratings yet
- Principles of Design 2Document1 pagePrinciples of Design 2api-294276749No ratings yet
- Elements of Design HandoutDocument1 pageElements of Design Handoutapi-294276749No ratings yet