Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amino Acids: Know How To Draw All 20 Amino Acid Structures From PH 0-14 For First Midterm
Amino Acids: Know How To Draw All 20 Amino Acid Structures From PH 0-14 For First Midterm
Uploaded by
Benneth BautistaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Amino Acids: Know How To Draw All 20 Amino Acid Structures From PH 0-14 For First Midterm
Amino Acids: Know How To Draw All 20 Amino Acid Structures From PH 0-14 For First Midterm
Uploaded by
Benneth BautistaCopyright:
Available Formats
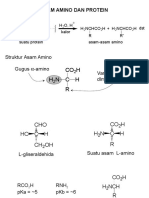
Amino Acids
*Know how to draw all
20 Amino Acid
structures from pH 0-14
for first midterm
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins
C-terminus
N-terminus
Peptide:
series of amino
acid residues
(Residue means
its not the full
amino acid)
amino acid residue
peptide bond
H2O
-most of any protein is nonpolar
nonpolar interior
-in an aqueous environment peptides
have evolved to change shaoe
globular protein
Amino acids
C
-pka depends
on R group
L-amino acid
D-amino acid
19/20
pka is the tendency of a weak acid --> H+
1/20
R-groups
asparagine
N
glutamine
Q
serine
S
threonine
T
glycine
G
H
CH2
CH2
CH2
H C OH
C O
CH2
OH
CH3
NH2
C O
NH2
aspartic acid glutamic acid
has 1
D
E more
ch2
lysine
K
arginine
R
group
(CH2)3
Ionizable
acidic
CH2
CH2
CH2
C O
CH2
O-
C O
O-
CH2
CH2
NH3+
(4.2)
CH2 H
N
C
NH
CH2
(3.9)
histidine
H
NH2+
HC
*hydrophobic
CH2
C H
H3C CH3
isoleucine
I
NH2
(12.5)
(6.0)
CH
H3C CH3
CH3
alanine
A
CH3
methionine
M
CH2
CH2
S
CH3
phenylalanine
CH2
F
CH2
C
N
H
cysteine
C
CH2
SH
CH
N
H
valine
V
H C CH3
CH2
CH2
(10.5)
leucine
L
tyrosine
Y
(8.3)
OH
magic
7
either
grab or
donate
proton
(10.1)
proline
P
COO+ CH
H2N
CH2
H2C
CH2
tryptophan
W
predominant form at pH 7, except for histidine
Other amino acid properties:
1. Glycine does not rotate plane
polarized light
2. Three amino acids absorb
UV light
W>Y>F
3. Cysteine side chain reacts with O2
Cystine
disulfide exchange reaction
intermolecular reaction
CH2-SH
HO
1. faster
OH
intramolecular reaction
2. use a smaller concentration
CH2-SH
Dithiothreitol (DTT)
thermodynamically stable
In vivo
electron transport chain
outer membrane
cytosol
plasma membrane
inner membrane
mitochondrion
Cells use glutathione (E-C-G), NADPH and
enzymes to keep SH
You might also like
- Lecture 3 PDFDocument16 pagesLecture 3 PDFNazir KhanNo ratings yet
- Proteins Part IDocument33 pagesProteins Part INikka Mia AbadiesNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Amino AcidsDocument0 pagesStructure of The Amino AcidsMalvina BurdujanNo ratings yet
- Student Copy True Lipids TrueDocument113 pagesStudent Copy True Lipids TrueSree Balaji Srinivas KatakamNo ratings yet
- Proteins Part I: Amino Acids and PeptidesDocument62 pagesProteins Part I: Amino Acids and PeptidesDaniele Joseph HizonNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument2 pagesAmino AcidsJohnNo ratings yet
- The Amino Acid: Optical IsomersDocument2 pagesThe Amino Acid: Optical IsomersLeonardoMorenoPerezNo ratings yet
- Aminoacid and Protein Structure (I)Document24 pagesAminoacid and Protein Structure (I)Game OverNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins: Dr. Clower Chem 4202Document55 pagesChapter 3: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins: Dr. Clower Chem 4202Vikas YadavNo ratings yet
- PROTEIN (Polypeptide) : Protein: Senyawa Organik Yang Merupakan Polimer Asam Amino Penyusun ProteinDocument79 pagesPROTEIN (Polypeptide) : Protein: Senyawa Organik Yang Merupakan Polimer Asam Amino Penyusun ProteinDwinur ChasanahNo ratings yet
- AMINO ACID 1 (200 Level)Document10 pagesAMINO ACID 1 (200 Level)Eduardo OcampoNo ratings yet
- PROTEINSDocument56 pagesPROTEINSJoltPacy100% (1)
- Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated Fatty AcidsDocument12 pagesMonounsaturated and Polyunsaturated Fatty AcidsmonikawadhanNo ratings yet
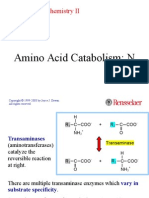
- Amino Acid Catabolism: N: Molecular Biochemistry IIDocument36 pagesAmino Acid Catabolism: N: Molecular Biochemistry IIbaderhistoNo ratings yet
- Formula of The 20 Common Amino AcidsDocument11 pagesFormula of The 20 Common Amino AcidsAngelica AngelesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PostDocument55 pagesChapter 3 PostNunnallyKallen MarieVi Lacre-HimuraNo ratings yet
- Amines: - Organic Compounds of Nitrogen N - Classified As Primary, Secondary, TertiaryDocument44 pagesAmines: - Organic Compounds of Nitrogen N - Classified As Primary, Secondary, Tertiaryshah_jalpan92911No ratings yet
- Amino Acid BIOCHEMDocument3 pagesAmino Acid BIOCHEMCayla Jean T. NavascaNo ratings yet
- Proteins Part IDocument33 pagesProteins Part INikka Mia AbadiesNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument2 pagesAmino AcidsHeaven Ashley ludrietaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid NotesDocument15 pagesAmino Acid NotesChris_Barber09No ratings yet
- Functional GroupsDocument1 pageFunctional GroupsStan SmithNo ratings yet
- 27 Amino Acids, ProteinsDocument73 pages27 Amino Acids, ProteinsRimisha NabeelNo ratings yet
- Topic19 Amino AcidsDocument27 pagesTopic19 Amino AcidsYoungNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument10 pagesProteingelary sousaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Amino: Acids, Peptides, and ProteinsDocument45 pagesBiomolecules: Amino: Acids, Peptides, and ProteinsShimi VicenteNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid ChartDocument6 pagesAmino Acid ChartCleveland BrownNo ratings yet
- Notes - Chapt.25 Amino Acids and PeptidesDocument51 pagesNotes - Chapt.25 Amino Acids and PeptidesSiddarth PalletiNo ratings yet
- De Novo Synthesis of Fatty AcidsDocument29 pagesDe Novo Synthesis of Fatty Acidslovelots1234100% (1)
- Amino AcidsDocument26 pagesAmino Acidsrumela1504No ratings yet
- LipidsDocument75 pagesLipidsanaNo ratings yet
- Nombre Grupo Funcional Formula Desarrollada Semi-Desarrollada EjemploDocument1 pageNombre Grupo Funcional Formula Desarrollada Semi-Desarrollada EjemploGerardo Salas SánchezNo ratings yet
- Chem 241 242 Formula SheetDocument2 pagesChem 241 242 Formula SheetClara RyuNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids: Dr. Goma Kathayat Lecturer Department of BiochemistryDocument37 pagesAmino Acids: Dr. Goma Kathayat Lecturer Department of BiochemistryAnjali KshtriNo ratings yet
- Bab 19. Asam AminoDocument58 pagesBab 19. Asam AminoSisca Ayu VerawatiNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Abbreviations Molecular Formula Linear FormulaDocument1 pageAmino Acid Abbreviations Molecular Formula Linear FormulaBeatrix RossNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar AminaDocument44 pagesBahan Ajar AminaAnindya Putri KurniasariNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid: Amino Acids With Uncharged Side Chains Polar Side Chains Non Polar Side ChainsDocument3 pagesAmino Acid: Amino Acids With Uncharged Side Chains Polar Side Chains Non Polar Side ChainsArghya SenNo ratings yet
- Amino Ácid OsDocument2 pagesAmino Ácid OsSelene JuarezNo ratings yet
- Asam SikimatDocument11 pagesAsam SikimatIhfan PriyantoNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids, PeptideDocument4 pagesAmino Acids, PeptideBronnNo ratings yet
- Primary AminesDocument12 pagesPrimary AminesPhillimonNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinDocument32 pagesAmino Acids and ProteinArchishmaan UdgataNo ratings yet
- Non Polar-Hydrophobic-Buried in Protein Core-AliphaticDocument4 pagesNon Polar-Hydrophobic-Buried in Protein Core-AliphaticRob FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Has SanDocument17 pagesHas Saninam64No ratings yet
- Mareial Complementar Unidade 4 Quimica Organica Gupos FuncionaisDocument10 pagesMareial Complementar Unidade 4 Quimica Organica Gupos FuncionaisepambarbaNo ratings yet
- Diktat Asam AminoDocument67 pagesDiktat Asam AminoWisnu GalihNo ratings yet
- Key Functional GroupsDocument24 pagesKey Functional GroupsThuan Tăng NguyenNo ratings yet
- XII Chem Amines To Students...Document17 pagesXII Chem Amines To Students...Seemacma100% (1)
- Amino AcidDocument38 pagesAmino AcidHassan Mehmood Subhani100% (1)
- New 104 Nucleophilic SubstDocument11 pagesNew 104 Nucleophilic SubstEva PannemanNo ratings yet
- Amino KiselineDocument23 pagesAmino KiselineLjubica TosicNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Catabolism: N: Molecular Biochemistry IIDocument36 pagesAmino Acid Catabolism: N: Molecular Biochemistry IIRaja Friska YulandaNo ratings yet
- SolventDocument1 pageSolventlycheatnstealNo ratings yet
- Appendix: Functional GroupsDocument3 pagesAppendix: Functional GroupsbibronsNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument56 pagesAmino Acids and Proteinstahaniu gouaouNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Catabolism: N: Molecular Biochemistry IIDocument36 pagesAmino Acid Catabolism: N: Molecular Biochemistry IIsandalailaNo ratings yet
- Asam AminoDocument31 pagesAsam Aminoekapratista26No ratings yet