Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Actual Indicator Diagram For A Two Stroke Cycle Diesel Engine
Uploaded by
BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Actual Indicator Diagram For A Two Stroke Cycle Diesel Engine
Uploaded by
BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANCopyright:
Available Formats
ME6412
THERMAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I 2015
7. ACTUAL INDICATOR DIAGRAM FOR A two
STROKE CYCLE diesel ENGINE
Exp. No. :
Date:
Aim :
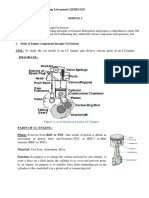
To study the actual indicator diagram for a two stroke cycle diesel engine.
Actual Indicator Diagram For A Two Stroke Cycle Diesel Engine:
The actual indicator diagram for a two-stroke cycle diesel engine is shown. The
suction is shown by the line: 1-2-3 i.e. from the instant transfer port opens (TPO) and
transfer port closes (TPC). We know that during the suction stage, the exhaust port is also
open. In the first half of suction stage, the volume: of air and burnt gases increases. This
happens as :the piston moves from 1-2 (i.e. BDC). In the second half of the suction stage,
the volume of air and burnt gases decreases. This happens as the piston moves upwards
from 2-3. A little beyond 3, the exhaust port closes (EPC) at 4. Now the air inside the
engine cylinder is compressed which is shown by the line 4-5. At the end of compression,
there is an increase in the pressure inside the engine cylinder. Shortly before the end of
compression (i. e. TDC), fuel valve opens (FVO) and the fuel is injected into the engine
cylinder. The fuel is ignited by high temperature of the compressed air. The ignition
suddenly increases volume and temperature of the products of combustion. But the
pressure, practically, remains constant as shown by the line 5-6. The expansion IS shown
by the line 6-7, Now the exhaust port opens (EPO) at 7 and the burnt gases are exhausted
into the atmosphere through the exhaust port. It reduces the pressure. As the piston is
G1 PREPARED BY BIBIN.C and S.GOBINATH, AP/MECH, RMKCET
ME6412
THERMAL ENGINEERING LABORATORY I 2015
moving towards BDC, therefore volume of burnt gases increases from 7 to 1. At 1, the
transfer port opens (TPO) and the suction starts.
Result:
Thus the actual indicator diagram for a two stroke cycle diesel engine was
studied.
G2 PREPARED BY BIBIN.C and S.GOBINATH, AP/MECH, RMKCET
You might also like
- The Petrol Engine: A Text-book dealing with the Principles of Design and Construction, with a Special Chapter on the Two-stroke EngineFrom EverandThe Petrol Engine: A Text-book dealing with the Principles of Design and Construction, with a Special Chapter on the Two-stroke EngineNo ratings yet
- Actual Indicator Diagram For A Two Stroke Cycle Petrol EngineDocument3 pagesActual Indicator Diagram For A Two Stroke Cycle Petrol EngineBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN75% (4)
- Actual Indicator Diagram For A Four Stroke Cycle Petrol EngineDocument2 pagesActual Indicator Diagram For A Four Stroke Cycle Petrol EngineBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN100% (1)
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SFrom EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNo ratings yet
- ACTUAL INDICATOR DIAGRAM FOR A FOUR STROKE CYCLE Diesel ENGINE PDFDocument3 pagesACTUAL INDICATOR DIAGRAM FOR A FOUR STROKE CYCLE Diesel ENGINE PDFBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN100% (4)
- CHAPTER 5 Internal Combustion EngineDocument49 pagesCHAPTER 5 Internal Combustion EngineYann YeuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Two Stroke EngineDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Two Stroke Enginevsputhaman100% (1)
- Basic Mech Civil EnggDocument94 pagesBasic Mech Civil EnggVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument27 pagesThermodynamicsRichard MascarenhasNo ratings yet
- Air Standed Cycles Lec-7Document20 pagesAir Standed Cycles Lec-7pleasename1No ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering Lab ManualDocument64 pagesThermal Engineering Lab ManualERKATHIR86% (7)
- Experiment No. 4-To Study Two & Four Stroke Petrol EngineDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 4-To Study Two & Four Stroke Petrol EngineShahed0% (1)
- Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 40: Internal Combustion EngineDocument9 pagesModule 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 40: Internal Combustion EngineAryyama JanaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Mechanical Engineering Lab Manual (21EME15/25) : Figure 1:-Cut Model of 4 Sroke I.C EngineDocument8 pagesElements of Mechanical Engineering Lab Manual (21EME15/25) : Figure 1:-Cut Model of 4 Sroke I.C Enginenihal shaikhNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 13 14Document8 pagesLab Report 13 14waleed rajpootNo ratings yet
- Valve Timing Diagram of 2 Stroke Petrol EngineDocument5 pagesValve Timing Diagram of 2 Stroke Petrol EngineMuhammad Toseef Chohan67% (3)
- Powerplant 1 FilesDocument91 pagesPowerplant 1 FilesArleigh Jan Igot PangatunganNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Notes For MEO Class IVDocument101 pagesConsolidated Notes For MEO Class IVIM0% (1)
- Mayur Jadhav Aen MicroprojectDocument14 pagesMayur Jadhav Aen Microprojectgjumde940No ratings yet
- Module 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 40: Internal Combustion EngineDocument9 pagesModule 5: Combustion Technology Lecture 40: Internal Combustion EngineSwaksharJyoti HazarikaNo ratings yet
- Pe Lab ManualDocument30 pagesPe Lab ManualAnshikha NautiyalNo ratings yet
- 4 Stroke IC Engine Valve Timing DiagramDocument2 pages4 Stroke IC Engine Valve Timing DiagramEngineer_SAM75% (4)
- Working of SI & CI Engines (2S & 4S) : Power Unit (Engine)Document12 pagesWorking of SI & CI Engines (2S & 4S) : Power Unit (Engine)Satish BheleNo ratings yet
- Lec9 PDFDocument34 pagesLec9 PDFshravanNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine - FundamentalDocument20 pagesDiesel Engine - FundamentalSoumen BhattaNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering Lab ExperimentDocument7 pagesAutomobile Engineering Lab ExperimentNidhi BharatiyaNo ratings yet
- IC EnginesDocument55 pagesIC EnginesRhydham PNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Title: Types of Engines General Objective: Specific ObjectivesDocument16 pagesUnit 1: Title: Types of Engines General Objective: Specific ObjectivesAtika MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Valve Timing Diagram-5 PDFDocument6 pagesValve Timing Diagram-5 PDFdhirendra singh100% (1)
- 1477552111913-Fundamentals of Diesel Engines PDFDocument23 pages1477552111913-Fundamentals of Diesel Engines PDFAjaykuamrNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering Lab ManualDocument74 pagesThermal Engineering Lab ManualYudhisthar SainiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 IntroductionDocument18 pagesExperiment 1 IntroductionMohamad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Engines: Machine: A Device Whose Components Have Constrained Relative Motions UsesDocument13 pagesEngines: Machine: A Device Whose Components Have Constrained Relative Motions UsesIbrahim HossainNo ratings yet
- Materi - Otto CycleDocument21 pagesMateri - Otto CycleRydho Putra PradanaNo ratings yet
- Me6412 Thermal Engineering Laboratory Manual - IDocument126 pagesMe6412 Thermal Engineering Laboratory Manual - IBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN100% (4)
- FICE 1 KeyDocument4 pagesFICE 1 KeyK. Swaminathan Asst Prof - Automobile DeptNo ratings yet
- IC Engines Chapter 3 PDFDocument28 pagesIC Engines Chapter 3 PDFnauman khanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 IntroductionDocument17 pagesExperiment 1 IntroductionMohamad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Heat Power Lab ManualDocument68 pagesHeat Power Lab ManualRaghu KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Automobile Engineering Lab II (ETPM Lab)Document4 pagesAutomobile Engineering Lab II (ETPM Lab)Souvik BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- IC Engine ManualDocument36 pagesIC Engine ManualShailesh TekaleNo ratings yet
- Valve Timing DiagramDocument5 pagesValve Timing DiagramkaranNo ratings yet
- Diesel Cycle - Process, PV Diagram, Efficiency With Derivation & Applications (Explanation & PDF)Document7 pagesDiesel Cycle - Process, PV Diagram, Efficiency With Derivation & Applications (Explanation & PDF)Shivam SinghNo ratings yet
- Ic LaboratoryDocument28 pagesIc LaboratoryMd ChandNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics Lab 2k9ee-834Document22 pagesApplied Thermodynamics Lab 2k9ee-834himsdon100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document14 pagesChapter 2Abdullah OmerNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of T He Diesel C YcleDocument9 pagesFundamentals of T He Diesel C YcleMasudRanaNo ratings yet
- ATD Unit 1Document39 pagesATD Unit 1Sateesh KumarNo ratings yet
- EX.1 - Valve Timing DiagramDocument5 pagesEX.1 - Valve Timing Diagrammanojkhadka23No ratings yet
- Energy Conversions: SubjectDocument37 pagesEnergy Conversions: SubjectprabhjotbhangalNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of Prime MoversDocument8 pagesThermodynamics of Prime MoversSelva KumarNo ratings yet
- Ic Engines: Four Stroke Cycle Diesel EnginesDocument10 pagesIc Engines: Four Stroke Cycle Diesel Enginesmechjobs4meNo ratings yet
- IC Engines Lab Manual StudyDocument26 pagesIC Engines Lab Manual StudyKaka Drishti100% (1)
- Valve Timing Diagram of Four Stroke Cycle Petrol EngineDocument5 pagesValve Timing Diagram of Four Stroke Cycle Petrol EngineBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN67% (3)
- Diesel Engine Combustion ProcessDocument8 pagesDiesel Engine Combustion Processvmike63100% (1)
- Internal Combustion EnginesDocument28 pagesInternal Combustion Enginesshanumech100% (1)
- Valve Timing DiagramDocument8 pagesValve Timing DiagramEr Dinesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate IMEPDocument9 pagesHow To Calculate IMEPpramodNo ratings yet
- Ic Engines Lab ManualDocument33 pagesIc Engines Lab ManualupenderdhullNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2015Document3 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2015BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me 6301 - Engineering Thermodynamics Unit Test 1 - Set 1Document2 pagesMe 6301 - Engineering Thermodynamics Unit Test 1 - Set 1BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- ME 8391 Engineering Thermodynamics Workbook - UNIT 1Document154 pagesME 8391 Engineering Thermodynamics Workbook - UNIT 1BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me6016 Advanced I.C Engines - Unit - 1Document60 pagesMe6016 Advanced I.C Engines - Unit - 1BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN75% (4)
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2012Document4 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2012BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN100% (1)
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2014Document3 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2014BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - April May 2015Document3 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - April May 2015BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2011Document3 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2011BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHAN100% (1)
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - April May 2010Document4 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - April May 2010BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016Document4 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2013Document2 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2013BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2011Document3 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2011BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2015Document3 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2015BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2014Document3 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2014BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2012Document4 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2012BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2014Document4 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2014BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- ME 2202 - ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Mech 3rrdDocument5 pagesME 2202 - ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Mech 3rrddharmaraj_meapNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics May June 2013Document3 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics May June 2013BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2010Document4 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - Nov Dec 2010BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics May June 2011Document3 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics May June 2011BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics (Nov, Dec2008) R2004Document4 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics (Nov, Dec2008) R2004Vijaya Prabhu KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016Document4 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2016BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics May June 2011Document3 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics May June 2011BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics (May2009)Document3 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics (May2009)Siva2sankarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics Question Paper Maj June 2007Document4 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics Question Paper Maj June 2007Anirudhan RaviNo ratings yet
- Me2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - April May 2015Document3 pagesMe2202 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - April May 2015BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics (Nov, Dec2009) R2004Document4 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics (Nov, Dec2009) R2004Siva2sankarNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2007Document3 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2007BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2006Document3 pagesMe6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2006BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Me1201 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2012Document3 pagesMe1201 Engineering Thermodynamics - Uq - May June 2012BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet
- The ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemFrom EverandThe ISO 45001:2018 Implementation Handbook: Guidance on Building an Occupational Health and Safety Management SystemNo ratings yet
- Solar Power Demystified: The Beginners Guide To Solar Power, Energy Independence And Lower BillsFrom EverandSolar Power Demystified: The Beginners Guide To Solar Power, Energy Independence And Lower BillsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Shorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridFrom EverandShorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Well Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsFrom EverandWell Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Photovoltaic Solar Energy: From Fundamentals to ApplicationsFrom EverandPhotovoltaic Solar Energy: From Fundamentals to ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Idaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentFrom EverandIdaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Handbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemFrom EverandHandbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electric Motors and Drives: Fundamentals, Types and ApplicationsFrom EverandElectric Motors and Drives: Fundamentals, Types and ApplicationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesFrom EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Heat Transfer Engineering: Fundamentals and TechniquesFrom EverandHeat Transfer Engineering: Fundamentals and TechniquesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Offshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsFrom EverandOffshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsNo ratings yet
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsFrom EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Live Off Grid: Escape The City, Learn How To Travel Intelligently Using Solar PowerFrom EverandLive Off Grid: Escape The City, Learn How To Travel Intelligently Using Solar PowerNo ratings yet
- A Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandA Complete Guide to Safety Officer Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&AFrom EverandAir Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&ANo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Initiating Events and Independent Protection Layers in Layer of Protection AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsFrom EverandElectric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Renewable Energy Sources - Wind, Solar and Hydro Energy Revised Edition : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksFrom EverandRenewable Energy Sources - Wind, Solar and Hydro Energy Revised Edition : Environment Books for Kids | Children's Environment BooksNo ratings yet
- Redefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesFrom EverandRedefining Work Health and Safety: Systems, Strategies, and Progressive ApproachesNo ratings yet
- The Permaculture City: Regenerative Design for Urban, Suburban, and Town ResilienceFrom EverandThe Permaculture City: Regenerative Design for Urban, Suburban, and Town ResilienceNo ratings yet
- Smart Power Distribution Systems: Control, Communication, and OptimizationFrom EverandSmart Power Distribution Systems: Control, Communication, and OptimizationNo ratings yet
- Asphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical ProspectsFrom EverandAsphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical ProspectsNo ratings yet