Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment IR Inclass
Uploaded by
Amir FirdausCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment IR Inclass
Uploaded by
Amir FirdausCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment IR
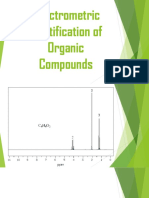
1. The IR spectrum of phenylacetylene is shown in the figure below. What absorption
bands can you identify?
2. How might you use IR spectroscopy to distinguish among the three isomers but-1-yne,
buta-1,3-diene and but-2-yne?
3. Would you expect two enantiomers such as (R)-2-bromobutane and (S)-2bromobutane to have identical or different IR spectra? Explain.
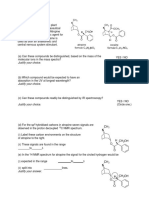
4. Propose structures for compounds that meet the following description:
a. C5H8, with IR absorptions at 3300 and 2150 cm-1
b. C4H8O, with a strong IR absorption at 3400 cm-1
c. C4H8O, with a strong IR absorption at 1715 cm-1
d. C8H10, with IR absorption at 3030 and 1600 cm-1
5. How could you use infrared spectroscopy to distinguish between the following pairs of
isomers?
a. HCCCH2NH2 and CH3CH2CN
b. CH3COCH3 and CH3CH2CHO
6. At what approximate positions might the following compounds show IR absorptions?
7.
Assume you are carrying out the dehydration of 1-methylcyclohexanol to yield 1methylcyclohexene. How could you use infrared spectroscopy to determine when the
reaction is complete?
8. Which is stronger, the C=O bond in an ester (1735cm-1) or the C=O bond in a
saturated ketone (1715cm-1)? Explain.
9. Grignard reagents undergo a general and very useful reaction with ketones.
Methylmagnesium bromide, for example, reacts with cyclohexanone to yield a product
with the formula C7H14O. What is the structure of this product if it has an IR absorption
at 3400cm-1?
You might also like
- S2 Assign2 QnsDocument8 pagesS2 Assign2 QnsFiona OyatsiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Part C PDFDocument6 pagesTutorial 2 Part C PDFMuhammad Azri HaziqNo ratings yet
- Reductions in Organic ChemistryDocument13 pagesReductions in Organic ChemistryNikola PudjaNo ratings yet
- CHM580-Tutorial IR Dan RamanDocument6 pagesCHM580-Tutorial IR Dan RamanSuhailyShukri100% (1)
- III Semester SPECTROS PDFDocument11 pagesIII Semester SPECTROS PDFArangaNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Exercise 1 - Analytical TechniquesDocument2 pagesTopic 9 Exercise 1 - Analytical TechniquesChryssa EconomouNo ratings yet
- CH301 Tutorial IRDocument2 pagesCH301 Tutorial IRArjun MaharajNo ratings yet
- Guía de Estudio EspectrosDocument5 pagesGuía de Estudio EspectrosCésar CidNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1: IR Spectroscopy (Chapter 2) Name: Fatin Wahida Binti Hashim Student ID: 2017680232 Group: A4AS1205 - 10Document5 pagesQuiz 1: IR Spectroscopy (Chapter 2) Name: Fatin Wahida Binti Hashim Student ID: 2017680232 Group: A4AS1205 - 10fatin hashimNo ratings yet
- EBatistil - Problem Set 1Document8 pagesEBatistil - Problem Set 1essielveNo ratings yet
- Looking at Infrared Spectra:: ExampleDocument4 pagesLooking at Infrared Spectra:: ExampleRamshaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry With Biological Applications 2Nd Edition Mcmurry Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument55 pagesOrganic Chemistry With Biological Applications 2Nd Edition Mcmurry Test Bank Full Chapter PDFmisstepmonocarp1b69100% (7)
- Worksheet 2 With AnswersDocument1 pageWorksheet 2 With AnswersCheng FuNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7Document10 pagesExperiment 7NathanianNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 PDFDocument20 pagesUnit 14 PDFAnonymous Y75qPkj2jNo ratings yet
- Infrared Spectrum Formal Lab ReportDocument10 pagesInfrared Spectrum Formal Lab ReportAnonymous 1z7otENo ratings yet
- Application of IR Spectroscopy and Interpretation of IR SpectrumDocument10 pagesApplication of IR Spectroscopy and Interpretation of IR SpectrumMuhammad HussnainNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7Document2 pagesTutorial 7nabilNo ratings yet
- bài tập tổng hợp GỬI LỚPDocument4 pagesbài tập tổng hợp GỬI LỚPĐinh Hoàng Bích TrâmNo ratings yet
- 4.11 Structure DeterminationDocument46 pages4.11 Structure DeterminationJaslinder Kaur Dhillon100% (1)
- Chapter 9Document5 pagesChapter 9Stephen BrownNo ratings yet
- Assignment UVDocument2 pagesAssignment UVshafNo ratings yet
- Clayden 2e - End of Chapter Questions - Ch3Document4 pagesClayden 2e - End of Chapter Questions - Ch3Nikola NinkovNo ratings yet
- IR Spectroscopy Problem Set 2Document5 pagesIR Spectroscopy Problem Set 2Jules BrunoNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT CHM557-mergedDocument3 pagesASSIGNMENT CHM557-mergedAhmad ZakwanNo ratings yet
- CHM260 Ftir Lab ReportDocument6 pagesCHM260 Ftir Lab ReportAIN NABILA SHAHARUDDINNo ratings yet
- UV Spectroscopy QuestionsDocument3 pagesUV Spectroscopy QuestionsRashmiNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Study Groups WorksheetDocument5 pagesWeek 4 Study Groups WorksheetreallechuaNo ratings yet
- CH301 Tutorial Solutions On IR Spectros PDFDocument4 pagesCH301 Tutorial Solutions On IR Spectros PDFArjun MaharajNo ratings yet
- t1-p1-2 Spectra-Structure Correlations in The Mid and Far InfraredDocument34 pagest1-p1-2 Spectra-Structure Correlations in The Mid and Far InfraredCorvusdav EspinNo ratings yet
- Structural Methods in Molecular Inorganic Chemistry: Worked ExamplesDocument14 pagesStructural Methods in Molecular Inorganic Chemistry: Worked ExamplesChelsea ClarkNo ratings yet
- Optional SpectrosDocument4 pagesOptional SpectrosPhil LiuNo ratings yet
- AssiDocument3 pagesAssiScott BoothNo ratings yet
- Kelas Xiii Semester Gasal: Elusidasi Struktur Senyawa Organik Mata Diklat: Kimia OrganikDocument12 pagesKelas Xiii Semester Gasal: Elusidasi Struktur Senyawa Organik Mata Diklat: Kimia OrganikLutphiaNo ratings yet
- IR Spectroscopy LabDocument10 pagesIR Spectroscopy LabChristian AmpeNo ratings yet
- L1 Mass Spec and IRDocument15 pagesL1 Mass Spec and IRCheng FuNo ratings yet
- Assignment UVDocument2 pagesAssignment UVNaufal Syafiq Mohd IsaNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of IR Compounds BY KhanDocument7 pagesInterpretation of IR Compounds BY KhanShamsheer KhanNo ratings yet
- 1455787242CHE P12 M30 EtextDocument8 pages1455787242CHE P12 M30 EtextSaurav PaulNo ratings yet
- RMN ProblemsDocument7 pagesRMN ProblemsAnonymous llSDP0tNo ratings yet
- 2425 Chapt 13Document10 pages2425 Chapt 13Ivan Alberto NinaNo ratings yet
- 4101-A - Application of Mass Spectrometry To Inorganic CompoundsDocument9 pages4101-A - Application of Mass Spectrometry To Inorganic CompoundsGuRi JassalNo ratings yet
- Final Examination of Elsus 23052019Document1 pageFinal Examination of Elsus 230520191177040053 Nur Ainun NisaNo ratings yet
- 11.3 Revision IB CHEMDocument9 pages11.3 Revision IB CHEMlunaisdrowsyNo ratings yet
- Virtual Experiment 2: Instrumentation and Working Principles of Infrared (IR) SpectrosDocument10 pagesVirtual Experiment 2: Instrumentation and Working Principles of Infrared (IR) SpectrosBernadette Virola CuevasNo ratings yet
- 1455877785CHE P12 M35 EtextDocument8 pages1455877785CHE P12 M35 EtextSaurav PaulNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION To IR 2Document21 pagesINTRODUCTION To IR 2Rabia KhanNo ratings yet
- Exam Analytical ChemDocument4 pagesExam Analytical ChemSNo ratings yet
- MCAT Review SmithDocument47 pagesMCAT Review SmithMonu KadianNo ratings yet
- Chm622 Slide BookDocument14 pagesChm622 Slide Bookzatty kimNo ratings yet
- Chem 24 Pal Worksheet IrDocument4 pagesChem 24 Pal Worksheet IrAmbreen latif Abdul latifNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2Document1 pageWorksheet 2Cheng FuNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Biological and Clinical Mass Spectrometry: An IntroductionFrom EverandQuantitative Biological and Clinical Mass Spectrometry: An IntroductionNo ratings yet
- Carotenoids – 4: Main Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Symposium on Carotenoids, Berne, Switzerland, 25-29 August 1975From EverandCarotenoids – 4: Main Lectures Presented at the Fourth International Symposium on Carotenoids, Berne, Switzerland, 25-29 August 1975B. C. L. WeedonNo ratings yet
- Iridium(III) in Optoelectronic and Photonics ApplicationsFrom EverandIridium(III) in Optoelectronic and Photonics ApplicationsEli Zysman-ColmanNo ratings yet
- Experimental and Theoretical Approaches to Actinide ChemistryFrom EverandExperimental and Theoretical Approaches to Actinide ChemistryJohn K. GibsonNo ratings yet
- Immunohistochemistry and Immunocytochemistry: Essential MethodsFrom EverandImmunohistochemistry and Immunocytochemistry: Essential MethodsSimon RenshawNo ratings yet
- HeatDocument37 pagesHeatAmir FirdausNo ratings yet
- Malaysian Snakebite Management GuidelineDocument113 pagesMalaysian Snakebite Management GuidelineMohd Syamirulah Rahim100% (2)
- WBS N MilestoneDocument4 pagesWBS N MilestoneAmir Firdaus100% (1)
- Types of InceneratorDocument1 pageTypes of InceneratorAmir FirdausNo ratings yet
- Guideline Report Writing - Che697Document22 pagesGuideline Report Writing - Che697Nurul AiniNo ratings yet
- Turnitin Training Guide - StudentsDocument2 pagesTurnitin Training Guide - StudentsAmir FirdausNo ratings yet
- Integrated Projects-Grouping (Eh220/4A) : Title:Production of Methanol Semester:MARCH-JUNE 2014 Kumpulan: EH2204ADocument1 pageIntegrated Projects-Grouping (Eh220/4A) : Title:Production of Methanol Semester:MARCH-JUNE 2014 Kumpulan: EH2204AAmir FirdausNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Fluid FlowDocument8 pagesAssignment 2 Fluid FlowAmir FirdausNo ratings yet
- Intro To Pressure VesselDocument18 pagesIntro To Pressure VesselSanjay Jay SanjayNo ratings yet
- ReactorDocument9 pagesReactorSalim ChohanNo ratings yet
- Route To MethanolDocument20 pagesRoute To Methanolruk1921No ratings yet
- Introduction To UV-Vis SpectrosDocument5 pagesIntroduction To UV-Vis SpectrosShahul0% (1)
- Chapter 3 Colloids and Fine ParticlesDocument30 pagesChapter 3 Colloids and Fine ParticlesAmir FirdausNo ratings yet