Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English Cheat Sheet 1 (19/09/2015) : Types of Sentences Nouns
English Cheat Sheet 1 (19/09/2015) : Types of Sentences Nouns
Uploaded by
Muhammad RizwanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
English Cheat Sheet 1 (19/09/2015) : Types of Sentences Nouns
English Cheat Sheet 1 (19/09/2015) : Types of Sentences Nouns
Uploaded by
Muhammad RizwanCopyright:
Available Formats
English Cheat Sheet 1 [19/09/2015]
Types of Sentences
Declarative
Imperative
Interrogative
Exclamatory
Parts of Speech
Nouns
Verbs
Adjectives
Pronouns
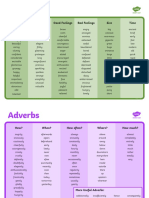
Adverbs
Preposition
Conjunction
Interjection
Verbs
Action Verbs
Linking Verbs
Sensory Verbs
Auxiliary Verbs
Nouns
Proper Nouns
Common Nouns
Count Nouns
Non-count Nouns
Collective Nouns
Subject Verb Agreement
REAL SUBJECT: Prepositional Phrases between the
subject and the verb do not affect the verb.
e.g. John as well as his wife and two children is taking
a long vacation.
Es: Everybody, Everyone, Every, Each SINGULAR
e.g. Each of the two boys takes a music class.
WHO: Since the who refers to the noun before it, the
verb agrees with that noun.
e.g. Sue is one of the women in my office who smoke.
Ns: Neither, Nor Verb agrees with the SECOND
NOUN
e.g. Neither his sisters nor Jack smokes.
UNITS: Units of distance, time, weight, and money are
always SINGULAR.
e.g. Forty-five miles is a long way to walk.
UNCOUNTALBLE & GERUNDS: ncountable nouns
and gerunds are always SINGULAR.
e.g. Mathematics takes a lot of time to master.
OF: Half of, A third of, All of, A majority of, Most of,
Some of, Many, ... etc. Verb agrees with the NOUN
AFTER these phrases.
e.g. Half of the students in this school are rich.
Used at the very beginning of a document:
\documentclass{class}. Use \begin{document} to start
contents and \end{document} to end the document.
THERE: There is, There are Verb agrees with the
ONE NOUN AFTER these phrases.
e.g. There is a mouse and two rats in the corner.
c 2015 RiZ
Copyright
You might also like
- ODE Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesODE Cheat SheetMuhammad Rizwan88% (8)
- LA Cheat SheetDocument1 pageLA Cheat SheetMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- NounsDocument13 pagesNounsGonzalo SardiñaNo ratings yet
- Report Writing in English: Penulisan Laporan Berbahasa InggrisDocument21 pagesReport Writing in English: Penulisan Laporan Berbahasa InggrisRiaNo ratings yet
- English Grammar at A GlanceDocument7 pagesEnglish Grammar at A Glancehemisphereph2981No ratings yet
- Verb Patterns Gerunds InfinitivesDocument22 pagesVerb Patterns Gerunds InfinitivesHüseyin KurtNo ratings yet
- The Fun They Had PDFDocument9 pagesThe Fun They Had PDFDivyam PandeyNo ratings yet
- Good Points: The Letter To GodDocument24 pagesGood Points: The Letter To GodPaarth PrakashNo ratings yet
- Danny The Dog!: We Are Going To Have Help Learning About Adverbs FromDocument13 pagesDanny The Dog!: We Are Going To Have Help Learning About Adverbs FromCleo Abegail PalomadoNo ratings yet
- Question TagsDocument7 pagesQuestion TagsemilromenNo ratings yet
- How Do Organism Reproduce-1Document11 pagesHow Do Organism Reproduce-1Land LordNo ratings yet
- 100 Golden Rules of English Grammar For Error DetectionDocument13 pages100 Golden Rules of English Grammar For Error DetectionShivamSinghNo ratings yet
- p.3 English Lesson Notes Term 1-3Document83 pagesp.3 English Lesson Notes Term 1-3arduuzaekkyNo ratings yet
- 02 Context CluesDocument94 pages02 Context CluesJeanina delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Eng 8 q1 w5 6 ModuleDocument6 pagesEng 8 q1 w5 6 ModuleKenneth Lei D. HadjilatipNo ratings yet
- Gerund Vs InfinitiveDocument17 pagesGerund Vs InfinitiveSidiq WiranataNo ratings yet
- Pronoun WorksheetDocument2 pagesPronoun WorksheetMalak KleitNo ratings yet
- Verb and Preposition: SO Somebody ST SomethingDocument17 pagesVerb and Preposition: SO Somebody ST SomethingDelia CatrinaNo ratings yet
- ParticipleDocument2 pagesParticipleAsiale AlmoceraNo ratings yet
- Tenses English ClubDocument46 pagesTenses English ClubShah AkNo ratings yet
- Tense ReviewDocument43 pagesTense ReviewGrejsa KarajfilajNo ratings yet
- Food Speaking PDFDocument2 pagesFood Speaking PDFBetina RoselliniNo ratings yet
- Bsee 39 - Lesson 1Document37 pagesBsee 39 - Lesson 1BALLARES, GERALDINE E.No ratings yet
- Live Beat Video Activities All LevelsDocument23 pagesLive Beat Video Activities All LevelsNadia Lucía Vazquez0% (1)
- Degrees of Comparsion EnglishDocument21 pagesDegrees of Comparsion EnglishPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- 150 Common Mistakes in English Grammar and Their Correct AnswersDocument8 pages150 Common Mistakes in English Grammar and Their Correct AnswersMaisam100% (1)
- 40 Imporant English GrammarDocument93 pages40 Imporant English Grammarbenbouchta sanaa100% (1)
- Curso de Inglés GramáticaDocument30 pagesCurso de Inglés GramáticaOmar SolanoNo ratings yet
- Regular Irregular VerbsDocument4 pagesRegular Irregular VerbsGerard24100% (1)
- Carnivores Vs Herbivores WorksheetDocument4 pagesCarnivores Vs Herbivores Worksheetsandapeharda9717No ratings yet
- English ReductionDocument6 pagesEnglish ReductionNguyễn Hoài NamNo ratings yet
- Word Families BuildingDocument3 pagesWord Families BuildingAndri KarnandaNo ratings yet
- TAG QUESTION PresentationDocument6 pagesTAG QUESTION PresentationSergio SuarezNo ratings yet
- Exclamations - SO, SUCH, WHAT, WHAT A, HOWDocument2 pagesExclamations - SO, SUCH, WHAT, WHAT A, HOWlucaNo ratings yet
- Exercises in EnglishDocument5 pagesExercises in EnglishAnjo SingsonNo ratings yet
- Grammar For WrittingDocument34 pagesGrammar For WrittingDuy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- English Spelling RulesDocument3 pagesEnglish Spelling RulesAmirahNo ratings yet
- Daily RoutinesDocument39 pagesDaily RoutinesAna Cifuentes OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Basic Writing Skills IIDocument1 pageBasic Writing Skills IIJayanthiNo ratings yet
- From Tasting To DigestingDocument7 pagesFrom Tasting To DigestingSanket Sinai PaussoNo ratings yet
- KP 8 - Diet and Nutrition A 2019Document39 pagesKP 8 - Diet and Nutrition A 2019Luthi PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Grammar 3 PDFDocument87 pagesGrammar 3 PDFHiba AkelNo ratings yet
- Ephesians Leader GuideDocument46 pagesEphesians Leader GuidedavelopezNo ratings yet
- Presents:: The Dirty DozenDocument21 pagesPresents:: The Dirty DozenAwais TareqNo ratings yet
- What Are Nouns?Document33 pagesWhat Are Nouns?unser1941No ratings yet
- Adjective PhrasesDocument11 pagesAdjective PhrasesMariel EfrenNo ratings yet
- Making PluralsDocument72 pagesMaking Pluralsvishu6387No ratings yet
- Transformation Exercises (CPE)Document12 pagesTransformation Exercises (CPE)Denise MartinsNo ratings yet
- English Essay (Narrative Essay)Document1 pageEnglish Essay (Narrative Essay)Faiqa Malik100% (1)
- Science (English Version) For Class 9-10Document223 pagesScience (English Version) For Class 9-10আভাস আসিফ0% (1)
- T L 4358 Adjective Adverb and Verb Mat Pack Ver 5Document4 pagesT L 4358 Adjective Adverb and Verb Mat Pack Ver 5Eiman Mounir100% (1)
- Adverbs CollocationsDocument24 pagesAdverbs CollocationsRita OteroNo ratings yet
- Tag QuestionsDocument6 pagesTag QuestionsJeshwary KumarNo ratings yet
- Class X - CH - 10 The Sermon at BenarasDocument19 pagesClass X - CH - 10 The Sermon at BenarasVaishu UparkarNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple/present Perfect Progressive/modal VerbsDocument24 pagesPresent Perfect Simple/present Perfect Progressive/modal VerbsCindy Lizeth Valle SalasNo ratings yet
- Rules On Adjective and AdverbsDocument2 pagesRules On Adjective and AdverbsAudrey100% (1)
- SOC 340 Full Semester PackageDocument19 pagesSOC 340 Full Semester PackageNerdy Notes Inc.No ratings yet
- Grammar NotesDocument8 pagesGrammar NotesShahriya Habib MuhamadNo ratings yet
- The Eight Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesThe Eight Parts of SpeechDyan LestariNo ratings yet
- Compound Sentence ExerciseDocument3 pagesCompound Sentence ExerciseHalimaton SaodahNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Notes MainDocument101 pagesEnglish Grammar Notes Mainnaftaly gaksNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Feedforward Neural Networks (Hugo)Document78 pages01 Introduction To Feedforward Neural Networks (Hugo)Muhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- 07 Deep Reinforcement Learning (John)Document52 pages07 Deep Reinforcement Learning (John)Muhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- On The Move - Dynamical Systems For Modeling, Measurement and Inference in Low Dimensional Signal ModelsDocument50 pagesOn The Move - Dynamical Systems For Modeling, Measurement and Inference in Low Dimensional Signal ModelsMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Automated Low-Level Analysis and Description of Diverse Intelligence (Aladdin) VideoDocument11 pagesAutomated Low-Level Analysis and Description of Diverse Intelligence (Aladdin) VideoMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- NMF TutorialDocument189 pagesNMF TutorialMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Convolutional Neural Network: From Theory To ImplementationDocument5 pagesConvolutional Neural Network: From Theory To ImplementationMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Sidebar 1Document4 pagesSidebar 1Muhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Linear Factor Models and Auto-EncodersDocument28 pagesLinear Factor Models and Auto-EncodersMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Example ThesisDocument17 pagesExample ThesisMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Thesis PDFDocument25 pagesThesis PDFMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- The cornell document class for L TEX 2εDocument20 pagesThe cornell document class for L TEX 2εMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Bare Demo of Ieeetran - Cls For T M: Ransactions On AgneticsDocument1 pageBare Demo of Ieeetran - Cls For T M: Ransactions On AgneticsMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- 1 Example 1: This Is The Text in Example OneDocument1 page1 Example 1: This Is The Text in Example OneMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- L TEX 2ε Cheat Sheet: Document classesDocument2 pagesL TEX 2ε Cheat Sheet: Document classesMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Title: Section 3Document1 pageTitle: Section 3Muhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- Complex Cheat SheetDocument1 pageComplex Cheat SheetMuhammad RizwanNo ratings yet
- L Texcheatsheet: 1 What Is L Tex?Document4 pagesL Texcheatsheet: 1 What Is L Tex?Muhammad RizwanNo ratings yet