Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activity 2 Linear Actuators
Uploaded by
api-2983086770 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesElectric actuators are often the solution of choice for repeatedly moving a load--or several loads--in a continuous fashion. Linear actuators are also used to control the rate of acceleration. Rotary actuators and parts are used in a variety of industrial, research and development, lab, production and quality inspection applications.
Original Description:
Original Title
activity 2 linear actuators
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentElectric actuators are often the solution of choice for repeatedly moving a load--or several loads--in a continuous fashion. Linear actuators are also used to control the rate of acceleration. Rotary actuators and parts are used in a variety of industrial, research and development, lab, production and quality inspection applications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views2 pagesActivity 2 Linear Actuators
Uploaded by
api-298308677Electric actuators are often the solution of choice for repeatedly moving a load--or several loads--in a continuous fashion. Linear actuators are also used to control the rate of acceleration. Rotary actuators and parts are used in a variety of industrial, research and development, lab, production and quality inspection applications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Activity 2: Please explain/define the following actuators,
including their most appropriate applications: Linear,
Rotational
Linear- is a mechanical device that converts energy (power from
air, electricity or liquid) to create motion in a straight line;
contrasted with circular motion of a conventional electric motor. It
can also be used to apply a force.
Repeated Linear MovementElectric actuators are often the solution of choice for repeatedly
moving a loador several loadsto a consistent locationor
locationsin a continuous fashion. Repeated linear movement
sometimes requires synchronizing multiple axes to facilitate
coordinated moves. If you need to repeat motion continuously
and consistently, as well as coordinate several different motions
simultaneously, this type of actuator is often the best solution.
Adaptable MovementLinear motion that changes or adaptsfrequently referred to as
adaptable movement is another important application.
Whenever load, positions, or the very nature of the motion itself
changesas often is necessary for synchronizing movements with
other machine operationsyou can use these actuators to control
and facilitate adaptable movement.
Controlled Precision MovementPrecisely controlled motion the accuracy of which is beyond the
capabilities of an actual person without exhibiting human erroris
another important electric actuator use. With these linear
actuators, you can control position with extreme levels of
precision, duplicate and repeat precise movements within the full
stroke, and even reprogram or reconfigure precise motions to
support multiple applications.
Acceleration Controlled Movement-
Electric linear actuators are also used to control the rate of
acceleration. Because you can precisely control speed, position,
and torque, you can make the actuator accelerate or decelerate
as quickly and as often as you need.
Rotational- is an actuator that produces a rotary motion or torque.
The simplest actuator is purely mechanical, where linear motion
in one direction gives rise to rotation. The most common
actuators though are electrically powered.
Rotary actuators and parts are used in a variety of industrial,
research and development, lab, production and quality inspection
applications all of which require rotary motion. These pneumatic
actuators are appropriate for payloads of all sizes, and can be
mounted and operated in any direction. Parkers efficient line of
actuators and parts enable productivity improvements through
automation of repetitive tasks.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Circuit Symbol Part 1 RoboticsDocument2 pagesCircuit Symbol Part 1 Roboticsapi-298308677No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Introduction To ElectronicsDocument6 pagesUnit 2 Introduction To Electronicsapi-298308677No ratings yet
- Simple Machines ProjectDocument1 pageSimple Machines Projectapi-298308677No ratings yet
- Robotics Questions 2Document2 pagesRobotics Questions 2api-298308677No ratings yet
- Robotics 4Document1 pageRobotics 4api-298308677No ratings yet
- Robotics 3Document4 pagesRobotics 3api-298308677No ratings yet
- Robotic Sensory DefinitionDocument2 pagesRobotic Sensory Definitionapi-298308677No ratings yet
- Robotics 2Document1 pageRobotics 2api-298308677No ratings yet
- Robot Picture CollageDocument1 pageRobot Picture Collageapi-298308677No ratings yet
- Load Flow Analysis of Advance PowerDocument4 pagesLoad Flow Analysis of Advance PowerIvan Fajar ArismawanNo ratings yet
- Flash Gas CompressorsDocument7 pagesFlash Gas CompressorsMartin FernandezNo ratings yet
- The Basics of SpectrosDocument133 pagesThe Basics of SpectrosMidabel100% (6)
- Lecture 1 Fluid PropertiesDocument40 pagesLecture 1 Fluid PropertiesRIZWAN KHANNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Theory I (PH-424) Problem Set 4Document2 pagesElectromagnetic Theory I (PH-424) Problem Set 4DEBANJAN ADHIKARINo ratings yet
- Maxwell's Equations and EM WavesDocument20 pagesMaxwell's Equations and EM WavesMeghana Chowdary ArumilliNo ratings yet
- 2017 Havlik J. Dlouhy T. Experimental Determination of The Heat Transfer Coefficient in SheDocument6 pages2017 Havlik J. Dlouhy T. Experimental Determination of The Heat Transfer Coefficient in SheWilmer Garcia DelgadoNo ratings yet
- PHD ThesisDocument310 pagesPHD ThesisOlivia OeyNo ratings yet
- Shri B. V. V. Sangha'S: "Solar Powered Airplanes"Document15 pagesShri B. V. V. Sangha'S: "Solar Powered Airplanes"Prajwal UtturNo ratings yet
- Light Wave PropertiesDocument27 pagesLight Wave PropertiesDom Christian LastNo ratings yet
- Convection&RadiationDocument40 pagesConvection&RadiationdesdainedmanNo ratings yet
- Like Dissolves Like MeaningDocument1 pageLike Dissolves Like MeaningAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Atom Unit 3 GuideDocument3 pagesAtom Unit 3 GuideJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- FCAT Science Glossary Grade 8Document4 pagesFCAT Science Glossary Grade 8api-271960049No ratings yet
- 6.1 Working Principle of Equipment:: 6.2.1 Steady State Heat TransferDocument35 pages6.1 Working Principle of Equipment:: 6.2.1 Steady State Heat TransferAthar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy: Zainab Khalid (FA17-BPH-033) Sadia Tufail (FA17-BPH-067) DR - Shahid NazirDocument11 pagesSpectroscopy: Zainab Khalid (FA17-BPH-033) Sadia Tufail (FA17-BPH-067) DR - Shahid NazirBeenish HassanNo ratings yet
- The Diagram Below Shows The Structure of An Atom of Element XDocument6 pagesThe Diagram Below Shows The Structure of An Atom of Element XsharontaoNo ratings yet
- p-n Junction Diode OperationDocument6 pagesp-n Junction Diode OperationMuhamad Hanif RidhaNo ratings yet
- What Is Orgone EnergyDocument19 pagesWhat Is Orgone EnergyRadu Badoiu100% (2)
- Me 27 Ef - Fluid Mechanics/Hydraulics: W V m γ= mg ρg mDocument67 pagesMe 27 Ef - Fluid Mechanics/Hydraulics: W V m γ= mg ρg mJoseph NjugunaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics WorksheetDocument3 pagesDynamics Worksheetgirma workuNo ratings yet
- Earth MatDocument6 pagesEarth MatSmitha PatelNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Steady-State Circuits and AC PowerDocument27 pagesSinusoidal Steady-State Circuits and AC PowerRoaa almNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering-Octave LevenspielDocument24 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering-Octave Levenspielfekremariam AmbawNo ratings yet
- Electronics For Analog Signal Processing - K. Radhakrishna RaoDocument26 pagesElectronics For Analog Signal Processing - K. Radhakrishna RaoJULIAN MEJIANo ratings yet
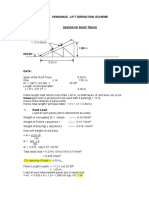
- Design of Roof TrussDocument25 pagesDesign of Roof TrusshemanatuNo ratings yet
- Ohiou1174932976 PDFDocument252 pagesOhiou1174932976 PDFChristian Camilo Romero VeraNo ratings yet
- MR DampersDocument6 pagesMR DampersAnupam SonarNo ratings yet
- Simple PendulumDocument32 pagesSimple PendulumGnana Vishnu Varma PothuriNo ratings yet
- Bachman Weber PDFDocument10 pagesBachman Weber PDFLeonor Braula ReisNo ratings yet