Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Inventory CH7
Inventory CH7
Uploaded by
notabilansfahrOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Inventory CH7
Inventory CH7
Uploaded by
notabilansfahrCopyright:
Available Formats
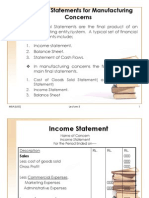
Inventory is assets held for sale or assets used to produce goods that will be sold as part of the
entity's normal business activities.
Raw materials The inputs into the production process. For example, raw materials inventory for a
furniture manufacturer includes wood used to build the furniture.
Work-in-process or WIP Inventory that is partially completed on the financial statement date. For a
car manufacturer, a partially completed car would be classified as WIP inventory.
Finished goods Inventory that has been completed and is ready for sale. Also, one entity's
inventory is another's equipment, and one entity's finished good is another's raw material. For example,
the ovens used to bake bread are equipment for the bakery but finished goods inventory to the company
that makes ovens. The flour and sugar used to make bread are the bakery's raw materials but finished
goods for the flour mill and the sugar refiner.
There are some important questions about accounting for inventory:
How should inventory be measured in financial statements?
What costs should be included in inventory?
How should inventory costs flow through the inventory account on the balance sheet to cost of goods
sold on the income statement?
What information should be disclosed?
Overhead is the costs in a manufacturing process other than direct labour and direct materials.
Overhead costs can be very difficult to associate directly with the product being made.
You might also like
- Manufacturing Accounts NotesDocument9 pagesManufacturing Accounts NotesFarrukhsg100% (5)
- Accounting For Manufacturing BusinessDocument56 pagesAccounting For Manufacturing Businessrajahmati_2890% (20)
- 03 Cost BehaviorDocument71 pages03 Cost BehaviorKrizah Marie CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Account MainDocument21 pagesManufacturing Account Mainlloydbwalya588No ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument12 pagesCost AccountingAntonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management AccountingDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Management AccountingnikkinikkzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document51 pagesChapter 19Yasir MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint - Cost AccountingDocument24 pagesPowerpoint - Cost AccountingDan RyanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing AccountsDocument6 pagesManufacturing Accountsdhanyasugukumar100% (2)
- Logistics23 B6 - Day4 - Types of InventoriesDocument24 pagesLogistics23 B6 - Day4 - Types of InventoriesmartinrecileNo ratings yet
- 5 Cost Accounting CycleDocument16 pages5 Cost Accounting CycleZenCamandang67% (3)
- Cost Classifications For Preparing External Financial StatementsDocument4 pagesCost Classifications For Preparing External Financial StatementsEduNo ratings yet
- Organ I GramaDocument11 pagesOrgan I Gramacristian jose espinel pedrazaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting and CostDocument19 pagesManagerial Accounting and CostIqra MughalNo ratings yet
- Accounting CH 4Document7 pagesAccounting CH 4sabit hussenNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - InventoriesDocument28 pagesCH 4 - InventoriesFarhadMohsinNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis Professor Julian Yeo: 1 You May Only Share These Materials With Current Term StudentsDocument32 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis Professor Julian Yeo: 1 You May Only Share These Materials With Current Term StudentsHE HUNo ratings yet
- Accounting 2Document4 pagesAccounting 2umar afzalNo ratings yet
- Int To Management AccDocument53 pagesInt To Management AccPUTTU GURU PRASAD SENGUNTHA MUDALIARNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Cost Accounting Cycle: 4.1 Difference Between Merchandising and Manufacturing OperationDocument13 pagesUnit 4: Cost Accounting Cycle: 4.1 Difference Between Merchandising and Manufacturing OperationCielo PulmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Updated Cost Accounting and Control by de LeonDocument6 pagesLecture Updated Cost Accounting and Control by de LeonwaddeornNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document51 pagesChapter 19Kanika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Accounting For InventoryDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Accounting For InventoryLee HailuNo ratings yet
- Cost Acc Chapter 3Document2 pagesCost Acc Chapter 3ElleNo ratings yet
- Inventory ManagementDocument11 pagesInventory Managementseathu07No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document29 pagesChapter 1MadCube gamingNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting: A Business PartnerDocument24 pagesManagement Accounting: A Business PartnerIsbah INo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - FinalDocument24 pagesChapter 16 - FinalMuhammad Saad UmarNo ratings yet
- MA CH 1 HighlightsDocument12 pagesMA CH 1 HighlightsnidaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Cost AcctgDocument34 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To Cost AcctgRovic OrdonioNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting RefresherDocument15 pagesCost Accounting Refresherfat31udm100% (1)
- 3.1v - Definitions and Costs Included in InventoriesDocument8 pages3.1v - Definitions and Costs Included in InventoriesMohammadreza ChangiziNo ratings yet
- Tugas Summary Bab 6Document11 pagesTugas Summary Bab 6Meirna LarasatiNo ratings yet
- Cost of Good Sold StatementDocument10 pagesCost of Good Sold Statementumar jilaniNo ratings yet
- Inventory and Warehousing ManagementDocument10 pagesInventory and Warehousing Managementshabeena shahNo ratings yet
- Chuong 1Document43 pagesChuong 1Phạm Thùy DươngNo ratings yet
- Uses of Product Cost Data Cost of Goods Sold and InventoriesDocument6 pagesUses of Product Cost Data Cost of Goods Sold and InventoriesNikki MendozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Cost Terms, Concepts and ClassificationsDocument72 pagesChapter Two: Cost Terms, Concepts and ClassificationsYuvaraj SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Final Accounts PDFDocument32 pagesChapter 4 Final Accounts PDFkamalkavNo ratings yet
- Inventory Valuation Methods: Treatment in Financial StatementDocument10 pagesInventory Valuation Methods: Treatment in Financial Statementneten_dkjNo ratings yet
- 10° AC Inventory Costing-1Document8 pages10° AC Inventory Costing-1celina lopezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document5 pagesAssignment 3Nabeel BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing AccountsDocument9 pagesManufacturing AccountsCrystal Johnson100% (1)
- These Are The Key Points You Should Know For Chapter 1Document7 pagesThese Are The Key Points You Should Know For Chapter 1Jane VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- What Is Included in Operating Income?: Sales - Cost of Goods Sold Gross ProfitDocument3 pagesWhat Is Included in Operating Income?: Sales - Cost of Goods Sold Gross ProfitUWatch TVNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Accounting For MFG-1Document9 pagesChapter Four Accounting For MFG-1History and EventNo ratings yet
- Journal Entries For ManufacturersDocument2 pagesJournal Entries For Manufacturersايهاب غزالةNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Accounting For Other BusinessDocument27 pagesChapter 5 Accounting For Other BusinessNUR IRDINA SOFEA MOHD YUSRINo ratings yet
- Framework Manufacturing Costs 2021Document13 pagesFramework Manufacturing Costs 2021Boi NonoNo ratings yet
- P2 Manufacturing Learning MaterialDocument5 pagesP2 Manufacturing Learning Materialchen.abellar.swuNo ratings yet
- Principles of Cost Accounting 14EDocument30 pagesPrinciples of Cost Accounting 14Etegegn mogessieNo ratings yet
- 04 Handout 115Document5 pages04 Handout 115Pearl Jade YecyecNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document13 pagesChapter 5abraha gebruNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Accounts Departmental 1Document12 pagesManufacturing Accounts Departmental 1nandarsoe105No ratings yet
- Ekotek Chapter 10Document9 pagesEkotek Chapter 10muhammad cayoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cost AccountingDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Cost AccountingKrazy ButterflyNo ratings yet
- Import Business: A Guide on Starting Up Your Own Import BusinessFrom EverandImport Business: A Guide on Starting Up Your Own Import BusinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)