0% found this document useful (0 votes)
111 views1 pageHypothesis Testing Overview
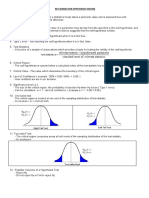
The document outlines the steps for hypothesis testing which include: 1) stating the null and alternative hypotheses; 2) selecting a significance level such as 0.05; 3) calculating the test statistic using a z-score or t-score formula; 4) determining the critical region based on the alternative hypothesis and distribution; 5) using the decision rule to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis based on where the test statistic falls relative to the critical value; and 6) stating the conclusion.
Uploaded by
calliepearsonCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
111 views1 pageHypothesis Testing Overview
The document outlines the steps for hypothesis testing which include: 1) stating the null and alternative hypotheses; 2) selecting a significance level such as 0.05; 3) calculating the test statistic using a z-score or t-score formula; 4) determining the critical region based on the alternative hypothesis and distribution; 5) using the decision rule to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis based on where the test statistic falls relative to the critical value; and 6) stating the conclusion.
Uploaded by
calliepearsonCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd