Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Water Filteration Is To Remove Impurities From Water by Means of A Fine Physical Barrier
Uploaded by
alyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Water Filteration Is To Remove Impurities From Water by Means of A Fine Physical Barrier
Uploaded by
alyCopyright:
Available Formats
A water filteration is to remove impurities from water by means of a fine
.physical barrier, a chemical process or a biological process
Water is filtered for many purposes like irrigation, drinking water,
.aquariums, ponds and swimming pools
A lot of techniques is used in water filteration process such as ,
,Distillation, Ion Exchange
.Carbon Adsorption and many other techniques
In this report , we are going to talk about the three techniques mentioned
over there
. Explaining how ,when and why each of it could be carried out
Distillation
.the oldest method of water purification
Water is first heated to boiling. Then the water vapor rises to a
condenser where cooling water lowers the temperature so the vapor
.is condensed, collected and stored
Most contaminants stay behind in the liquid phase vessel. However
there can sometimes be what is called carry-overs found in the
.distilled water
: Advantages
Removes a broad range of contaminants
Reusable
:
Disadvantages
Some contaminants can be carried into the condensate
Requires careful maintenance to ensure purity
Consumes large amounts of energy
System usually takes a large space on counter
Ion Exchange
The ion exchange process percolates water through bead-like
spherical resin materials (ion-exchange resins). Ions in the water are
exchanged for other ions fixed to the beads. The two most common
.ion-exchange methods are softening and deionization
Softening is used primarily as a pretreatment method to reduce
water hardness prior to reverse osmosis (RO) processing. The
softeners contain beads that exchange two sodium ions for every
.calcium or magnesium ion removed from the "softened" water
Deionization (DI) beads exchange either hydrogen ions for cations or
hydroxyl ions for anions. The cation exchange resins, made of
styrene and divinylbenzene containing sulfonic acid groups, will
exchange a hydrogen ion for any cations they encounter (e.g., Na+,
Ca++, Al+++). Similarly, the anion exchange resins, made of
styrene and containing quaternary ammonium groups, will exchange
a hydroxyl ion for any anions (e.g., Cl-). The hydrogen ion from the
cation exchanger unites with the hydroxyl ion of the anion
.exchanger to form pure water
:Advantages
Removes dissolved inorganics effectively.
Regenerable (service deionization).
Relatively inexpensive initial capital investment
:Disadvatages
Does not effectively remove particles, pyrogens or bacteria.
DI beds can generate resin particles and culture bacteria.
High operating costs over long-term.
Carbon Adsorption
Carbon absorption is a widely used method of home water filter
treatment because of its ability to improve water by removing
.disagreeable tastes and odors, including objectionable chlorine
Activated carbon effectively removes many chemicals and gases,
and in some cases it can be effective against microorganisms.
However, generally it will not affect total dissolved solids, hardness,
or heavy metals. Only a few carbon filter systems have been
.certified for the removal of lead, asbestos, cysts, and coliform
There are two types of carbon filter systems, each with advantages
and disadvantages: granular activated carbon, and solid block
.carbon
The carbon adsorption process is controlled by the diameter of the
pores in the carbon filter and by the diffusion rate of organic
.molecules through the pores
The rate of adsorption is a function of the molecular weight and the
.molecular size of the organics
Carbon is usually used in combination with other treatment
.processes
The placement of carbon in relation to other components is an
.important consideration in the design of a water purification system
:Advatages
Removes dissolved organics and chlorine effectively.
Long life (high capacity).
:Disadvantages
Adsorbent regeneration requiring a steam or vacuum source
Relatively high capital cost
You might also like
- Corrosion 2Document8 pagesCorrosion 2alyNo ratings yet
- Types of Trays The Packing MaterialDocument5 pagesTypes of Trays The Packing MaterialalyNo ratings yet
- PH Measurements ResultsDocument3 pagesPH Measurements ResultsalyNo ratings yet
- Determination of Emf by Compensation MethodDocument8 pagesDetermination of Emf by Compensation MethodalyNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Ebook - Proteus LibraryDocument67 pagesEbook - Proteus LibraryAkhmad GuiNo ratings yet
- A Proposed Model For Creep Relaxation of Soft Gaskets in Bolted Joints at Room TemperatureDocument6 pagesA Proposed Model For Creep Relaxation of Soft Gaskets in Bolted Joints at Room TemperatureSubhadip SadhukhanNo ratings yet
- Kurva-S Arjasa - 2020 FebruariDocument57 pagesKurva-S Arjasa - 2020 FebruariIshaqNo ratings yet
- Process Capability Study With MinitabDocument36 pagesProcess Capability Study With MinitabVishalNaranjeNo ratings yet
- Vembu Offsitedr Server WhitepaperDocument18 pagesVembu Offsitedr Server WhitepaperMotion InteractiveNo ratings yet
- Mobile JammerDocument14 pagesMobile Jammervivekanand_bonalNo ratings yet
- Correlations Between Lizard Cranial Shape and Diet: A Quantitative, Phylogenetically Informed AnalysisDocument34 pagesCorrelations Between Lizard Cranial Shape and Diet: A Quantitative, Phylogenetically Informed Analysisalexandra gonzalez castilloNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word Tips and Tricks To Increase ProductivityDocument16 pagesMicrosoft Word Tips and Tricks To Increase ProductivitySams RajaNo ratings yet
- Software ReliabilityDocument24 pagesSoftware ReliabilityNikhil DangiNo ratings yet
- HWY - AIR Brochure (Web)Document16 pagesHWY - AIR Brochure (Web)MudduKrishna shettyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 08Document22 pagesLecture 08Abdur RafayNo ratings yet
- 988H M&O ManualDocument170 pages988H M&O Manualr1p2100% (4)
- U2000 - General PunctuationDocument6 pagesU2000 - General PunctuationSándor NagyNo ratings yet
- SCINT 9181 4f LowendDocument152 pagesSCINT 9181 4f LowendImam BuchairiNo ratings yet
- Afcona - 6220 Tds EngDocument1 pageAfcona - 6220 Tds EngHamood AbdoNo ratings yet
- Scott Shenker Fundamental Design Issues of Future InternetDocument13 pagesScott Shenker Fundamental Design Issues of Future InternetSarah KhaleelNo ratings yet
- FAQ - How To Auto Approve Specific Override Raised Via IRIS APIDocument3 pagesFAQ - How To Auto Approve Specific Override Raised Via IRIS APIMrCHANTHANo ratings yet
- GD B Cheat SheetDocument6 pagesGD B Cheat SheetakhiyarwaladiNo ratings yet
- Sistem Thinking Dan Analisa Pengambilan KeputusanDocument47 pagesSistem Thinking Dan Analisa Pengambilan KeputusanyudiferiandiNo ratings yet
- 05 BOPF ActionsDocument27 pages05 BOPF ActionsKalikinkar LahiriNo ratings yet
- Operating Inistructions For The: Transistor Tester 22-024Document7 pagesOperating Inistructions For The: Transistor Tester 22-024P JNo ratings yet
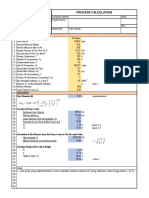
- Process Calculation: Flare Diameter (D)Document2 pagesProcess Calculation: Flare Diameter (D)kristian08No ratings yet
- Geochemist S Workbench Dongle Crack PDFDocument3 pagesGeochemist S Workbench Dongle Crack PDFJohnNo ratings yet
- Factorial DesignDocument30 pagesFactorial Designsarmiladz2077No ratings yet
- Ais For 9800Document32 pagesAis For 9800Macro LoveNo ratings yet
- Kony For SAP Tech Library 24.03Document2,352 pagesKony For SAP Tech Library 24.03suryananda sapbasis3No ratings yet
- Barriers and Isolators: AccessoriesDocument3 pagesBarriers and Isolators: Accessoriestidjani73No ratings yet
- Utilization of Ceramic Waste by Partial Replacement ofDocument12 pagesUtilization of Ceramic Waste by Partial Replacement ofDhandapany Arun50% (2)
- 1ST Quarterly Exam in MATH 10Document2 pages1ST Quarterly Exam in MATH 10Mariel PastoleroNo ratings yet
- Loading and HaulDocument27 pagesLoading and HaulAUGEN AMBROSENo ratings yet