Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8 - Signal Flow Diagram
Uploaded by
Moorthy Ganesan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views10 pagesThis document discusses signal flow diagrams as an alternative to block diagrams for representing systems. It explains how to convert block diagrams into equivalent signal flow graphs by:
1. Drawing signal nodes to represent system inputs and outputs.
2. Connecting the nodes with branches to show the flow of signals between systems.
3. Applying Mason's Rule to obtain a single transfer function from the signal flow graph.
Examples are provided for converting cascaded, parallel, and feedback block diagrams into their corresponding signal flow graph representations.
Original Description:
its from sum1 i knew
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses signal flow diagrams as an alternative to block diagrams for representing systems. It explains how to convert block diagrams into equivalent signal flow graphs by:
1. Drawing signal nodes to represent system inputs and outputs.
2. Connecting the nodes with branches to show the flow of signals between systems.
3. Applying Mason's Rule to obtain a single transfer function from the signal flow graph.
Examples are provided for converting cascaded, parallel, and feedback block diagrams into their corresponding signal flow graph representations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views10 pages8 - Signal Flow Diagram
Uploaded by
Moorthy GanesanThis document discusses signal flow diagrams as an alternative to block diagrams for representing systems. It explains how to convert block diagrams into equivalent signal flow graphs by:
1. Drawing signal nodes to represent system inputs and outputs.
2. Connecting the nodes with branches to show the flow of signals between systems.
3. Applying Mason's Rule to obtain a single transfer function from the signal flow graph.
Examples are provided for converting cascaded, parallel, and feedback block diagrams into their corresponding signal flow graph representations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
SIGNAL FLOW DIAGRAM
Objectives: Convert block diagrams, consisting of multiple
subsystems to signal flow graphs
Use Masons Rule to obtain a single transfer
function
Signal flow graphs are an alternative to
block diagrams
Consists only of branches, which
represent systems and nodes, which
represent signal
SIGNAL FLOW DIAGRAM
SIGNAL FLOW DIAGRAM
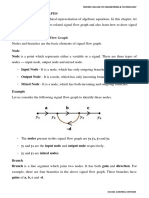
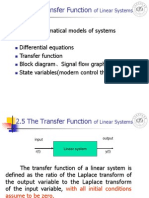
Figure (c) shows the interconnection
of the systems and the signals.
Each signal is the sum of signals
flowing into it.
For example: The signal V(s):
V ( s ) R1 ( s)G1 ( s ) R2G2 ( s) R3G3 ( s )
SIGNAL FLOW DIAGRAM
The signal C2(s):
C2 ( s ) V1 ( s )G5 ( s )
R1 ( s )G1 ( s )G5 ( s ) R2G2 ( s )G5 ( s ) R3G3 ( s )G5 ( s )
The signal C3(s):
C3 ( s ) V1 ( s )G6 ( s )
R1 ( s )G1 ( s )G6 ( s ) R2G2 ( s )G6 ( s ) R3G3 ( s )G6 ( s )
BLOCK DIAGRAM TO SIGNAL FLOW
GRAPH
Start by drawing the signal nodes for
the system.
Next, interconnect the signal nodes
with system branches.
BLOCK DIAGRAM TO SIGNAL FLOW
GRAPH
Cascaded Block Diagram
BLOCK DIAGRAM TO SIGNAL FLOW
GRAPH
Parallel block diagram
BLOCK DIAGRAM TO SIGNAL FLOW
GRAPH
Feedback Block Diagram
BLOCK DIAGRAM TO SIGNAL FLOW
GRAPH
Ex. 5.6 (Nise)
BLOCK DIAGRAM TO SIGNAL FLOW
GRAPH
You might also like
- Signals Flow GraphsDocument14 pagesSignals Flow GraphsMAFOQ UL HASSANNo ratings yet
- FME 326 - Module 5 - Signal Flow and Block Diagram ModelsDocument47 pagesFME 326 - Module 5 - Signal Flow and Block Diagram ModelsJesse Jon FerolinoNo ratings yet
- Block Reduction and Masons Rule - 1Document52 pagesBlock Reduction and Masons Rule - 1dedekNo ratings yet
- 6 - Signal Flow GraphsDocument59 pages6 - Signal Flow GraphsSuyash Dahake VlogsNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering MT-353: Signal Flow GraphsDocument21 pagesControl Engineering MT-353: Signal Flow GraphsTahaKhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Signal Flow GraphsDocument56 pagesLecture Signal Flow GraphsFahadKhNo ratings yet
- Signal Flow GraphDocument48 pagesSignal Flow GraphsufyanNo ratings yet
- 1509846749lecture 11. 2k14eee Signal Flow GraphDocument62 pages1509846749lecture 11. 2k14eee Signal Flow GraphAmin KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Signal FlowDocument60 pagesUnit1 Signal FlowPrasidha PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Mec500 Chapter 2 - AtmaDocument31 pagesMec500 Chapter 2 - AtmaFaez FeakryNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Theory: Reduction of Multiple Subsystems STB 35103Document45 pagesControl Systems Theory: Reduction of Multiple Subsystems STB 35103Akula VeerrajuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document60 pagesLecture 10Dilshad CiziriNo ratings yet
- Blok DiagramDocument43 pagesBlok DiagramBagoessngenger DwiNo ratings yet
- Lesson M3a Signal Flow Graphs Block DiagramsDocument30 pagesLesson M3a Signal Flow Graphs Block DiagramsAsif NoorNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Control Systems (BCS) : Module Leader: DR Muhammad ArifDocument31 pagesBiomedical Control Systems (BCS) : Module Leader: DR Muhammad ArifBhavik PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Control Chapter 3 Signal Flow - Lecture 4Document42 pagesControl Chapter 3 Signal Flow - Lecture 43re0oooNo ratings yet
- 33333CON1 (Signal Flow Graph)Document60 pages33333CON1 (Signal Flow Graph)Ahmed JamalNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Signal Flow GraphDocument33 pages1.3 Signal Flow Graphearnest normanNo ratings yet
- Rohini 27072873676Document7 pagesRohini 27072873676VIKASH YADAVNo ratings yet
- lecture - 5-2 - signal - flow - graphs المنهج PDFDocument60 pageslecture - 5-2 - signal - flow - graphs المنهج PDFTariq ZeyadNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 Signal Flow Graphs and Mason, S RuleDocument27 pagesLecture 13 Signal Flow Graphs and Mason, S RuleHamza KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Block DiagramDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Block DiagramAini SalwaNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Theory: Introduction To Block DiagramDocument47 pagesControl Systems Theory: Introduction To Block DiagramFadly ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Analysis of Digital Control SystemsDocument68 pagesModeling and Analysis of Digital Control SystemsRonald GeorgeNo ratings yet
- SFG 2Document14 pagesSFG 2Emmanuel AmoakoNo ratings yet
- Feedback and Control System: Signal Flow GraphsDocument59 pagesFeedback and Control System: Signal Flow GraphsBenj MendozaNo ratings yet
- CISE302 Linear Control Systems: Blok Diagram and Signal Flow and State Space Modeling Dr. Amar KhoukhiDocument56 pagesCISE302 Linear Control Systems: Blok Diagram and Signal Flow and State Space Modeling Dr. Amar Khoukhisubbu2051No ratings yet
- Transfer Functions, Block Diagram and Signal Flow Graph (Week 2 & 3)Document17 pagesTransfer Functions, Block Diagram and Signal Flow Graph (Week 2 & 3)Wan TingNo ratings yet
- Block Diagrams and Signal Flow Graphs: Lesson PlanDocument23 pagesBlock Diagrams and Signal Flow Graphs: Lesson PlanVARUN B MNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Theory: Reduction of Multiple Subsystems STB 35103Document45 pagesControl Systems Theory: Reduction of Multiple Subsystems STB 35103Ayub Abd RahmanNo ratings yet
- B - Lecture3 The Transfer Function and Block Diagram Automatic Control SystemDocument21 pagesB - Lecture3 The Transfer Function and Block Diagram Automatic Control SystemAbaziz Mousa OutlawZz100% (1)
- Lecture Part3Document11 pagesLecture Part3محمد عقيل عبد الامير ستارNo ratings yet
- Signal Fow GraphDocument14 pagesSignal Fow GraphLalith AbhiramNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5-2 Signal Flow Graphs PDFDocument60 pagesLecture 5-2 Signal Flow Graphs PDFالبياتي محمدNo ratings yet
- Overview of Signal Flow GraphsDocument45 pagesOverview of Signal Flow GraphsFahmeed Ali MeoNo ratings yet
- Introduction Signal Flow Graphs: Samuel Jefferson MasonDocument33 pagesIntroduction Signal Flow Graphs: Samuel Jefferson MasonAniket KumarNo ratings yet
- Signal Flow DiagramsDocument20 pagesSignal Flow DiagramsSingappuliNo ratings yet
- Hanani Abd Wahab BDA 3073 16 July 2008Document34 pagesHanani Abd Wahab BDA 3073 16 July 2008Hafzal GaniNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics Applications of Computer Graphics: Input DevicesDocument21 pagesComputer Graphics Applications of Computer Graphics: Input DevicesLeela PallavaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Switched-Mode Converter Modeling Using MATLAB/SimulinkDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Switched-Mode Converter Modeling Using MATLAB/SimulinkAhana MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram Algebra in Control Systems - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument6 pagesBlock Diagram Algebra in Control Systems - GATE Study Material in PDFPraveen AgrawalNo ratings yet
- W EE 418 - Lecture 3 Block Diagram and Signal Flow GraphDocument32 pagesW EE 418 - Lecture 3 Block Diagram and Signal Flow GraphGGAP LASTNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Mathematical Modeling of Dynamic SystemDocument56 pagesChapter 2 Mathematical Modeling of Dynamic SystemAmanuel AsfawNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document37 pagesChapter 3Izzat AiresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - SFG and Masons RuleDocument23 pagesChapter 3 - SFG and Masons Rulevenosyah devanNo ratings yet
- 003 ME31002 - Block Diagram-2021febDocument54 pages003 ME31002 - Block Diagram-2021febShek Yu LaiNo ratings yet
- BlockDiagram and Signal Flow GraphsDocument29 pagesBlockDiagram and Signal Flow GraphsDienies TorresNo ratings yet
- UNIT 5 Session 6Document67 pagesUNIT 5 Session 6rocklinetoNo ratings yet
- l03 BackgroundDocument13 pagesl03 BackgroundDineshNewalkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Reduction of Multiple SystemDocument22 pagesChapter 2 - Reduction of Multiple SystemMustafa ManapNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Signal Flow Graph (SFG) : Samuel Jefferson MasonDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Signal Flow Graph (SFG) : Samuel Jefferson MasonSirshenduNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document14 pagesLecture 2Abdullah Mohammed AlsaadouniNo ratings yet
- M9 - Ch-5 - Reduction of Multiple Subsystems-Part-2 (D)Document68 pagesM9 - Ch-5 - Reduction of Multiple Subsystems-Part-2 (D)Shuvro Sankar SenNo ratings yet
- Detailed RoutingDocument57 pagesDetailed RoutingurajeshNo ratings yet
- MEC522 Chapter 2 - StudentDocument60 pagesMEC522 Chapter 2 - Studentazim khanafiahNo ratings yet
- Block Diagrams Control SystemsDocument25 pagesBlock Diagrams Control SystemsSingappuliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Reduction of Multiple SystemDocument46 pagesChapter 2 - Reduction of Multiple SystemHaqeemee HusseinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document24 pagesLecture 2iptradersNo ratings yet
- Power Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignFrom EverandPower Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignBruno AllardNo ratings yet
- Topographical Tools for Filtering and Segmentation 2: Flooding and Marker-based Segmentation on Node- or Edge-weighted GraphsFrom EverandTopographical Tools for Filtering and Segmentation 2: Flooding and Marker-based Segmentation on Node- or Edge-weighted GraphsNo ratings yet
- External Gear Pump Parameter Calculation Sheet: 2.972 Understanding How Things WorkDocument3 pagesExternal Gear Pump Parameter Calculation Sheet: 2.972 Understanding How Things WorkMoorthy GanesanNo ratings yet
- Sankyu (M) SDN BHD: in Case of EmergencyDocument4 pagesSankyu (M) SDN BHD: in Case of EmergencyMoorthy GanesanNo ratings yet
- Synn Fast Link SDN BHD: Company ProfileDocument2 pagesSynn Fast Link SDN BHD: Company ProfileMoorthy GanesanNo ratings yet
- Examples of Synthetic Plant Hormones and Their Role in Growth and DevelopmentDocument7 pagesExamples of Synthetic Plant Hormones and Their Role in Growth and DevelopmentMoorthy GanesanNo ratings yet
- MyClear - FPXDocument1 pageMyClear - FPXMoorthy GanesanNo ratings yet
- 7 November 2013Document1 page7 November 2013Moorthy GanesanNo ratings yet
- 1 ErsDocument1 page1 ErsMoorthy GanesanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank EORweDocument1 pageQuestion Bank EORweMoorthy GanesanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document9 pagesChapter 2Moorthy GanesanNo ratings yet