Professional Documents
Culture Documents
10slidessms-SMS Message Flow - Medium
10slidessms-SMS Message Flow - Medium
Uploaded by
AusOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
10slidessms-SMS Message Flow - Medium
10slidessms-SMS Message Flow - Medium
Uploaded by
AusCopyright:
Available Formats
SMS
The Telecom Source
10 Slide Technology Series
Telecom Source Consulting Inc.
www.thetelecomsource.com | 905-854-5400
Introduction
SMS stands for Short Message Service
SMS was first introduced in 1991 in Europe as a text messaging service based on European
Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) standards for mobile networks
SMS is being used in a wide range of social and business applications such as electronic voting,
delivery of stock quotations, delivery of e-mail notification
SMS is currently supported on the major mobile network technologies including:
GSM (Global System for Mobile communications)
GPRS (General Packet Radio Service)
CDMA (Carrier Division Multiplex Access)
SMS supports the sending and receiving of text, images, animation and sound
SMS messages are originated and received by Short Messaging Entities (SME). Examples of SMEs
are: mobile phones; servers; personal computers
Basic Network Architecture
SME
SMSC
SMS-GMSC/
SMS-IWMSC
MSC/SGSN
MS
Outside the scope
of GSM specifications
HLR
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
VLR
Short Message Entity (SME) sends or receives short messages
Short Message Service Centre (SC) stores-and-forwards messages between the SME and the MS
Gateway MSC For Short Message Service (SMS-GMSC) - receives messages from the SC, interrogates the HLR for
routing information and forward the messages to the MSC or SGSN
Home Location Register (HLR) - a database used for permanent storage and management of
user/subscriber profiles
Inter-Working MSC For Short Message Service (SMS-IWMSC) - receives messages from the MSC or SGSN and forwards
them to the SC
Mobile Service Centre (MSC) performs switching functions for mobile stations in a geographical area
Visitor Location Register (VLR) - a database that contains temporary information about roaming subscribers.
The MSC and the VLR are always on the same platform.
Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) performs packet switching functions for mobile stations in a geographical area.
The SGSN is used instead of the MSC when SMS info is transferred over GPRS.
Mobile Station (MS) a device on the mobile network capable of receiving and sending short messages
SMS Protocol Services and Features
SMS is a point-to-point store and forward technology with 2 basic services:
Short Message Mobile Terminated (SM-MT) - to transmit a message from the short message
service centre to the mobile station. SMS-DELIVER PDU (Protocol Data Unit)
Short Message Mobile Originated (SM-MO) to transmit a message from mobile station to
service centre SMS-SUBMIT PDU
SMS allows message delivery to handsets either active/in-use or powered off
Mobile stations receive transport data protocol units (TPDU) denoted as SMS-Deliver
Mobile stations send transport data protocol units (TPDU) denoted as SMS-Submit
Note: the TPDU contains the user data (the short message)
SMS protocol permits request of message delivery confirmation report
SMS messages contain up to 140 octets which is equivalent to:
160 Latin characters (7 Bit Coding) Text Mode
70 Unicode characters (double byte) e.g. Arabic Characters, Chinese Characters
SMS messages can also contain up to 140 octets of binary information
SMS messages are transported in the core network using SS7 (Signaling System 7)
SMS Service Elements
Validity Period is the service element that indicates the time period for which the SMSC will
guarantee the existence of the short message when attempting to deliver it
Service Centre Time Stamp is the service element that indicates the time stamp of message
arrival at the SMSC
Protocol Identifier is the service element in to indicate higher layer protocol or indicates interworking with certain types of telemetic services (e.g. paging, email)
More Messages to Send is the service element by which a SMSC informs the MS that there is
one or more messages waiting in the SC to be sent to the MS
Priority is the service element indicating that delivery of the message will be attempted
regardless of the MS being temporarily absent or having no free memory
Message Waiting is the service element that enables the mobile network to provide the HLR,
SGSN and VLR with the information that there is a message waiting in the originating SMSC for a
MS
Alert Service Centre is the service element used by mobile networks to inform an SMSC that a
previously unreachable MS (temporarily absent or no memory) is ready to receive messages
SM-MT Service SMS-Deliver TPDU Structure
1-10 Octets
1 Octet
2-12 Octets
PDUType
SCA
1 Octet
1 Octets
7 Octets
1 Octet
0-140 Octets
PID
DCS
SCTS
UDL
UD
OA
PDU Type:
7
RP
UDHI
SRI
2
MMS
Parameter
SCA
PDU Type
RP
UDHI
Bits
MTI
Description
Service Centre Address - Telephone number of the Service Centre
Protocol Data Unit Type
Reply Path - Parameter indicating that Reply Path exists
User Data Header Indicator - Parameter indicating that UD field contains a header
SRI
Status Report Indication - Parameter indicating if the SME has requested a status report
MMS
More Messages to Send - Parameter indicating whether or not there are more messages to send
MTI
Message Type Indicator - Parameter describing the message type 00 means SMS-Deliver
OA
Originator Address - Address of the originating SME
PID
Protocol Identifier - Parameter indicating the SMSC how to process the Short Message (e.g. Fax)
DCS
Data Coding Scheme - Parameter identifying the coding scheme within the User Data (UD)
SCTS
Service Centre Time Stamp - Parameter identifying the time when the SMSC received the message
UDL
User Data Length - Parameter indicating the length of the UD-field
UD
User Data - Data Field of the Short Message
MTI bit 1 = 0
bit 0 = 0
SM-MO Service SMS-Submit TPDU Structure
1-10 Octets
1 Octet
1 Octet
2-12 Octets
1 Octet
1 Octets
0, 1 or 7 Octets
1 Octet
0-140 Octets
SCA
PDUType
MR
DA
PID
DCS
VP
UDL
UD
PDU Type:
7
RP
UDHI
SRR
VPF
2
RD
Parameter
SCA
PDU Type
RP
Bits
MTI
Description
Service Centre Address - Telephone number of the Service Centre
Protocol Data Unit Type
Reply Path - Parameter indicating that Reply Path exists
UDHI
User Data Header Indicator - Parameter indicating that UD field contains a header
SRR
Status Report Request - Parameter indicating if the MS has requested a status report
VPF
Validity Period Format - Parameter indicating whether or not the VP field is present
RD
Reject Duplicates parameter indicating if SMSC will accept a message with same MR and DA from the same OA
MTI
Message Type Indicator - Parameter describing the message type 01 means SMS-Submit
MR
Message Reference - Successive numbers (0255) of all SMS-SUBMIT frames sent by the MS.
DA
Destination Address - Address of the destination SME
PID
Protocol Identifier - Parameter indicating the SMSC how to process the Short Message (e.g. Fax)
DCS
Data Coding Scheme - Parameter identifying the coding scheme within the User Data (UD)
SCTS
Service Centre Time Stamp - Parameter identifying the time when the SMSC received the message
UDL
User Data Length - Parameter indicating the length of the UD-field
UD
User Data - Data Field of the Short Message
MTI bit 1 = 0
bit 0 = 1
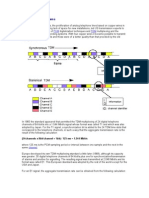
Message Flow SM-MT
SMSC
GMSC
HLR
MSC
VLR
MS
Message
Transfer
sendRoutingInfoForShortMsg
forwardShortMessage
sendInfoForMT-SMS
Page
Authenticate
Deliver Report
Message Transfer
SM-Delivery
Delivery
ReportStatus
Report
Note: ETSI/GSM MAP sendRoutingInforForShortMsg equivalent in IS41 (North American standard) is SMSrequest
mechanism, while forwardShortMessage is Short Message Delivery-Point-to-Point (SMD-PP)
Message Flow SM-MO
SMSC
SMSIWMSC
HLR
MSC
VLR
MS
Access Request
Authenticate
Message Transfer
sendInfoForforwardShortMessage
MO-SMS
Message
Transfer
Delivery
Report
Delivery Report
Delivery
Report
Note: ETSI/GSM MAP forwardShortMessage equivalent in IS41 (North American Standard) is Short Message
Delivery-Point-to-Point (SMD-PP) mechanism
Short Message Service Centre - SMSC
Short Message service Centre plays a central role in the management of SMS message
origination and SMS message delivery
Interestingly, detailed functionality of SMSC is outside the scope of standardization, hence several
vendor specific products and protocols:
EMI (External Machine Interface) CMG, now LogicaCMG
UCP (Universal Computer Protocol) Logica, now LogicaCMG
CIMD (Computer Interface to Message Distribution) Nokia
OIS (Open Interface Specification) SEMA Group, now Airwide Solutions
Computer Access Service and Protocol Ericsson
SMS Forum is an industry initiative to create a common standard SMPP (Short Message Peerto-Peer) using Internet as the transport network
The ETSI/GSM standard does specify minimum mandatory SMSC requirements:
Each SMS-Deliver to a MS must have unique time stamp with one second accuracy
Only one outstanding SMS-Deliver (i.e. message for which a report not yet received)
If requested by MS or SME, initiate overwriting of previously received short messages
Additional Features and Issues
SMS standard allows concatenation of messages to enable transmission of longer messages (i.e.
messages longer than 140 octets)
Short Messages may be compressed with algorithms described in GSM 03.42
Compression only applies to user-data and excludes user-data-header
If compressed message are greater than 140 octets, then the messages can be concatenated
In North America wireless subscribers can address text messages using 5-digit numbers (short codes)
An example of the use of short codes is for SMS voting
One objective of short codes is to reduce or minimize Spam
Short codes are being used to price and market services (e.g charge back to application provider)
Service gateway products are available that address multi-network (GSM/CDMA) and multi-protocol
(e.g. EMI/OIS) inter-working
Security is an emerging concern similar to that with e-mail, for example:
SPAM sending of unsolicited messages and ads via SMS (e.g. to entice users to call numbers
that have a high per minute charge)
Virus - resend of message to all numbers in the phones address book (e.g. via a Trojan Horse)
Identity Theft - retrieval of personal information from a SIM (Subscriber Interface Module) card
Telecom Source Consulting Inc.
www.thetelecomsource.com
info@thetelecomsource.com
You might also like
- Telecom Basics: E1 Voice Theorm ErlangDocument23 pagesTelecom Basics: E1 Voice Theorm ErlangCheikh Ahmet Tidiane DiengNo ratings yet
- Configuration MOP Aircel ICRDocument7 pagesConfiguration MOP Aircel ICRKaran ParmarNo ratings yet
- Wireless Short Message Service (SMS) TutorialDocument9 pagesWireless Short Message Service (SMS) TutorialItzik IfrachNo ratings yet
- SmsDocument4 pagesSmsmberege1991No ratings yet
- SMS DocumentDocument80 pagesSMS Documentvetonim47No ratings yet
- MOBILINK - Trainnig Workshop For Optimization GSM BASICDocument89 pagesMOBILINK - Trainnig Workshop For Optimization GSM BASICAli MurtazaNo ratings yet
- NSN - GSM ArchitectureDocument23 pagesNSN - GSM ArchitectureChidhuro OwenNo ratings yet
- SMS Flow - Aditya GhaiDocument5 pagesSMS Flow - Aditya Ghaiunme_11No ratings yet
- Sigtran Connectuon by CiscoDocument75 pagesSigtran Connectuon by CiscoKomunitasGerakanCintaJagapuraNo ratings yet
- 2G SMS FlowDocument37 pages2G SMS FlowShaharyar KhanNo ratings yet
- TCAP - Transaction Capabilities Application Part Is Used byDocument7 pagesTCAP - Transaction Capabilities Application Part Is Used byramarneh100% (1)
- SGSN Commands Global Title TranslationDocument4 pagesSGSN Commands Global Title TranslationChristopher NicholsNo ratings yet
- IS-54 Dan IS-136Document29 pagesIS-54 Dan IS-136hasbiiie100% (1)
- Insert Subscriber Data (Isd)Document28 pagesInsert Subscriber Data (Isd)Santosh NayakNo ratings yet
- CDR RolloutDocument38 pagesCDR RolloutmbhagavanprasadNo ratings yet
- Alcatel BSC Counters Catalogue - B10Document631 pagesAlcatel BSC Counters Catalogue - B10SamiNo ratings yet
- GSM Basics Call FlowsDocument56 pagesGSM Basics Call Flowskguru2807No ratings yet
- Protocol BroucherDocument11 pagesProtocol Brouchermanojsingh474No ratings yet
- Signalling Training IuPs v4Document51 pagesSignalling Training IuPs v4mainmemNo ratings yet
- Admission Control in GPRS-EDGEDocument10 pagesAdmission Control in GPRS-EDGEVivek UttamNo ratings yet
- SIGTRANDocument57 pagesSIGTRANRaghav ReddyNo ratings yet
- Home Location RegisterDocument30 pagesHome Location RegistermushishinaNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Networks (In) and CAMELDocument11 pagesIntelligent Networks (In) and CAMELnaggu1983No ratings yet
- QoS LTE IEEE16mDocument16 pagesQoS LTE IEEE16mBityong Yusuf AutaNo ratings yet
- Chap 2. LTE Channel Structure .EngDocument57 pagesChap 2. LTE Channel Structure .Engaudi_r8No ratings yet
- GSM Mobile Terminated CallDocument2 pagesGSM Mobile Terminated CallE-Trần CmNo ratings yet
- Signalling and Control in GSMDocument22 pagesSignalling and Control in GSMFebri DoangNo ratings yet
- Call FlowDocument30 pagesCall Flownaveedraza4213No ratings yet
- IR.34-V9.1 - Guidelines For IPX Provider Networks (Previously Inter-Service Provider IP Backbone Guidelines)Document50 pagesIR.34-V9.1 - Guidelines For IPX Provider Networks (Previously Inter-Service Provider IP Backbone Guidelines)a_big_friendNo ratings yet
- CCS7 (Common Channel Signaling Number 7)Document16 pagesCCS7 (Common Channel Signaling Number 7)Michella Y0% (1)
- Figure: Transcoder Free Operation (Trfo)Document5 pagesFigure: Transcoder Free Operation (Trfo)aqahmedNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication SystemsDocument136 pagesMobile Communication SystemsJoseph JeremyNo ratings yet
- M3UA Message Classes and Types:: Management (MGMT) Messages Transfer MessagesDocument8 pagesM3UA Message Classes and Types:: Management (MGMT) Messages Transfer MessagesSaurabh BarabdeNo ratings yet
- UMTS Presentation EricssonDocument45 pagesUMTS Presentation EricssonDev SinghNo ratings yet
- 5282.SMS Over M2PA Lab Instructions PDFDocument4 pages5282.SMS Over M2PA Lab Instructions PDFAhmed SharifNo ratings yet
- 10WG001207 Interworking With MSC Server Data Configuration ISSUE 1.0Document19 pages10WG001207 Interworking With MSC Server Data Configuration ISSUE 1.0Mohamed H. GooniNo ratings yet
- GSM Word FileDocument11 pagesGSM Word FileevilanubhavNo ratings yet
- Generic Mediation DeviceDocument33 pagesGeneric Mediation DeviceAnonymous sHbFhuzNo ratings yet
- BSNL MNP Call FlowsDocument34 pagesBSNL MNP Call FlowsdharamNo ratings yet
- HLR Interface - CFUDocument17 pagesHLR Interface - CFUpoppy tooNo ratings yet
- LTE White PaperDocument0 pagesLTE White PaperkidreckNo ratings yet
- MTP3 & M3uaDocument40 pagesMTP3 & M3uaduranga1988No ratings yet
- TK150 Rel 45 - SG - v1.0.Document136 pagesTK150 Rel 45 - SG - v1.0.Fred_SPbNo ratings yet
- How To Read SIP TracesDocument4 pagesHow To Read SIP TracesZeeshan DawoodaniNo ratings yet
- VOIP Roaming Call PricesDocument83 pagesVOIP Roaming Call PricesVOIP RoamingNo ratings yet
- GSMDocument12 pagesGSMTanveer MehdiNo ratings yet
- T1 and E1 PCM SystemsDocument10 pagesT1 and E1 PCM SystemsPrafull BNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Traffic SteeringDocument2 pagesIntelligent Traffic SteeringmuradghaziNo ratings yet
- User Plane RoutingDocument96 pagesUser Plane RoutingLuca Siddhartha100% (1)
- GPRS For 2 Hours TrainingDocument105 pagesGPRS For 2 Hours Trainingh_hadidiNo ratings yet
- Presentation On: Rajat Singla It-B 274109Document25 pagesPresentation On: Rajat Singla It-B 274109Garima KapoorNo ratings yet
- EIGRPDocument102 pagesEIGRPNguyễn Mạnh ThếNo ratings yet
- 411 9001 213 - 18.06 - Fundamentals bts9000Document162 pages411 9001 213 - 18.06 - Fundamentals bts9000Garry LiuNo ratings yet
- A5 3 Ciphering PDFDocument16 pagesA5 3 Ciphering PDFmudassar2k4No ratings yet
- 32426-c00 - EPC KPIsDocument84 pages32426-c00 - EPC KPIsbhushan7408No ratings yet
- NokiaDocument40 pagesNokiasooriyakrishnaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Cellular Network Planning and Optimisation: 2G/2.5G/3G... Evolution to 4GFrom EverandFundamentals of Cellular Network Planning and Optimisation: 2G/2.5G/3G... Evolution to 4GNo ratings yet