Professional Documents
Culture Documents
10 Elasticities
Uploaded by
Anonymous RnapGaSIZJOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
10 Elasticities
Uploaded by
Anonymous RnapGaSIZJCopyright:
Available Formats
Finding Elasticities
Definitions
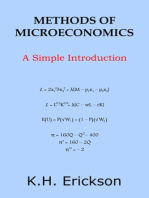
If the demand for good 1 is x1 (p2 , p2 , m) where p1 and p2 are prices and m is
income the own price elasticity of demand is defined as
x1 p1
.
p1 x1
This is the limit of the
proportional change in quantity
proportional change in price
as the change in price becomes smalller and smaller. As the proportional change
does not depend on the units in which something has been measured so has no
units elasticity also does not depend on units.
The income elasticity of demand measures the eect of changes in income
on demand. It is
x1 m
.
m x1
The cross price elasticity of demand measures the eect of changes in
one price on demand for another. Where there are two goods the cross price
elasticity of demand for good 1 is
x1 p2
.
p2 x1
Example
Given a demand function elasticity should be expressed in terms of p1 , p2 and
m. If demand for good 1 is
x1 (p2 , p2 , m) =
then
and
so
2m
5 p1
x1
2m
= 2
p1
5 p1
x1
1
=
p1
p1
2m
5 p1
p1
5 p21
=
x1
2m
2m
5 p21
so the own price elasticity of demand is
2
2m
5 p1
x1 p1
=
= 1.
2
p1 x1
5 p1
2m
Similarly if
2m
5 p1
x1 (p2 , p2 , m) =
then
and
x1
2 1
=
m
5 p1
x1
1
=
m
m
so
2m
5 p1
2 1
5 p1
5
m
= p1
x1
2
so the income elasticity of demand for good 1
2 1
5
x1 m
=
p1 = 1.
m x1
5 p1
2
If
x1 (p2 , p2 , m) =
then
and
so
2m
5 p1
x1
=0
p2
1
x1
=
p2
p2
2m
5 p1
2 m
5 p1 p2
5 p1 p2
p2
=
x1
2 m
so the cross price elasticity of demand is
5 p1 p2
x1 p2
=0
= 0.
p2 x1
2 m
You might also like
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument18 pagesElasticity of Demand and SupplyMochimNo ratings yet
- Demand ExamplesDocument7 pagesDemand ExampleskittuNo ratings yet
- The Slutsky EquationDocument10 pagesThe Slutsky Equationsergio camperoNo ratings yet
- 8 TopicsinConsumerBehaviour PDFDocument20 pages8 TopicsinConsumerBehaviour PDFAnshu JainNo ratings yet
- ECON 201 Lecture 1Document21 pagesECON 201 Lecture 1SquishyPoopNo ratings yet
- Economics 401 The Choice-Based ApproachDocument3 pagesEconomics 401 The Choice-Based ApproachGD AminNo ratings yet
- Assinment 1Document8 pagesAssinment 1suhaspujari93No ratings yet
- Elasticity of Substitutionrevised - TexDocument12 pagesElasticity of Substitutionrevised - TexRodrigoOdónSalcedoCisnerosNo ratings yet
- Mathimatical For Econo UNIT 2Document22 pagesMathimatical For Econo UNIT 2Sitra AbduNo ratings yet
- Deriving Demand Functions ExamplesDocument8 pagesDeriving Demand Functions ExamplesKanika MahajanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - ElasticityDocument5 pagesLecture Notes - ElasticityRizwan KhanNo ratings yet
- Point Elasticity vs. Midpoint/Arc Elasticity: Elasticity Percent Change Quantity Percent Change PriceDocument3 pagesPoint Elasticity vs. Midpoint/Arc Elasticity: Elasticity Percent Change Quantity Percent Change PriceJing SongNo ratings yet
- Economics 101: Introductory Microeconomics Fall 2012Document3 pagesEconomics 101: Introductory Microeconomics Fall 2012Falmeta EliyasNo ratings yet
- Varian - Chapter06 - Demand - Properties of Demand FunctionsDocument14 pagesVarian - Chapter06 - Demand - Properties of Demand FunctionsBella NovitasariNo ratings yet
- Slutsky TheoremDocument14 pagesSlutsky TheoremSHRESTHA AGRAWAL 2337059No ratings yet
- Slutsky EquationDocument8 pagesSlutsky EquationYiyao100% (1)
- Micro Formula SheetDocument2 pagesMicro Formula SheetMC BulletproofNo ratings yet
- DemandDocument54 pagesDemandjamesyuNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument38 pagesElasticityNizhum FarzanaNo ratings yet
- M P P P F X: Demand Functions and ElasticityDocument18 pagesM P P P F X: Demand Functions and ElasticityDevansh SodhiNo ratings yet
- Economics NotesDocument71 pagesEconomics NotesUmer PrinceNo ratings yet
- ELASTICITYDocument17 pagesELASTICITYlemma4aNo ratings yet
- Managerial Economics (M.com IVth Sem.) - L5 14-4Document8 pagesManagerial Economics (M.com IVth Sem.) - L5 14-4Govinda RajuNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics: Chapter 6 DemandDocument5 pagesMicroeconomics: Chapter 6 DemandRulojyNo ratings yet
- 8.3.6 - Elasticity of DemandDocument3 pages8.3.6 - Elasticity of DemandJunior PyareNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand and SupplyDocument38 pagesElasticity of Demand and SupplyJoe BannerNo ratings yet
- ElasticityDocument58 pagesElasticityAryan AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Elasticities of DemandDocument13 pagesElasticities of DemandMeharunnessa AkifaNo ratings yet
- Econ11 09 Handout4 PDFDocument23 pagesEcon11 09 Handout4 PDFkwameNo ratings yet
- Tugas Ekonomi MakroDocument2 pagesTugas Ekonomi MakroSelvi MomentNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand ECODocument45 pagesElasticity of Demand ECOYash TRIPATHINo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Managerial EconomicsDocument50 pagesChapter 3 Managerial EconomicsMahmoud KassemNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Part 2 Consumer Choice PT 1 Consumer Theory and Budget ConstraintDocument27 pagesLecture 1 Part 2 Consumer Choice PT 1 Consumer Theory and Budget ConstraintToshia Mc DonaldNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six: DemandDocument120 pagesChapter Six: DemandAtif AslamNo ratings yet
- Econ11 09 Handout4 PDFDocument23 pagesEcon11 09 Handout4 PDFAshley BobNo ratings yet
- Elasticities PDFDocument1 pageElasticities PDFVibhu VishwakrmaNo ratings yet
- Vandermonde DeterminantsDocument8 pagesVandermonde DeterminantsAmada LopezNo ratings yet
- Elasticity ConceptDocument35 pagesElasticity Conceptsomera kcNo ratings yet
- Elasticity - II BBA, BCIS ModifiedDocument36 pagesElasticity - II BBA, BCIS ModifiedSubrat PantaNo ratings yet
- Pseudo PrimesDocument10 pagesPseudo PrimesyeshaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Elasticity of DemandDocument30 pagesLecture 4 Elasticity of DemandHendrix NailNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of DemandDocument3 pagesElasticity of DemandPrianshu BagNo ratings yet
- Elasticity: The Degree To Which Individuals, Consumers or Producers Change TheirDocument8 pagesElasticity: The Degree To Which Individuals, Consumers or Producers Change TheirZamalek NewsNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand For BBADocument82 pagesElasticity of Demand For BBAinfinity warzNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Demand SupplyDocument65 pagesElasticity of Demand SupplyAkarsh BhattNo ratings yet
- The Concept of elasticity-Module3-gINADocument8 pagesThe Concept of elasticity-Module3-gINAshekNo ratings yet
- CU Ecoh Demand and Supply Part BDocument40 pagesCU Ecoh Demand and Supply Part BDr.S.MaitraNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines and Functions Lec. 5 A ClassDocument4 pagesStraight Lines and Functions Lec. 5 A ClassSuman Samal MagarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15: Competitive Equilibrium in A Pure Exchange EconomyDocument6 pagesLecture 15: Competitive Equilibrium in A Pure Exchange Economyamrith vardhanNo ratings yet
- Price Elasticity of DemandDocument5 pagesPrice Elasticity of DemandAymanTounsiNo ratings yet
- Elasticity of Supply and DemandDocument17 pagesElasticity of Supply and DemandArianne Joy ViñegasNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Lecture 5Document52 pagesMicroeconomics Lecture 5Megumi TsuchiyaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document40 pagesTopic 3Minato MeaNo ratings yet
- Elasticities of DemandDocument5 pagesElasticities of DemanddijojnayNo ratings yet
- Lec2 DemandSlutskyDocument44 pagesLec2 DemandSlutskyebbamorkNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-Elasticity and Its TypesDocument33 pagesLecture 4-Elasticity and Its Typeszahra naheedNo ratings yet
- Elasticity, Consumer Surplus and Producer SurplusDocument88 pagesElasticity, Consumer Surplus and Producer SurplusCkristeneJean Baltazar De VeraNo ratings yet
- Chapter Fifteen: Market DemandDocument53 pagesChapter Fifteen: Market DemandJUNY KEN BLANCONo ratings yet
- Demand and Supply: Elasticity and Government-Set PricesDocument48 pagesDemand and Supply: Elasticity and Government-Set PricesOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Methods of Microeconomics: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMethods of Microeconomics: A Simple IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)