Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The 8 Parts of Speech
Uploaded by
kenjie26Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The 8 Parts of Speech
Uploaded by
kenjie26Copyright:
Available Formats
The 8 Parts of Speech
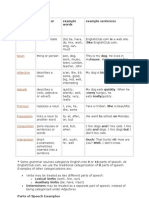
A part of speech is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) which have
similar grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display
similar behavior in terms of syntaxthey play similar roles within the grammatical structure of
sentencesand sometimes in terms of morphology, in that they undergo inflection for similar
properties. Commonly listed English parts of speech
are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, interjection, and
sometimes numeral, article or determiner.
Noun
a word or lexical item denoting any abstract (abstract noun: e.g. home) or concrete entity
(concrete noun: e.g. house); a person (police officer, Michael), place (coastline,London),
thing (necktie, television), idea (happiness), or quality (bravery). Nouns can also be classified
into count nouns or non-count nouns, or both categories.
Pronoun
a substitute for a noun or noun phrase (them, he)
Adjective
a modifier of a noun or pronoun (big, brave)
Verb
a word denoting an action (walk), occurrence (happen), or state of being (be)
Adverb
a modifier of an adjective, verb, or other adverb (very, quite)
Preposition
a word that relates a noun to another word or phrase in the sentence and aids in syntactic
context (in, of)
Conjunction
a syntactic connector; links words, phrases, or clauses (and, but)
Interjection
an emotional greeting or exclamation (Huzzah, Alas)
You might also like
- 100 Words Almost Everyone Mixes Up or ManglesFrom Everand100 Words Almost Everyone Mixes Up or ManglesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Part of Speech: Noun Verb Adjective Adverb Pronoun Preposition Conjunction Interjection Numeral Article DeterminerDocument7 pagesPart of Speech: Noun Verb Adjective Adverb Pronoun Preposition Conjunction Interjection Numeral Article DeterminerbadikNo ratings yet
- Classification of Parts of Speech: NounsDocument10 pagesClassification of Parts of Speech: NounsДенис МитрохінNo ratings yet
- NounDocument2 pagesNounCharmain Mae A. MamacNo ratings yet
- Open Class (Linguistics)Document15 pagesOpen Class (Linguistics)Muhammad Shofyan IskandarNo ratings yet
- Words ClassesDocument1 pageWords ClassesDR BaoucheNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech, Words Classified According To Their Functions in Sentences, For Purposes ofDocument3 pagesParts of Speech, Words Classified According To Their Functions in Sentences, For Purposes ofRhitzle AnnNo ratings yet
- Jump To Navigation Jump To Search: For Other Uses, SeeDocument10 pagesJump To Navigation Jump To Search: For Other Uses, SeePhantomlayenNo ratings yet
- Lexical and Gra-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesLexical and Gra-WPS OfficeSteve HaringgtonNo ratings yet
- Chapter IVDocument17 pagesChapter IVHoang Thi Hai YenNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesParts of SpeechsteinrizkyNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument11 pagesParts of Speechneeraj punjwaniNo ratings yet
- Vowel Phonemes: Phoneme ExamplesDocument6 pagesVowel Phonemes: Phoneme ExamplesAnna Rhea BurerosNo ratings yet
- Primary Grammar Glossary For ParentsDocument6 pagesPrimary Grammar Glossary For ParentsJack EdieNo ratings yet
- The Noun Its Grammatical CategoriesDocument4 pagesThe Noun Its Grammatical CategoriestemurlankuziboevNo ratings yet
- Proper Nouns Pirate, Caribbean, Ship, Freedom, Captain Jack SparrowDocument3 pagesProper Nouns Pirate, Caribbean, Ship, Freedom, Captain Jack SparrowBenice Hudierez Antonio-SantosNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument18 pagesEnglish GrammarMaria AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Lecture V. Working Definitions of Principal ConceptsDocument8 pagesLecture V. Working Definitions of Principal ConceptsHill CatNo ratings yet
- Is A Group of Words That Are Used in A Certain Way in A SentenceDocument6 pagesIs A Group of Words That Are Used in A Certain Way in A SentenceAyesha RehmanNo ratings yet
- IELTS GRAMMAR (From Basic To Types)Document18 pagesIELTS GRAMMAR (From Basic To Types)Builoan1986No ratings yet
- Syntactic Categories: Aura Satya Pinasti 1801050043 6BDocument2 pagesSyntactic Categories: Aura Satya Pinasti 1801050043 6BAura SatyaNo ratings yet
- Mohammad Fadly Fathon'a - F22120076Document3 pagesMohammad Fadly Fathon'a - F22120076MOHAMMAD FADLY FATHON'ANo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech COMPLETEDocument6 pagesParts of Speech COMPLETEhaseeb aslam khanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledreaderNo ratings yet
- Lexical Phonology & MorphologyDocument3 pagesLexical Phonology & MorphologyMaruf Alam MunnaNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech - WikipediaDocument8 pagesPart of Speech - WikipediaRain TolentinoNo ratings yet
- теор.осн.ин.яз 22Document21 pagesтеор.осн.ин.яз 22StrongsNo ratings yet
- English Grammar - WikipediaDocument33 pagesEnglish Grammar - WikipediaThulaniNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument4 pagesParts of Speechmuja dilahNo ratings yet
- JurafskyMartin2019Chapter8POS TaggingDocument28 pagesJurafskyMartin2019Chapter8POS TaggingSeraina BetschartNo ratings yet
- Guided Writing Part of SpeechDocument4 pagesGuided Writing Part of Speechgurning chanelNo ratings yet
- Nine Parts of Speech (Grammar) : Prepositions and Interjections. We Will Add One More Type: ArticlesDocument2 pagesNine Parts of Speech (Grammar) : Prepositions and Interjections. We Will Add One More Type: ArticlesReeta KannusamyNo ratings yet
- Grammar Evry Novita Situmorang..Document28 pagesGrammar Evry Novita Situmorang..Lesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- Lectures 7, 8 - Word Classes + ExercisesDocument28 pagesLectures 7, 8 - Word Classes + ExercisestbericaNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument23 pagesAdverbsChazia ZNo ratings yet
- Lexicology GlossaryDocument3 pagesLexicology GlossaryAiganymNo ratings yet
- English Grammar - Wikipedia PDFDocument129 pagesEnglish Grammar - Wikipedia PDFKuko sa paaNo ratings yet
- Syntactic CategoryDocument19 pagesSyntactic CategoryPinkyFarooqiBarfiNo ratings yet
- Grammar and Punctuation: The Parts of SpeechDocument2 pagesGrammar and Punctuation: The Parts of SpeechjonfoukNo ratings yet
- Tugas Orang Ganteng 2Document2 pagesTugas Orang Ganteng 2Hanif FikriyantitoNo ratings yet
- Types of Use : Latin Calque Ancient Greek Inflected DeclensionDocument3 pagesTypes of Use : Latin Calque Ancient Greek Inflected DeclensionPriya Samprith ShettyNo ratings yet
- RADFORD (Resumen)Document2 pagesRADFORD (Resumen)Agustina Alonso AlbianoNo ratings yet
- The 8 Parts of SpeechDocument6 pagesThe 8 Parts of SpeechGlycel Angela JacintoNo ratings yet
- NP From The NetDocument9 pagesNP From The NetAleksandra Sasha JovicNo ratings yet
- What Is Noun?Document4 pagesWhat Is Noun?Christian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument11 pagesPart of SpeechEvitiaaNo ratings yet
- RT of SpeechDocument7 pagesRT of SpeechDavid Vijay ColeNo ratings yet
- Materi Kuliah MorphologyDocument9 pagesMateri Kuliah MorphologyMuhammad Hidayatul RifqiNo ratings yet
- linguistics generative grammar φ person number gender case nouns pronounsDocument7 pageslinguistics generative grammar φ person number gender case nouns pronounsPOMIAN IONUTNo ratings yet
- Apuntinis Grammar II (Autoguardado) (Recuperado Automáticamente)Document22 pagesApuntinis Grammar II (Autoguardado) (Recuperado Automáticamente)amina.menehemNo ratings yet
- Grammar HandbookDocument111 pagesGrammar HandbookMieder van Loggerenberg100% (4)
- Makalah-Relationship LexemesDocument10 pagesMakalah-Relationship LexemesSoviatur rokhmaniaNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Parts of SpeechDocument23 pagesPresentation of Parts of SpeechTowsif MahdiNo ratings yet
- 1 Grammatical ElementsDocument2 pages1 Grammatical ElementsLidia NoreseNo ratings yet
- Makalah GrammarDocument10 pagesMakalah GrammarMonalisa AritonangNo ratings yet
- Basic Terminologies of Grammar Meeting 2Document7 pagesBasic Terminologies of Grammar Meeting 2Tary DumbelaNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech4664646Document6 pagesPart of Speech4664646MohanSharmaNo ratings yet
- Oral Exam Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesOral Exam Questions and AnswersFrancesca MastrapasquaNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument4 pagesPart of SpeechSrinivasan KannanNo ratings yet
- TaskDocument7 pagesTaskEvii HasbaNo ratings yet
- Guideline To Composition WritingDocument6 pagesGuideline To Composition Writingcuen32No ratings yet
- Styles of Metaphor: A. Metaphors in Everyday Discourse and in Literary DiscourseDocument3 pagesStyles of Metaphor: A. Metaphors in Everyday Discourse and in Literary Discoursekenjie26No ratings yet
- English Proficiency TestDocument12 pagesEnglish Proficiency Testkenjie2673% (15)
- English Proficiency TestDocument12 pagesEnglish Proficiency Testkenjie2673% (15)
- Importance of Instructional Materials in EducationDocument3 pagesImportance of Instructional Materials in EducationRhoderick Rivera67% (3)