Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Faqs On Co-Operative Banks
Faqs On Co-Operative Banks
Uploaded by
mbansal870 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageCo-operative banks are small banking units that operate in both urban and rural areas. They provide important banking services like deposits, loans, and money transfers, especially for small businesses, agriculture, and individual customers. Co-operative banks are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India and must meet requirements for capital, membership numbers, and statutory liquidity ratios. Weak urban co-operative banks are those that underperform on certain performance parameters.
Original Description:
Original Title
Faq
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCo-operative banks are small banking units that operate in both urban and rural areas. They provide important banking services like deposits, loans, and money transfers, especially for small businesses, agriculture, and individual customers. Co-operative banks are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India and must meet requirements for capital, membership numbers, and statutory liquidity ratios. Weak urban co-operative banks are those that underperform on certain performance parameters.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views1 pageFaqs On Co-Operative Banks
Faqs On Co-Operative Banks
Uploaded by
mbansal87Co-operative banks are small banking units that operate in both urban and rural areas. They provide important banking services like deposits, loans, and money transfers, especially for small businesses, agriculture, and individual customers. Co-operative banks are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India and must meet requirements for capital, membership numbers, and statutory liquidity ratios. Weak urban co-operative banks are those that underperform on certain performance parameters.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
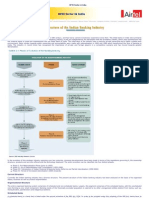
FAQs on co-operative banks
What are co-operative banks?
Co-operative banks are small-sized units organised in the co-operative sector which
opreate both in urban and non-urban centres.
What is the role of co-operative banks in India’s banking structure?
In India, co-operative banks finance small borrowers in industrial and trade sectors,
besides professional and salary classes.
What functions do co-operative banks perform?
Co-operative banks perform the main banking functions of deposit mobilisation,
supply of credit and provision of remittance facilities. They provide limited banking
products and are specialists in agriculture-related products.
Who acts as the regulator for co-operative banks?
Co-operative banks are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India and governed by the
Banking Regulations Act, 1949, and Banking Laws (Co-operative Societies) Act,
1965. Rural co-operative banks are regulated by state registrar of co-operatives.
What is the minimum capital requirement and membership required for co-
operative banks ?
Urban co-operative banks should have a minimum capital of Rs 4 crore and a
membership of at least 3,000 in a population of more than Rs 10 lakh. The figure of
minimum membership keeps decreasing with a decrease in population.
What is the minimum Statuatory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) for co-operative banks?
Urban co-operative banks are required to maintain a SLR equivalent to 25% of net
demand and bank liabilities.
What are weak urban co-operative banks?
Urban co-operative banks are divided into weak and urban banks, based on certain
parameters of their performance. India has a total of 261 weak banks at the end of
June 2001.
You might also like
- Theoretical Framework of Treasury ManagementDocument146 pagesTheoretical Framework of Treasury ManagementPrithviraj Kumar100% (1)
- SCFS Co-Operative Society LTDDocument23 pagesSCFS Co-Operative Society LTDLïkïth Räj100% (3)
- Co Opeartive BankingDocument3 pagesCo Opeartive Bankingjyotz777No ratings yet
- Types of Banks IndiaDocument3 pagesTypes of Banks India17-075 Upgna PatelNo ratings yet
- Co Operative BanksDocument13 pagesCo Operative Banksamyncharaniya100% (4)
- Cooperative BankingDocument8 pagesCooperative BankingvmktptNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking StructureDocument5 pagesIndian Banking StructurevivekNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Banks: School of Law, Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies, BangaloreDocument13 pagesCooperative Banks: School of Law, Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies, BangaloreHIMANSHU GOYALNo ratings yet
- 34 Cooperative BanksDocument10 pages34 Cooperative Banksjeevan chandra aryaNo ratings yet
- Banking Structure in IndiaDocument5 pagesBanking Structure in IndiaCharu Saxena16No ratings yet
- Banking Awarness Meritshine MaterialDocument162 pagesBanking Awarness Meritshine MaterialRagavi JoNo ratings yet
- 04 - Chapter 1Document27 pages04 - Chapter 1shantishree04No ratings yet
- Banking Practical 1 InformationDocument4 pagesBanking Practical 1 InformationMadhur AbhyankarNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Banks in IndiaDocument2 pagesCooperative Banks in IndiaGaurav TyagiNo ratings yet
- Origin of Banking and Banking Structure in IndiaDocument32 pagesOrigin of Banking and Banking Structure in IndiaShashank TiwariNo ratings yet
- Origin of Banking and Banking Structure in IndiaDocument32 pagesOrigin of Banking and Banking Structure in IndiaShashank TiwariNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Indian Banking Industry: Commercial BanksDocument2 pagesStructure of The Indian Banking Industry: Commercial BanksMayank AhujaNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Indian Banking System Sem IDocument2 pagesStructure of The Indian Banking System Sem IAshitosh ChavanNo ratings yet
- Banking StructureDocument3 pagesBanking StructureMayank AhujaNo ratings yet
- Full Info of Coperative BanksDocument15 pagesFull Info of Coperative BanksAkash ShirsatNo ratings yet
- Co Operative BankingDocument11 pagesCo Operative BankingMahesh VermaNo ratings yet
- Citizen Urban Co-Op. BankDocument55 pagesCitizen Urban Co-Op. BankSpUnky Rohit100% (1)
- 11 Chapter 4Document7 pages11 Chapter 419UEI014 , PRITAM DebNo ratings yet
- E Banking ServicesDocument90 pagesE Banking ServicesManjunath Leo100% (2)
- Study MaterialDocument42 pagesStudy MaterialLion Naresh PradhanNo ratings yet
- Banking System in India1Document7 pagesBanking System in India1Srikanth Prasanna BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument15 pagesChapter IIbhagathnagarNo ratings yet
- All About Cooperative Banks in India GK Notes For SSC Banking Exams in PDFDocument8 pagesAll About Cooperative Banks in India GK Notes For SSC Banking Exams in PDFramuvindiaNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking System - Structure and Other Details (With Diagrams)Document14 pagesIndian Banking System - Structure and Other Details (With Diagrams)krunaldedehiya100% (1)
- BankDocument9 pagesBankakashgulati007No ratings yet
- Cooperative Bank Whole InfoDocument9 pagesCooperative Bank Whole Infoyatin patilNo ratings yet
- Industry ProfileDocument15 pagesIndustry ProfileP.Anandha Geethan80% (5)
- A.2 AssignmentDocument5 pagesA.2 AssignmentNijiraNo ratings yet
- BFSI Sector in IndiaDocument3 pagesBFSI Sector in IndiaKenneth GallowayNo ratings yet
- Mission Vission and ValuesDocument8 pagesMission Vission and ValuesJiby JohnNo ratings yet
- Ibs F y B.com (H) Unit 1Document18 pagesIbs F y B.com (H) Unit 1Nikunj PatelNo ratings yet
- Role of Cooperative Bank in AgriculturalDocument65 pagesRole of Cooperative Bank in Agriculturalkaushal244280% (5)
- Finincial Analysis of Tumkur Grain Merchants Co-Operative BankDocument110 pagesFinincial Analysis of Tumkur Grain Merchants Co-Operative BankPrashanth PB50% (2)
- Economy Banking System in IndiaDocument21 pagesEconomy Banking System in Indiakrishan palNo ratings yet
- Types of Banks: Presented By: Roll NoDocument22 pagesTypes of Banks: Presented By: Roll NosnehalakhadeNo ratings yet
- Raj BankDocument56 pagesRaj BankSunny BhattNo ratings yet
- Projct 2Document46 pagesProjct 2Varinder BhukalNo ratings yet
- CO BanksDocument1 pageCO BanksAbhishek ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Commercial Bank (Icici and Idbi Bank)Document27 pagesComparative Analysis of Commercial Bank (Icici and Idbi Bank)GUDDUNo ratings yet
- Regional Rural BanksDocument4 pagesRegional Rural BanksSiddhartha BindalNo ratings yet
- Banking Structure in IndiaDocument9 pagesBanking Structure in IndiaDhanu BhardwajNo ratings yet
- BankingDocument8 pagesBankingDivya NathNo ratings yet
- Banking Practice Unit 1Document13 pagesBanking Practice Unit 1Nandhini VirgoNo ratings yet
- Regional Rural BankDocument26 pagesRegional Rural BankVijayeta Nerurkar100% (1)
- Evolution of The Indian Banking IndustryDocument7 pagesEvolution of The Indian Banking IndustryfasahmadNo ratings yet
- Evolution of The Indian Banking IndustryDocument6 pagesEvolution of The Indian Banking IndustryNeha ChandnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document28 pagesChapter 2ningegowdaNo ratings yet
- Banking Structure in India PDFDocument12 pagesBanking Structure in India PDFShantanu PorelNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Banks in India FinalDocument14 pagesCooperative Banks in India Finalsayali satonkarNo ratings yet
- Concept of BankingDocument36 pagesConcept of BankingDhaval B MasalawalaNo ratings yet
- Banking Structure in IndiaDocument13 pagesBanking Structure in IndiaharshNo ratings yet
- Commercial BanksDocument9 pagesCommercial BanksPrathyusha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Type of Banks: Different Types of Banks in India & Their FunctionsDocument15 pagesType of Banks: Different Types of Banks in India & Their FunctionscecilNo ratings yet
- Co Operative BankDocument7 pagesCo Operative Bankவிதை SOUNDAR CholaNo ratings yet
- Banking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingFrom EverandBanking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingNo ratings yet